IESO
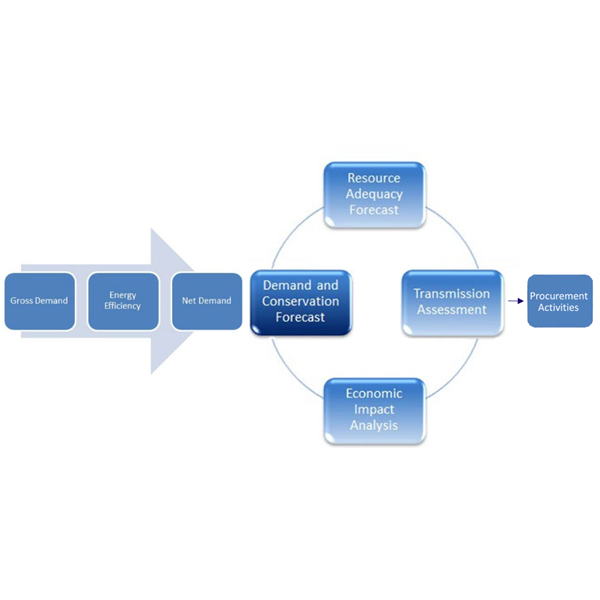
Ontario’s Independent Electricity System Operator is a government organization with a mixture of commercial and public-policy goals, owned by the government of Ontario. It was created to prepare for deregulation of the province’s electrical system and is governed by a board whose directors are appointed by the provincial government.
Ontario’s energy regulator is learning new ways to identify inefficiencies and malign behavior under IESO’s Market Renewal Program.
Ontario’s Progressive Conservative government continues to put its stamp on the province’s energy policy, proposing legislation that would add “economic growth” to the missions of IESO and the Ontario Energy Board.
The Ontario Energy Board plans a 22% increase in its 2025/26 budget with the addition of 32 employees, its biggest hiring surge in at least five years.
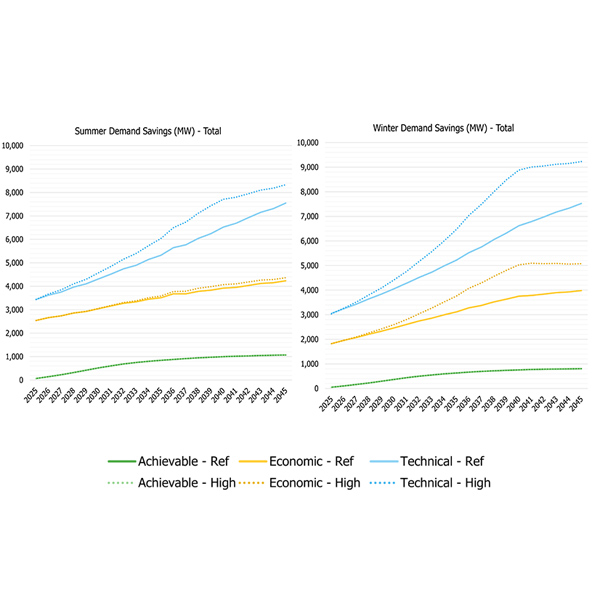
IESO officials say they will release more information on how the ISO constructed its study of the potential for incremental energy savings in Toronto after stakeholders complained they lack enough details to comment meaningfully.
IESO officials say they are shifting from correcting implementation problems to seeking structural improvements in their nodal market.
IESO will expand its industrial demand-side management program, increasing funding and allowing both larger and smaller participants than currently permitted.
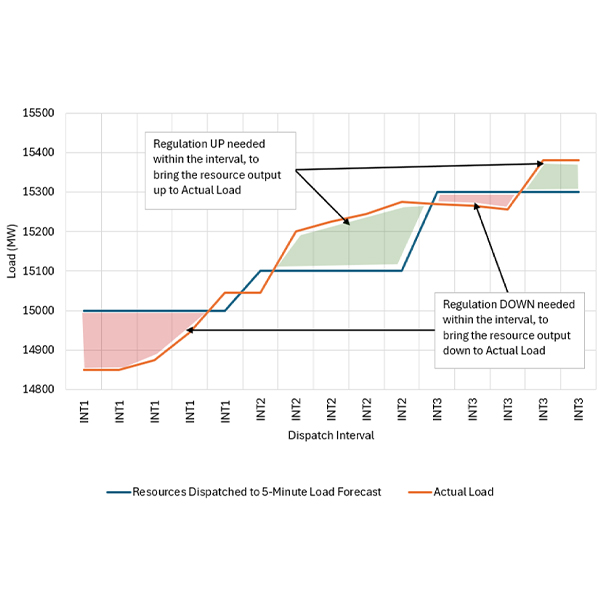
IESO will seek to fill its growing need for regulation services through competitive bids but will resort to bilateral procurements if there is insufficient interest.
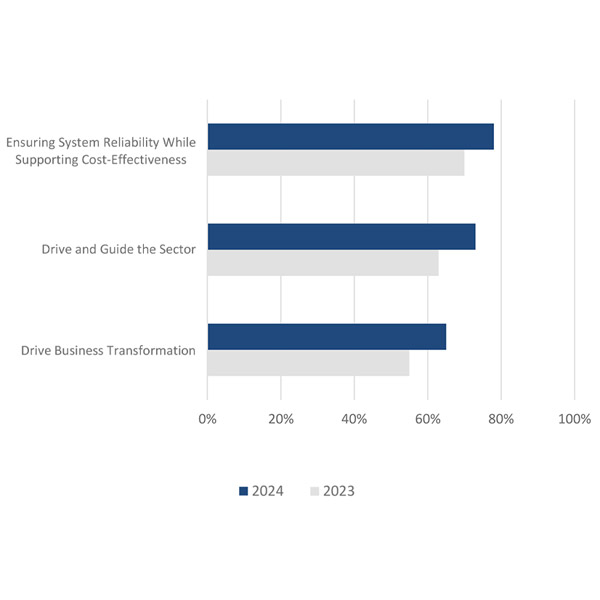
IESO saw “across the board improvement” in its 2024 stakeholder and community engagement survey.
IESO opened discussions on new rules for storage facilities and hybrid resources that will enable the provision of regulation service.
Canada’s utilities are encouraged by the country’s new government but say legislation to fast-track high-priority infrastructure projects doesn't address needs for permitting reform and more flexible clean energy targets and investment tax credits.
Want more? Advanced Search