Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
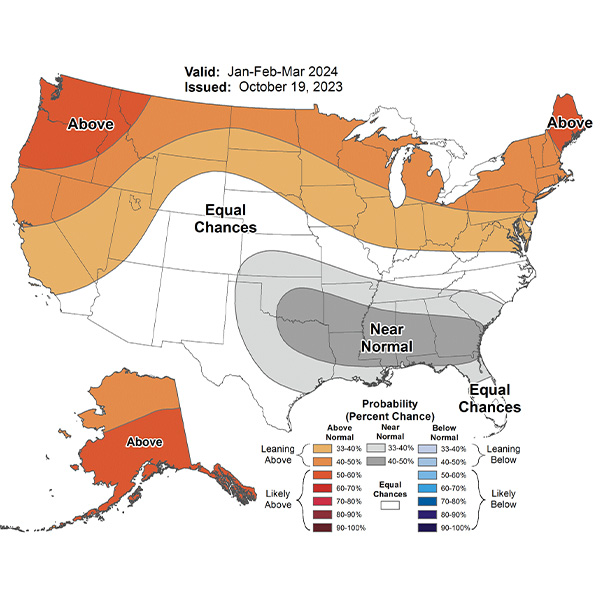
Higher-than-average temperatures in the U.S. could reduce electricity and natural gas demand and help prevent shortfalls this winter, FERC staff said in the commission's Winter Energy Market and Electric Reliability Assessment.
ERCOT canceled its effort to procure 3,000 MW of additional capacity this winter after “limited response” resulted in 11.1 MW of offers.
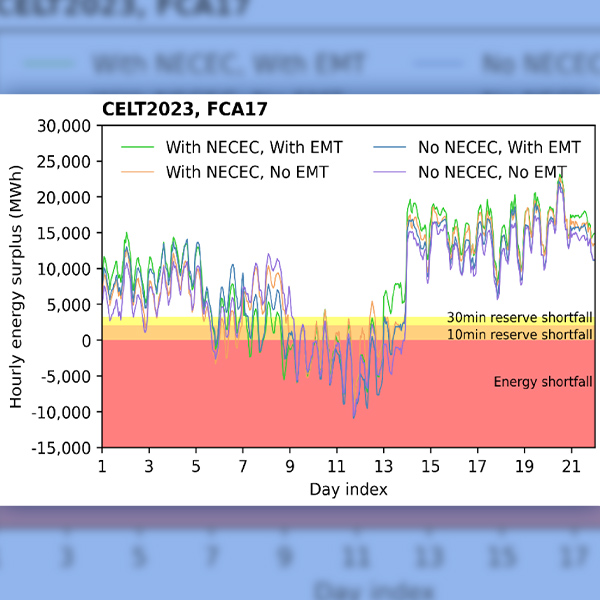
Potential changes to ISO-NE's capacity market include updates to its resource capacity accreditation (RCA) methodology, along with prompt and seasonal capacity market formats.
SPP says it has not identified any concerns within its 14-state footprint this winter that it is not capable of resolving.
ISO-NE presented the final stage of its Operational Impact of Extreme Weather Events study to stakeholders at the NEPOOL Reliability Committee on Nov. 14.
The Electric Power Supply Association has released a set of policy principles it hopes will inform legislators and regulators as they work to evolve the grid to cleaner supplies and greater demand from electrification.
The Resource and Energy Adequacy Leadership (REAL) Team, a cross-section group of regulators, directors and stakeholders, is the answer to SPP's No. 1 strategic priority: resource adequacy.
MISO won’t place conditions on either queue entrants or generation retirements in its quest to maintain system reliability by prescribing generating attributes.
MISO Continues to Find Mounting Retirements, Inadequate New Capacity in Abridged Resource Assessment
MISO again found planned generation retirements continue to outstrip additions in its third annual Regional Resource Assessment
EVs and data centers are expected to be major contributors to load growth, but each has unique challenges when it comes to load forecasting, speakers said during a WECC webinar.
Want more? Advanced Search