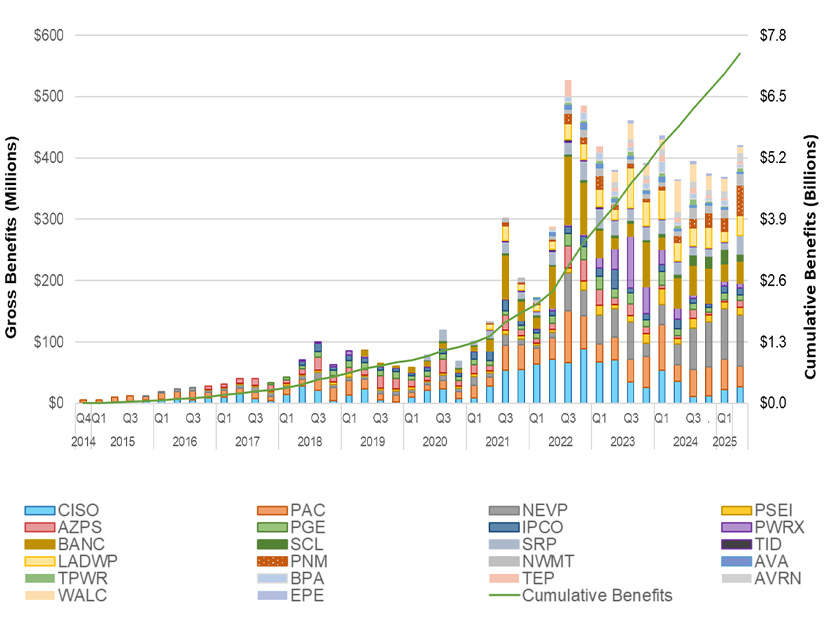
CAISO’s Western Energy Imbalance Market (WEIM) provided participants with $422.44 million in economic benefits during the second quarter of 2025, up 15% compared with the same period year earlier despite no change in membership.
Cumulative benefits since the 2014 launch of the market reached $7.41 billion, according to the benefits report released by the ISO on July 31. The WEIM has over time expanded to include 22 participating balancing authority areas — including CAISO — representing more than 80% of load in the Western Interconnection.
“The quarterly benefits have grown over time as a result of the participation of new BAAs, which results in benefits for both the individual BAA but also compounds the benefits to adjacent BAAs through additional transfers,” CAISO said in the report.
NV Energy raked in the largest share of benefits, at $84.12 million, followed by Public Service Company of New Mexico ($48.96 million), Balancing Authority of Northern California ($35.86 million), PacifiCorp ($33.02 million), Los Angeles Department of Water and Power ($32.17 million) and Salt River Project (SRP) ($30.01 million). Nearly all those participants have committed to joining CAISO’s Extended Day-Ahead Market, except for SRP, which plans to join SPP’s Markets+.
Maintaining a pattern of second-quarter market performance, solar-heavy CAISO was by far the largest net exporter of energy, with about 2.55 million MWh, down nearly 11% from a year earlier. PacifiCorp was the next largest next exporter at 931,263 MWh from both its East and West BAAs, followed by NV Energy (648,995 MWh), SRP (347,571 MWh), Puget Sound Energy (256,891 MWh) and the small Avangrid BAA in the Pacific Northwest (213,961 MWh).
PacifiCorp was the largest net importer at 659,549 MWh, followed by CAISO (641,660 MWh), Powerex (611,111 MWh) and SRP (603,028 MWh).
In the WEIM, a net export represents the difference between total exports and total imports for a BAA during a particular real-time interval, while a net import represents the inverse, meaning that a BAA can be both a heavy exporter and importer over an extended period based on varying momentary needs and trading positions over that period.
CAISO was also the site of the greatest volume of wheel-through transfers during the quarter at 581,943 MWh. The next largest amount of such transfers went through Arizona Public Service (413,625 MWh), NV Energy (388,671 MWh), PacifiCorp-West (384,732 MWh) and Idaho Power (233,497 MWh).
The ISO also noted that avoided renewable energy curtailments from WEIM operations reduced greenhouse gas emissions by 112,712 MWh over the quarter, displacing an estimated 48,241 metric tons of CO2 emissions from thermal sources that would have otherwise been needed to produce energy. Since 2015, the market has helped reduce CO2 emissions by more than 1.12 MT, the ISO said.



