By Tom Kleckner
The D.C. Circuit Court of Appeals on Tuesday denied Kansas regulators’ challenge to a 2014 FERC order approving SPP’s merger with the Integrated System (IS) (15-1447).
In its petition for review, the Kansas Corporation Commission contended that FERC’s approval of the merger allowed SPP to integrate Basin Electric Power Cooperative and Heartland Consumers Power District into its transmission footprint under agreements that shielded the two new members from paying certain transmission facility costs (ER14-2850, ER14-2851).
The Kansas commission argued that FERC “wrongly accepted a rate structure that disadvantaged the SPP participants” and “unreasonably accepted” what it called faulty data in the RTO’s calculation of the merger’s benefits.
At issue was the allocation of costs for SPP legacy facilities in the agreement between the RTO and the Integrated System parties. The KCC said FERC’s approval would establish inequitable precedent that entities desiring to join an RTO can negotiate “sweetheart deals” in exchange for reducing administrative rates.
In an opinion authored by Senior Judge Stephen F. Williams, the court rejected the KCC’s request to review FERC’s decision, saying the court found no basis for a claim of undue discrimination.
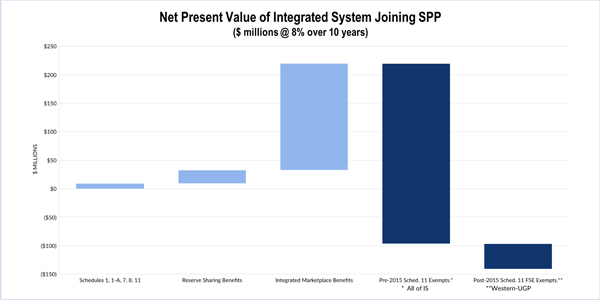
“Kansas argues, in effect, that by accepting these provisions, SPP got taken for a ride,” Williams wrote, pointing to a KCC expert’s calculations that SPP would have received almost $360.5 million in revenue (net present value) over 10 years were the Integrated System parties required to pay for the use of its legacy facilities. The system comprises its own transmission zone within SPP’s footprint, which is divided into 18 different zones.
While a Brattle Group study of the merger estimated the RTO would reap $220 million in benefits over 10 years, the KCC said the foregone revenue meant the integration will actually cost existing SPP members almost $141 million during that period.
The court noted FERC’s determination reflected “prior investment decisions and the fact that existing facilities were built principally to support load within the [pre-merger SPP] sub-region,” and said the commission’s approval of similar arrangements “has withstood judicial review in analogous circumstances.”
“FERC accurately described the agreement as reciprocal,” Williams wrote. “It would be difficult to label it otherwise, as the agreement and FERC’s approval assigned each side’s legacy costs to the power consumers in that side.” He said the arrangement’s reciprocity undermined the KCC’s contention that SPP left $475 million (nominal) lying on the table.
“Kansas never suggests any reason to believe that the IS parties would have agreed to share SPP members’ legacy costs without demanding that SPP members share the IS parties’ legacy costs,” Williams wrote.
The court also said the KCC overlooked other benefits to the merger, such as increased efficiency and reliability; improvement in SPP’s dispatch of power on its western edge; and a lower price of energy by virtue of reduced generation curtailment.
Williams said the Kansas regulators’ claim of lack of access to the Brattle study was “somewhat exaggerated.” The commission had access to a redacted, electronic version before the start of the FERC proceedings and other public data, he said, but it never pinpointed either a special reason to question the study “or some debilitating feature of the redaction.”
The KCC also asserted its expert’s testimony was “simply ignored” by FERC in disputing the proposed integration and SPP’s cost/benefit analysis.
“Not true,” Williams wrote. “As the … discussion demonstrates, the testimony was considered, but rejected on the merits.”
The court also found no fault in FERC’s decision not to order a hearing on the issue, noting the Kansas regulator was unable to point to any vulnerability in SPP’s expert witness testimony that could have been “better resolved” with cross-examination rather than the analysis of written testimony.
“We therefore find no abuse of FERC’s discretion,” Williams wrote.
A KCC spokesperson said the commission is still reviewing its options.