Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
DOE's senior leadership highlighted how the grid relies on fossil fuels to make it through winter peaks.
ERCOT says it leaned on Texas’ 15 mobile generating units and an RMR unit during the state’s first major cold-weather event since 2021’s disastrous Winter Storm Uri.
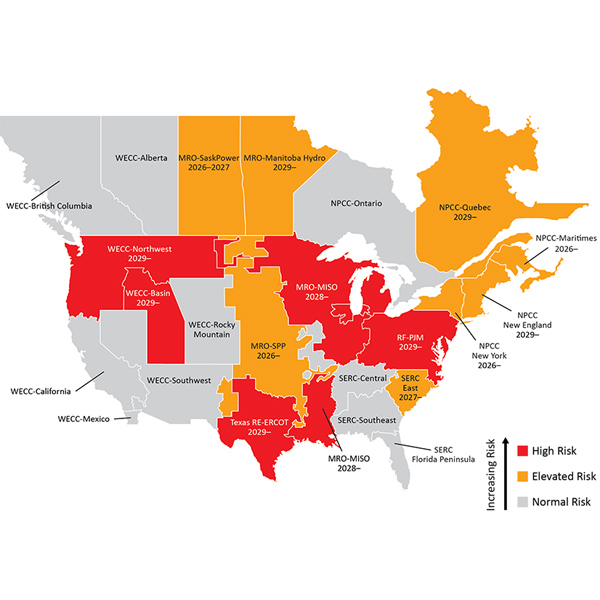
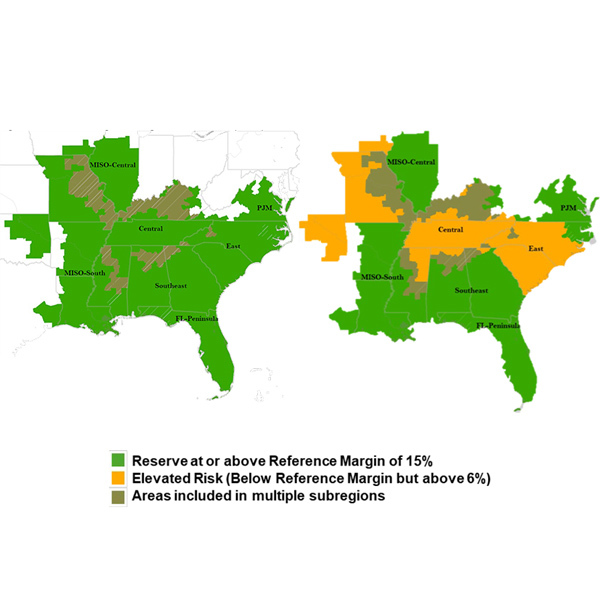
NERC's latest Long-Term Reliability Assessment projected more than half of all assessment areas will face high or elevated risk of energy shortfalls in the next 10 years.
The North American grid made it through the winter storm of Jan. 24-26 — dubbed “Fern” by The Weather Channel — relatively unscathed, but the cold weather gripping much of the U.S. and Canada continues, and cold snaps in the future will still stress the interconnected power and natural gas systems.
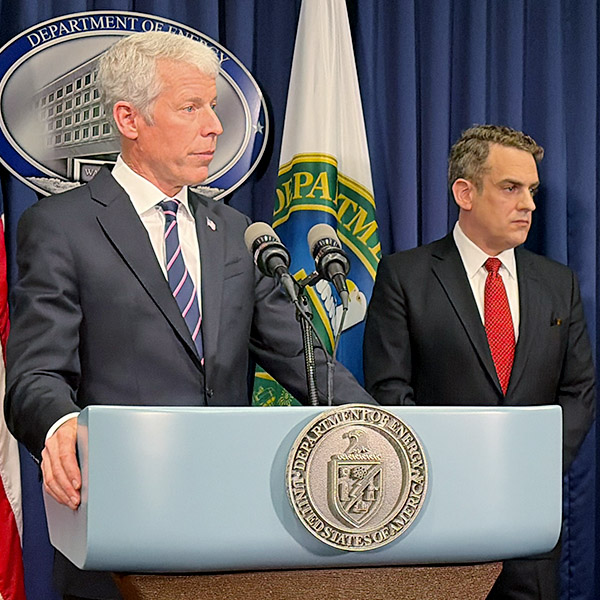
U.S. Energy Secretary Chris Wright said the department is ready to use its authority under Section 202(c) of the Federal Power Act to dispatch backup generation from large customers if needed ahead of a major winter storm.
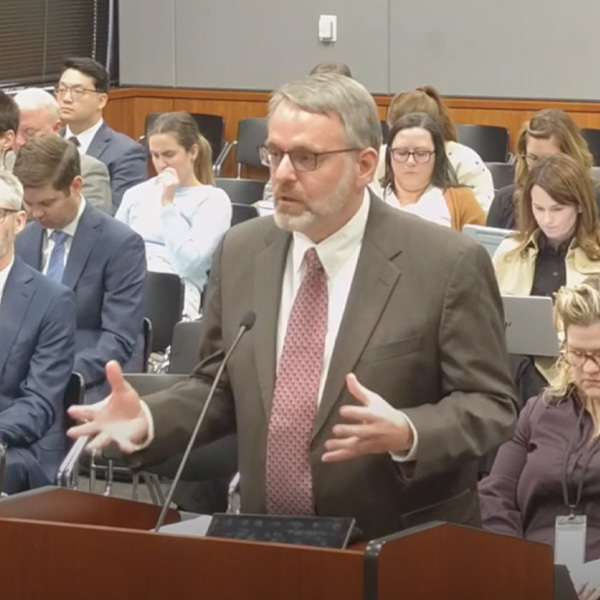
Democrats pressed a senior DOE official on recent decisions affecting PJM, including the agency's orders to keep coal plants running, while another agency shut down offshore wind projects nearing completion.
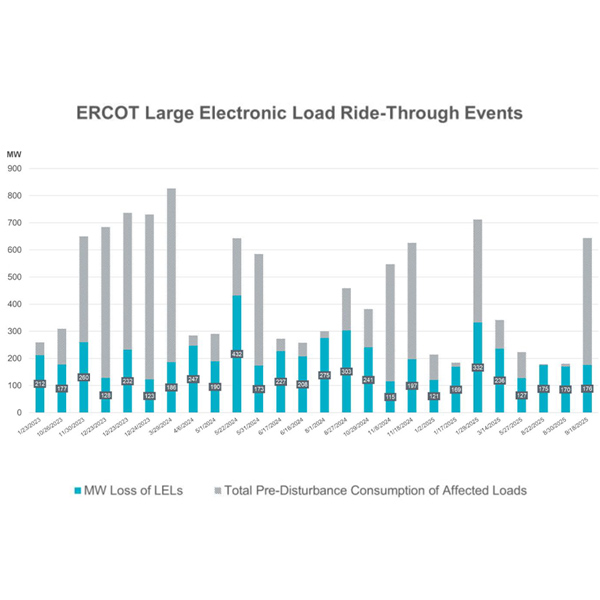
A new report from NERC discusses findings from a review of load-loss incidents involving cryptocurrency mining facilities in Texas.
NERC managers say the organization is well positioned to meet a variety of challenges coming in 2026.
A presenter from ReliabilityFirst said the regional entity expects a normal level of risk this winter, indicating a low chance of energy shortfalls.
SERC's Winter Reliability Assessment found that two subregions faced elevated risk of energy shortfalls in extreme weather.
Want more? Advanced Search