FERC & Federal
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission is an independent regulatory agency that oversees the transmission of electricity, natural gas and oil in interstate commerce, as well as regulating hydroelectric dams and natural gas facilities.
Lisa Einstein, who has served as CISA’s senior adviser for AI and as executive director of the agency’s Cybersecurity Advisory Committee, will take on the new role.
CISA has announced that Executive Director Brandon Wales will leave the agency after nearly five years, including a brief tenure as acting director.
NERC filed its performance assessment with FERC last week, highlighting its accomplishments over the last five years as ERO.
The FBI warned that inverter-based resources may be particularly vulnerable to malicious cyber actors in an industry alert.
FERC accepted NERC's plan for registering inverter-based resources, while dropping a proposal to require more frequent performance assessments from the ERO.
NERC highlighted its progress over the last five years in its draft performance assessment.
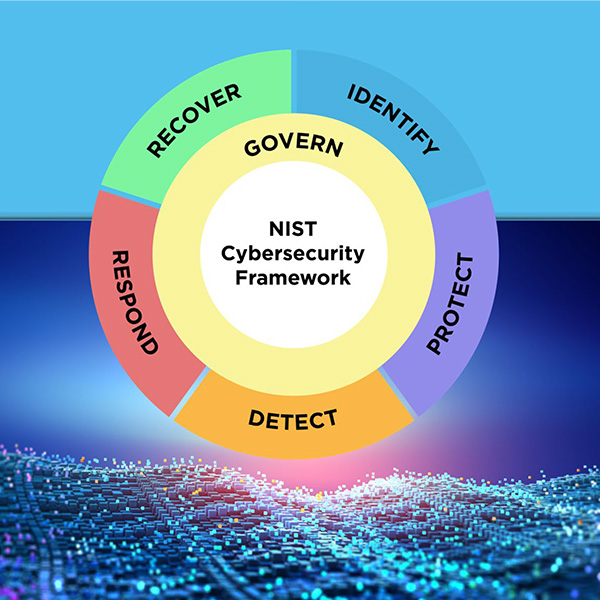
The National Institute of Standards and Technology's latest Cybersecurity Framework expands its focus beyond critical infrastructure to respond to a growing threat of cyberattacks.
Cyber threats from China topped the Joint Cyber Defense Force's priorities for 2024, according to the CISA.
Multiple cybersecurity officials warned lawmakers that China is likely to attempt attacks against U.S. critical infrastructure in a conflict over Taiwan.
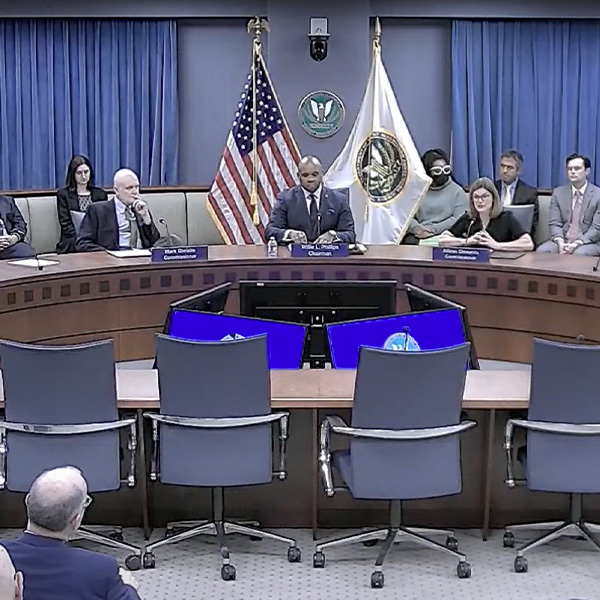
FERC Chair Willie Phillips expressed confidence that the commission will approve its NOPR on transmission planning and cost allocation this year.
Want more? Advanced Search