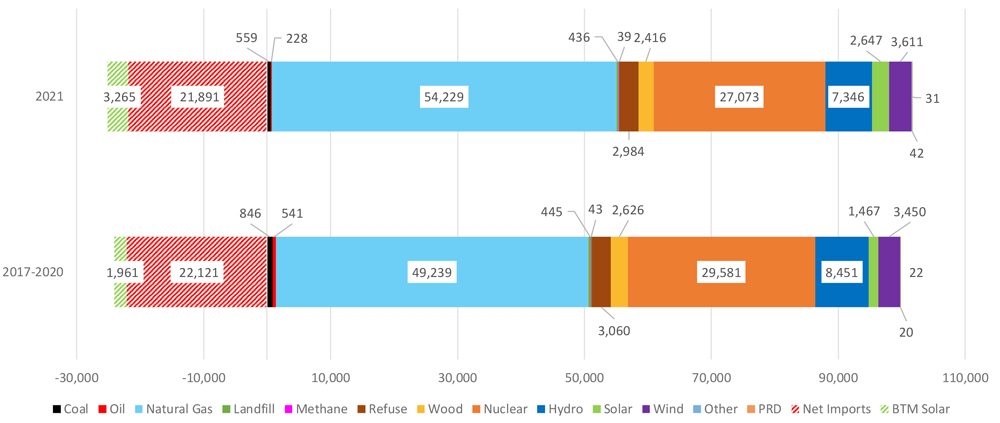
Emissions from power generation in New England rose in 2021 compared to the average of the prior four years, as load increased and more natural gas was burned.
According to ISO-NE, the estimated CO2 emissions from generation in its footprint in 2021 were 30.9 million metric tons (MMT), 2.6% higher than the four-year average from 2017 to 2020 of 30.1 MMT.
 New England used more natural gas and fewer renewables in 2021 than the average of the previous four years. | ISO-NE
New England used more natural gas and fewer renewables in 2021 than the average of the previous four years. | ISO-NE
That increase was fueled by a 10% hike in emissions from natural gas-fired generation, which rose from 19.8 MMT to 21.8 MMT over the same time period.
As gas generation rose in 2021 to 54,229 GWh in New England — a roughly 5,000-GWh increase over the previous four-year average — renewable generation fell by about 2,500 GWh to 27,073.
In ISO-NE’s presentation from analyst Patricio Silva to the Planning Advisory Committee on Thursday, the RTO emphasizes that emissions are still steadily declining in the long term, from a peak in 2005, and that year-to-year trends have shown variability.
 Emissions from power generation in New England increased by 2.6% in 2021 compared to the average of the previous four years. | ISO-NE
Emissions from power generation in New England increased by 2.6% in 2021 compared to the average of the previous four years. | ISO-NE
But in 2021, “winter and summer air pollution spikes occurred due to continued reliance on fossil fired-generators for peaking service,” Silva said.
The RTO pointed to higher demand as part of the culprit for the higher carbon intensity and deeper environmental impacts.
Power generation reached 101,640 GWh in 2021, compared to a four-year average of 99,784 GWh. Net imports declined in 2021 to 21,891 GWh, down from the four-year average of 22,121 GWh.
The update did include one piece of good news: Nitrogen oxide emissions from power generation in New England continued to fall in 2021, declining 6% compared to the past five-year average. Sulfur dioxide emissions fell too, down 15% from the five-year average.