PJM on Friday hosted an Interregional Planning Stakeholder Advisory Committee (IPSAC) meeting to provide input for the development of the Northeast Coordinated System Plan (NCSP), which outlines planning activities conducted jointly by ISO-NE, NYISO and PJM.
Nebiat Tesfa, a PJM transmission planning engineer, said the group will continue coordinating studies across the grid operators’ seams and issue the next NCSP by spring 2022.
PJM Tx Planning
Tesfa presented updates on PJM’s planning processes and Regional Transmission Expansion Plan (RTEP).
She noted FirstEnergy Solutions’ March announcement that it would withdraw its deactivation of the 1,872-MW Beaver Valley nuclear plant in Shippingport, Pa., citing Pennsylvania’s efforts to join the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI). (See Beaver Valley Nuclear Plant to Stay Open.) The company had filed a deactivation notice for the plant in March 2018, targeting a 2021 retirement.
“As a result, there are several baseline upgrades identified,” Tesfa said. “Beaver Valley only recently announced the withdrawal of their deactivation request, and as a result, PJM is evaluating the impacts of the reinstatement of those generators, and we’ll provide the results in the future meetings.”
PJM is working to determine which transmission upgrades it can cancel in response FirstEnergy Solutions’ reversal, she said.
ISO-NE Tx Planning
Brent Oberlin, ISO-NE director of transmission planning, presented updates on the RTO’s transmission planning evaluations of the New England system.
Oberlin highlighted Tariff changes to enhance the competitive transmission solicitation process, which FERC approved in December, including:
- creation of the Selected Qualified Transmission Project Sponsor Agreement (SQTPSA) to help determine the design and build of a new transmission project;
- improvements to Attachment K to the Open Access Transmission Tariff; and
- modifications to Schedule 12C of the Tariff to establish a new baseline for consideration of localized costs.
ISO-NE has completed a number of transmission planning studies, driven by the upcoming retirement of the Mystic generators in Connecticut, he said.
The RTO’s competitive transmission solicitation for Boston garnered 36 proposals from eight qualified parties by the March 4 deadline, Oberlin said. The RTO is confident that some proposals in the phase one study process are going to be available for New England ahead of the June 1, 2024, retirement date for Mystic 8 and 9. (See “Faster Boston RFP,” NEPOOL Participants Committee Briefs: May 7, 2020.)
ISO-NE received two submittals this year on the region’s public policy transmission planning process, one from National Grid and the other from the Episcopal Diocese of Rhode Island, each of whom identified public policy requirements or other actions that, in their view, drive transmission needs, he said.
“All that information was forwarded to the New England States Committee on Electricity (NESCOE), and the way that works is they have the option of providing a response to the ISO … and they can also supplement that information,” Oberlin said.
NESCOE responded that it does not think ISO-NE should be studying any public policy transmission upgrades for this cycle, he said.
“We did add two new projects, which were to address the time-sensitive needs in Boston,” Oberlin said.
Thirty-four new projects were added to the asset condition list, the lion’s share of which were for replacing aging infrastructure, such as wooden poles damaged by woodpecker holes, he said.
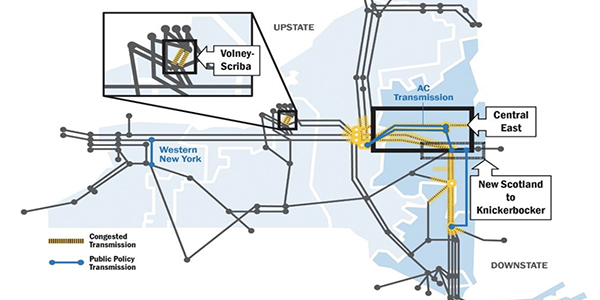
NYISO Tx Planning
Philip Chorazy, NYISO senior engineer for public policy and interregional planning, presented updates on the ISO’s Comprehensive System Planning Process (CSPP).
The 2020 Reliability Needs Assessment (RNA) will incorporate impacts of a new peaker rule into its base case reliability analysis, Chorazy said. The New York State Department of Environmental Conservation adopted a regulation to limit nitrogen oxide emissions from simple cycle combustion turbines, or peaking units, he said. The new regulations go into effect May 1, 2023, with initial rate limits of 100 parts per million on a dry volume basis, corrected to 15% oxygen. (See NY DEC Kicks off Peaker Emissions Limits Hearings.)
The RNA also will include a scenario evaluating the impacts of 70% of energy produced from renewable resources by 2030 for both transmission security and resource adequacy, with the first pass of RNA results to be presented next month, Chorazy said. New York’s Climate Leadership and Community Protection Act (A8429) signed into law last July calls for 70% of the state’s electricity to come from renewable energy resources by 2030, doubles the distributed solar generation target to 6 GW by 2025 and nearly quadruples the previous offshore wind energy target to 9 GW by 2035.
Chorazy also explained that the ISO’s the Congestion Assessment and Resource Integration Study (CARIS), which determines the top three congested locations in the New York Control Area and is intended to develop generic solutions for transmission, generation, demand response and energy efficiency. The 2019 CARIS Phase 1 draft report was presented at the ISO’s Electric System Planning Working Group in April, with a final draft scheduled for July, pending Board of Directors approval.
NYISO will initiate the 2020/21 Public Policy Transmission Planning Process cycle in August by issuing a solicitation for proposed transmission needs driven by public policy requirements, Chorazy said.