Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
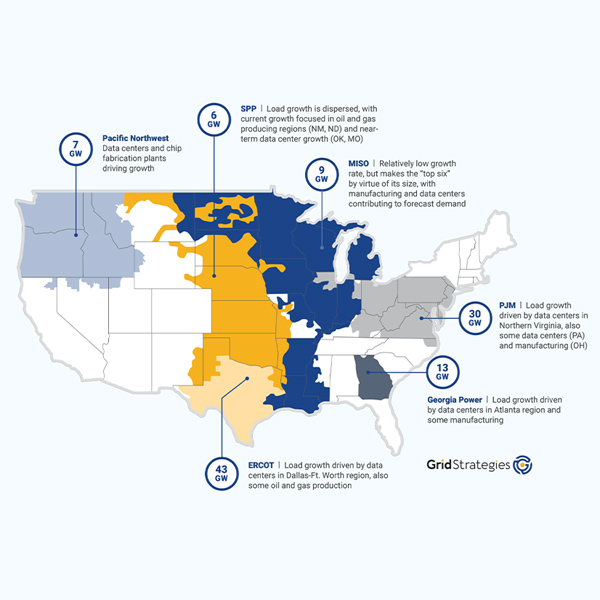
Utilities around the country expect peak demand to grow by 128 GW, or 15.8%, to 947 GW by 2029, according to the latest report from Grid Strategies.
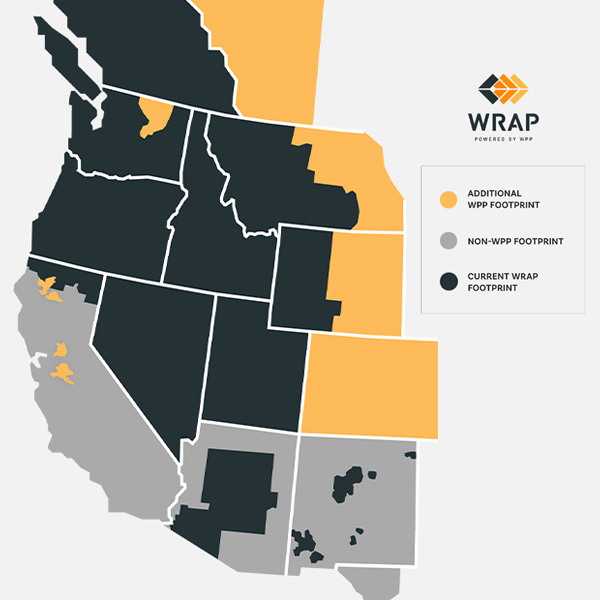
A WECC report predicts annual demand in the Western Interconnection will grow from 942 TWh in 2025 to 1,134 TWh in 2034, although it says the region should have the resources necessary to meet that load.
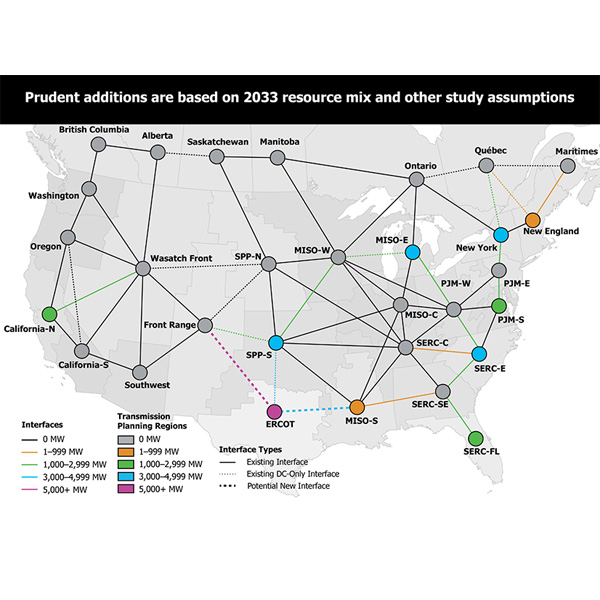
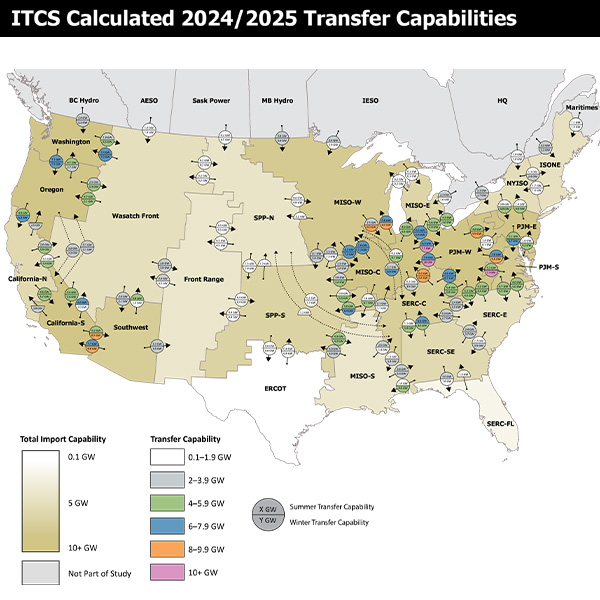
Webinar participants said NERC's study on interregional transfer capability is a solid foundation for future planning but leaves much work still to be done.
