New York State Reliability Council (NYSRC)
NYISO published the final, approved version of the 2024 Reliability Needs Assessment, which identifies a reliability need in New York City beginning in 2033.
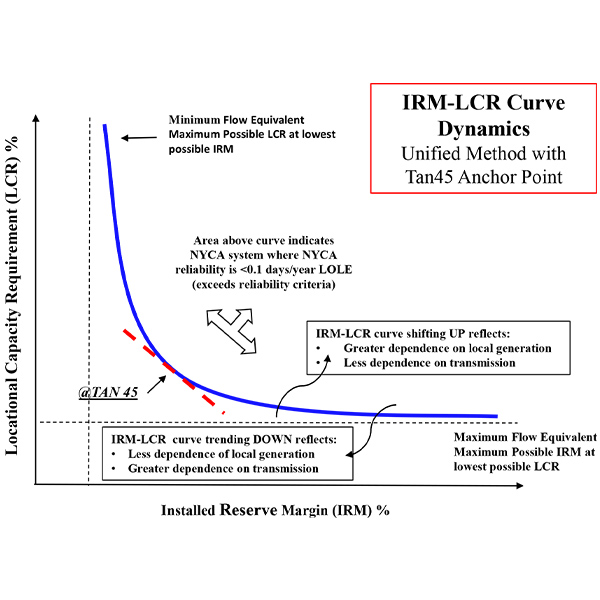
The New York State Reliability Council’s mathematical model for calculating the state’s installed reserve margin every year will need to be updated as more offshore wind and major transmission lines come online, NYISO told stakeholders.
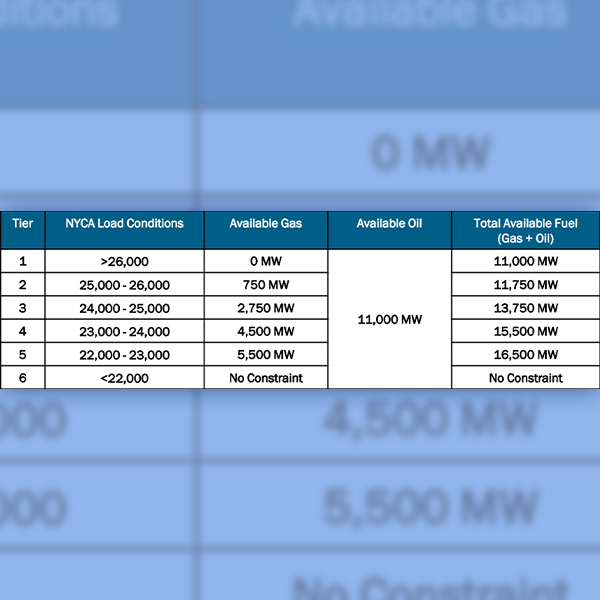
The New York State Reliability Council Executive Committee approved for industry review two new proposed reliability rules aimed at revising NYISO’s transmission planning requirements to account for fuel shortages at gas-fired power plants.
NYSRC approved a rule establishing minimum interconnection standards for large inverter-based resources in order to address a 120-GW bottleneck in NYISO's interconnection queue.
NYISO briefed the committee on an upcoming white paper to propose updates to the ISO’s resource adequacy modeling.
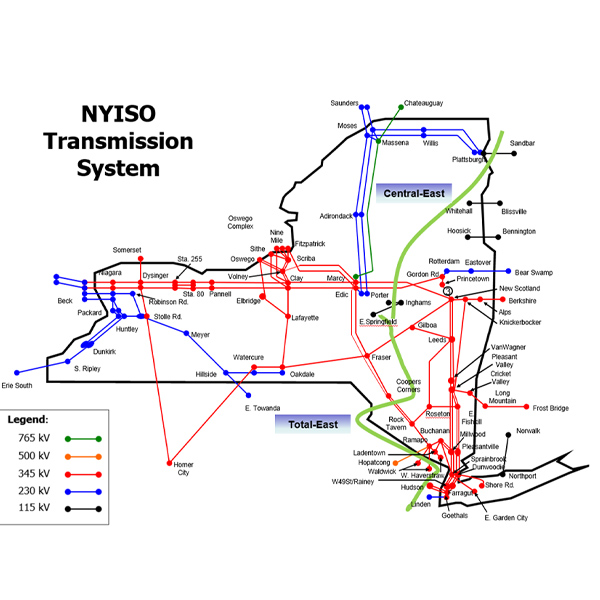
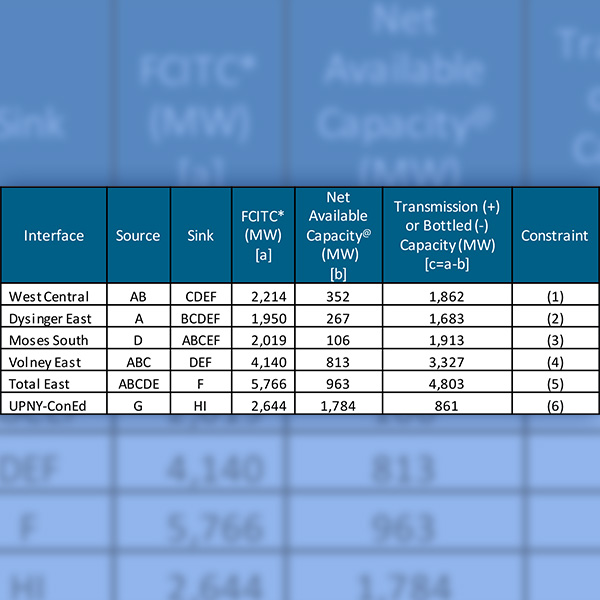
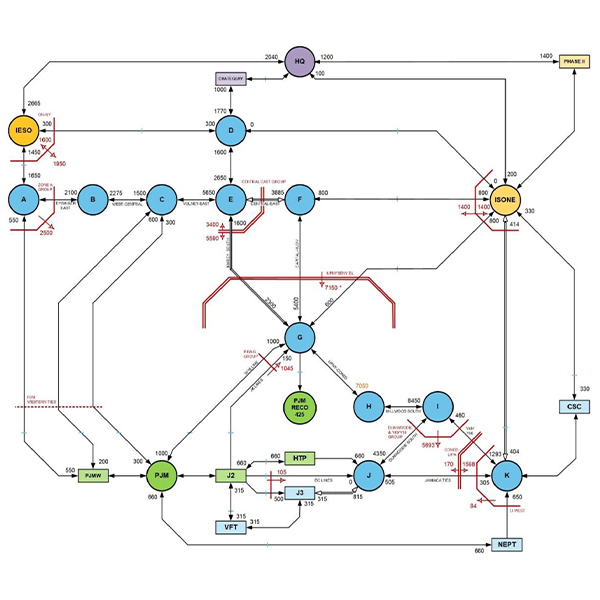
The ISO's New Capacity Zone study indicates that New York's six highway interfaces have sufficient transmission capacity, making establishment of new capacity zones unnecessary.
After four rounds of voting, the New York State Reliability Council Executive Committee approved a 22% IRM for 2024/25, up from 20% for the previous year.
The New York State Reliability Council OK'd interconnection standards for inverter-based resources larger than 20 MW.
The NYSRC Executive Committee approved the modeling assumptions for its 2024/25 installed reserve margin requirement study base case and discussed potential cap-and-invest updates.
NYSRC's Executive Committee approved the preliminary base case for the upcoming capability year and new emergency operating procedures aimed at enhancing grid reliability.
Want more? Advanced Search