By Michael Kuser
The NYISO Board of Directors on Thursday issued a mixed decision on the ISO Management Committee’s selections for the AC Public Policy Transmission Project.
While the board accepted the committee’s recommendation for one segment, it switched the other to a competing proposal by National Grid and New York Transco.
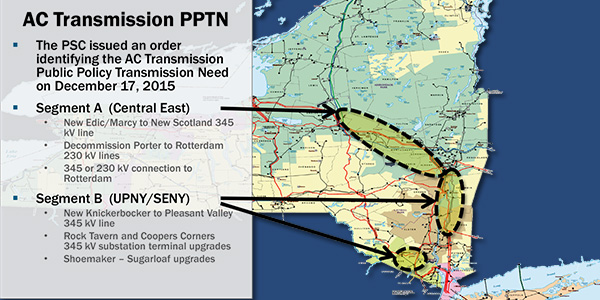
The Management Committee — along with ISO staff — had backed two joint proposals by North America Transmission and the New York Power Authority to build two 345-kV transmission projects to address persistent transmission congestion at the Central East (Segment A) electrical interface and Upstate New York/Southeast New York (UPNY/SENY, or Segment B) interface. (See NYISO MC Supports AC Transmission Projects.) Cost estimates for both projects ranged from $900 million to $1.1 billion.
Advised by consultant Substation Engineering Co., ISO staff recommended Project T027, a double-circuit 345-kV line from Edic to New Scotland for Segment A. For Segment B, it endorsed Project T029, a standard 345-kV line from Knickerbocker to Pleasant Valley, despite claims from one bidder that there was a “virtual” tie in benefits among competing projects.
But the board concluded that “the most efficient or cost-effective solution” for Segment B is Project T019, proposed by National Grid’s Niagara Mohawk Power and NY Transco.
“In evaluating Segment B projects, the Board concludes that Project T019’s additional transfer capability drives superior performance across a number of important selection metrics,” the board wrote in its decision.
The board directed ISO staff to modify the draft report for the project accordingly.
Listening to Stakeholders
NYISO staff had analyzed seven proposals for Segment A and six for Segment B before making their choices. However, when the Business Issues Committee recommended the projects last June, several losing bidders protested the ISO’s selection process. (See NYISO BIC Backs AC Tx Projects; Losing Bidders Protest.)
At the June BIC meeting, New York Transco general counsel Kathleen Carrigan read comments the company submitted jointly with National Grid, arguing NYISO’s own metrics showed the National Grid/NY Transco proposal paired with T029 would produce consistently better performance than the ISO’s favored project.
Project T019 includes “a basic controllable series compensation element to preserve the proposed 345-kV transmission line physical designs that the commission deemed the most environmentally and siting friendly in the underlying AC transmission proceedings,” the comments noted.
When combined, T027 and T019 increase voltage transfer across Central East by 875 MW and UPNY/SENY by 2,100 MW, the companies contended.
“This is a far greater increase than the combination of T027 and T029, which only increases transfer capability along Central East by 825 MW and UPNY/SENY by 1,325 MW,” Carrigan told RTO Insider after the June meeting.
“Projects T027 and T019 have the highest Central East N-1-1 voltage transfer capability of any studied project combination and far surpass combination T027 and T029 with respect to the incremental UPNY/SENY N-1-1 thermal transfer capability. The baseline 20-year incremental energy produced by projects T027 and T019 nearly doubles that of projects T027 and T029. And finally, T027 and T019 produce the highest production cost savings than any other Segment B combination,” Carrigan said.
Additional analysis ordered by the board supported Carrigan’s assertions, finding that when paired, T027 and T019 produced the lowest cost per MW, at $228k/MW.
The ISO estimated T027 will cost $577 million to $750 million, the higher figure including a 30% contingency, while T019 is estimated at $479 million.
The board’s conclusions are summarized in an Addendum to the Draft AC Transmission Public Policy Transmission Planning Report, which goes back to the MC for further review and comment before board members can make their final determination on project selection.