FERC Order 842
Utilities must prepare for the reliability challenges that increased penetration of inverter-based resources will pose, according to a NERC white paper.
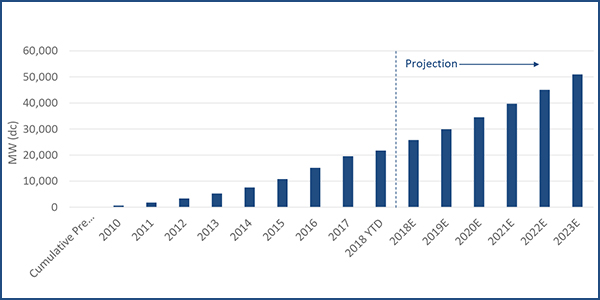
Despite the ongoing shift to renewables, the Eastern Interconnection has sufficient inertia to maintain system frequency for at least the next five years.
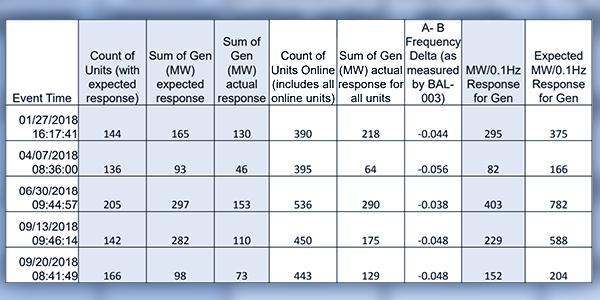
The number of generators providing primary frequency response in 2018 fell short of PJM’s expectations, according to the RTO’s most-recently analyzed data.
A summary of the issues scheduled to be brought to a vote at the PJM Markets and Reliability and Members committees on Feb. 21, 2019.
PJM will spend only $162,000 to test the winter capabilities of 21 generators totaling 477 MW in 2018, RTO officials told the Operating Committee.
NERC offered an upbeat report on the long-term health of the nation’s grid, celebrating results from its interconnection-wide frequency response studies.
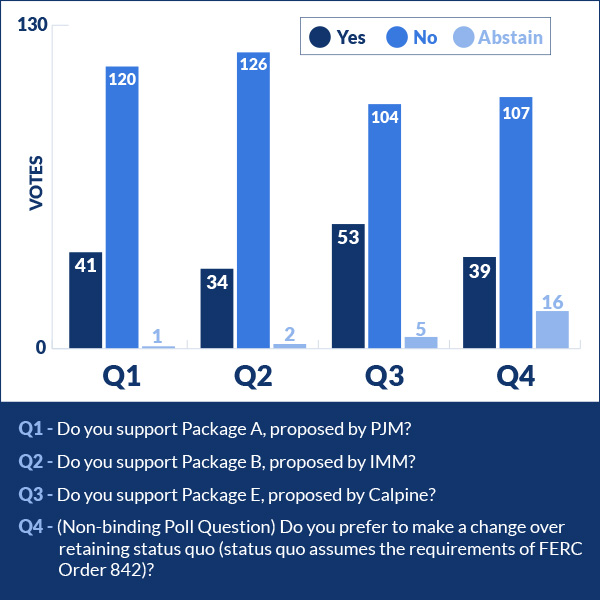
PJM stakeholder rejected the RTO's proposal to enforce primary frequency response requirements beyond the standards of FERC Order 842.
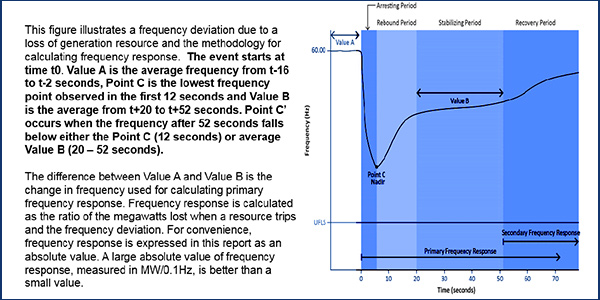
PJM is nearing the finish line in determining how it handles the primary frequency response requirements put in place by FERC Order 842.
FERC ruled that an existing Montana wind farm is exempt from a commission order requiring new generators to provide primary frequency response.
FERC clarified that Order 842 did not imply that existing generators are entitled to compensation for providing primary frequency response.
Want more? Advanced Search