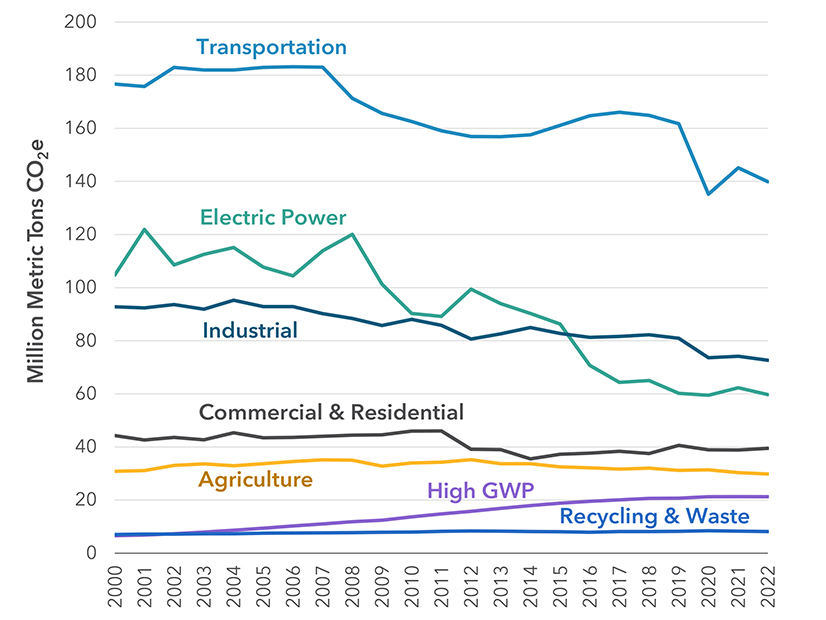
California’s greenhouse gas emissions fell by 2.4% in 2022 compared with the prior year, with the largest decrease seen in the transportation sector, according to a report released Sept. 20 by the California Air Resources Board.
The state’s total GHG emissions were 371 million metric tons (MMT) of CO2 equivalent in 2022, a figure that includes emissions from imported electricity. The decrease from 380 MMT in 2021 resumes the generally declining trend of GHG emissions that the state has seen since 2004.
The year 2021 was an exception to that trend, when GHG emissions grew by about 3%. The emissions increase in 2021 was viewed as rebound from the COVID-19 pandemic, which sent GHG emissions plummeting in 2020.
According to the CARB report, the transportation economic sector accounted for 39% of California’s GHG emissions in 2022, followed by the industrial sector at 23%. The electricity sector contributed 16% of the state’s GHG emissions: 11% from in-state generation and 5% from imports.
Transportation sector emissions fell by 5.2 MMT in 2022, a 3.6% decrease. Emission decreases were seen for passenger vehicles as well as heavy-duty vehicles. CARB attributed the drop to the increased use of renewable fuels and growth in the zero-emission vehicle market.
Emissions from electricity generation fell by 2.6 MMT, or 4.1%, in 2022 due to increases in in-state solar power and hydropower and an increase in imported wind power, according to the report.
GHG emissions dropped in five out of seven sectors that CARB tracked. Emissions were up by 1.7% in the residential and commercial sector, which CARB attributed to an increase in commercial activity following the pandemic. On the residential side, emissions fell slightly in 2022.
California’s agricultural sector accounted for 8.0% of statewide GHG emissions in 2022. Livestock emissions, which are responsible for 70% of the sector’s emissions, fell in 2022 due to the use of methane digesters funded by the California Climate Investments and incentivized by the Low Carbon Fuel Standard, CARB said.
Assembly Bill 32 of 2006 set a state limit of 431 MMT of GHG emissions in 2020. California emissions dropped below that limit in 2014, six years ahead of schedule. Now the state is working to reduce GHG emissions to 260 MMT by 2030, a limit set by Senate Bill 32 of 2016.
The state has set a target of net-zero emissions by 2045.