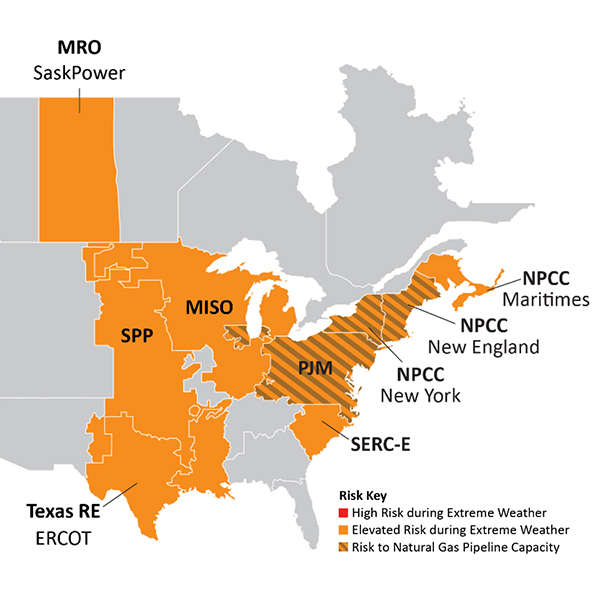
NERC staff said they see both signs of progress and looming challenges in the ERO's winter reliability assessment.
NERC released the final draft installments of the ITCS this week, identifying 35 GW of prudent transfer capability additions.
Grid stakeholders joined commissioners in Washington, D.C., for FERC's annual Reliability Technical Conference.
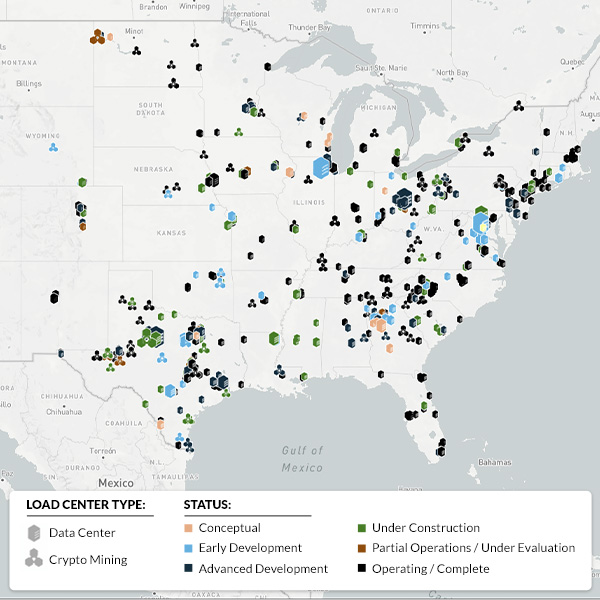
Pairing power-hungry data centers with clean energy resources is sparking mixed feelings among regulators, who say the grid already is straining with increased electrification and connecting new energy sources.
FERC's annual Reliability Technical Conference will feature discussions on resource adequacy and other pressing grid reliability concerns.
The Western Resource Adequacy Program’s key stakeholder body approved a plan that would postpone the start of its penalty phase by one year, to summer 2027.
NERC released the first installment of the federally mandated ITCS in draft form this week.
Want more? Advanced Search