California Energy Commission (CEC)
California’s reliance on a large amount of imported electricity and fossil fuels is a potential weakness in the state’s energy security portfolio, a California Energy Commission staff report finds.
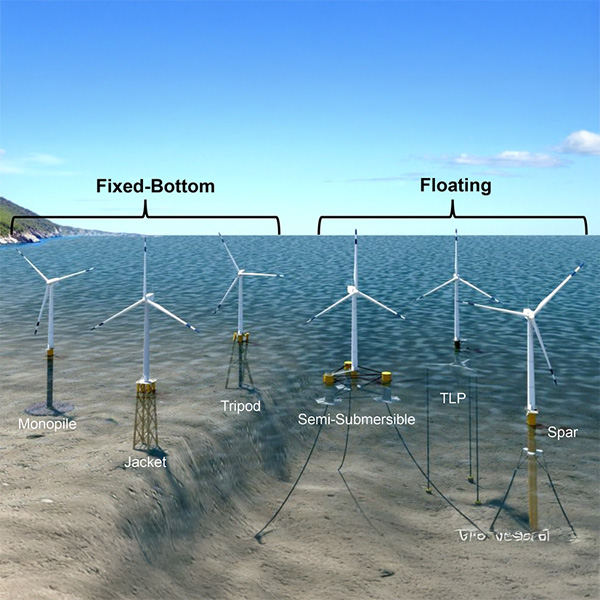
Offshore wind experts urged the California Public Utilities Commission to reconsider a forecasted 6-year delay to the Golden State’s offshore wind project in Humboldt County.
California’s two large offshore wind projects could be delayed by up to six years due to recent federal policy actions, a CPUC administrative law judge said.
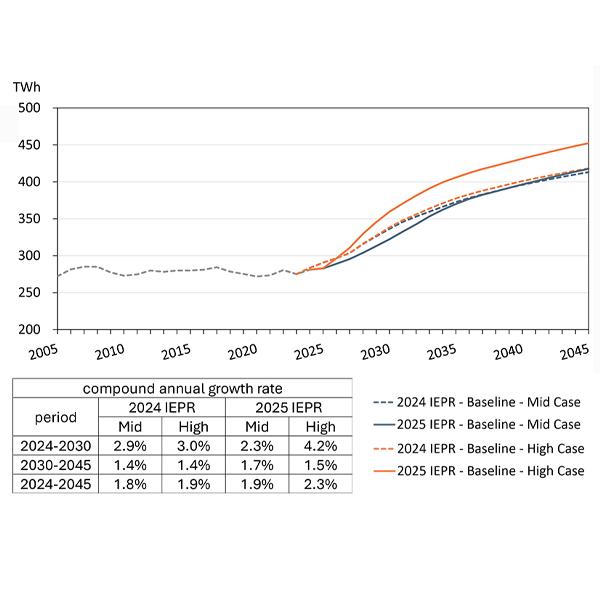
California’s electricity consumption is projected to increase dramatically over the coming decades due in large part to planned artificial intelligence data centers, although questions remain about how many of those data centers actually will be built.
The Extended Day-Ahead Market took center stage at CAISO in 2025 as the ISO tabled other long-term initiatives to ensure the market’s timely launch in May 2026, with PacifiCorp as its first participant.
The CEC approved a request to increase the output of a Burbank gas-fired power plant to address grid reliability issues, prompting some organizations and locals to protest out of concerns about the facility's emissions and costs.
At a two-day workshop held by the CEC, offshore wind experts and fishermen identified many challenges associated with building offshore wind turbines in Humboldt Bay and other parts of the coastline while not displacing the fishing industry.
A virtual power plant program with an indeterminate future set a record in 2025 for the capacity the plant contributed to California's electricity grid.
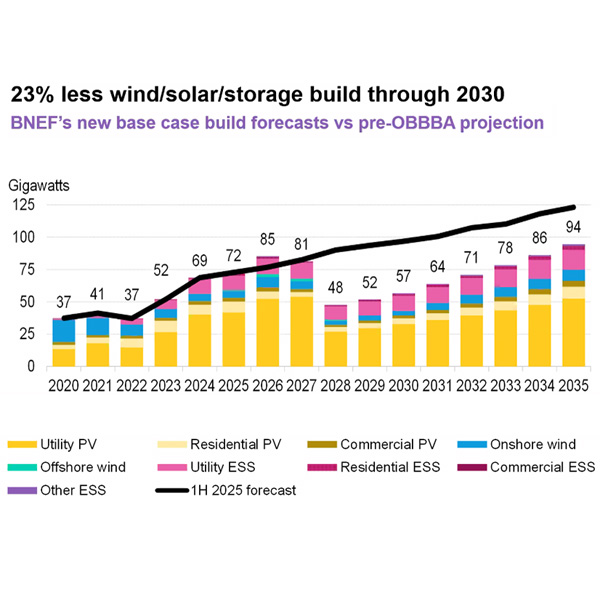
Construction of new wind, solar and energy storage facilities will decrease significantly over the next five years, a BloombergNEF analyst said in an presentation to the California Energy Commission.
A California PUC judge has proposed the commission order an additional 6 GW of capacity for the state between 2029 and 2032 to get ahead of disappearing federal tax credits and loans for renewable energy resources.
Want more? Advanced Search