FERC & Federal
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission is an independent regulatory agency that oversees the transmission of electricity, natural gas and oil in interstate commerce, as well as regulating hydroelectric dams and natural gas facilities.
CISA spotlighted supply chain risk management with the release of a guide intended to help buyers of electronics equipment identify and mitigate risks in their supply chains.
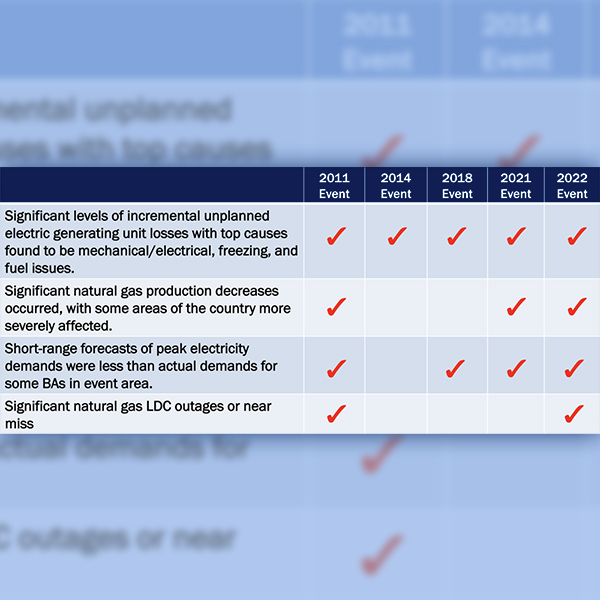
FERC and NERC called for completing winterization standards and strengthening natural gas infrastructure in response to widespread outages last Christmas.
An SPP Resource Adequacy Summit provided an opportunity for federal and state regulators, academics, market participants and stakeholders to discuss the reliability issues facing the grid.
FERC gave NERC the go-ahead to redirect already-budgeted funds and tap its reserves to pay for a congressionally mandated study.
FERC approved PJM's proposal to tighten the triggers initiating a performance assessment interval.
The chairs of NAESB's forum on gas-electric harmonization said significant reforms may be needed to bring the two industries into alignment.
Climate change is already causing billions of dollars in economic costs and infrastructure damage, including the power grid, the Senate Budget Committee heard.
Congressional Democrats have reintroduced legislation to require FERC to establish interregional transmission planning processes and increase RTO transparency.
NAESB is wrapping up a process to develop recommendations to improve coordination between the natural gas and electric industries, which needs to be improved after it contributed to recent cold weather reliability events.
DOE has announced $324 million in grants to 29 recipients so far this year.
Want more? Advanced Search