Federal Energy Regulatory Commission
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission is an independent regulatory agency that oversees the transmission of electricity, natural gas and oil in interstate commerce, as well as regulating hydroelectric dams and natural gas facilities.
Market Monitors Joe Bowring and David Patton have doubts about the wisdom of large-scale transmission expansions, warning they may crowd out market solutions.
U.S. Energy Secretary Jennifer Granholm said that while a lot of progress has been made, getting to a fully decarbonized economy is going to require new technologies.
FERC and DOE have plans in place they might have to use this weekend in the event Congress fails to fund the federal government, forcing its closure.
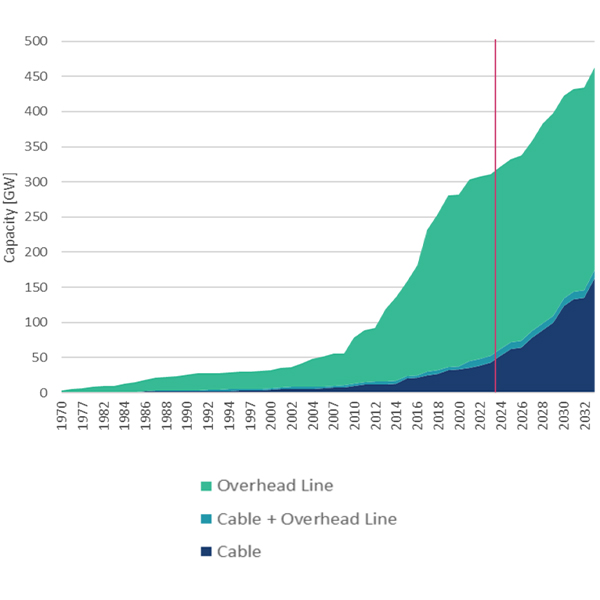
A report released by ACORE and Grid United highlighted how Europe is using HVDC transmission lines to advance its decarbonization efforts and explained how the U.S. could do the same.
The BIG WIRES Act would require FERC to set minimum transfer capabilities between regions to better connect the grid in order to promote reliability and ship cheap power around the country.
A House hearing looking into Republican bills aimed at curbing DOE's efficiency regulations displayed the partisan split on reliability and energy efficiency.
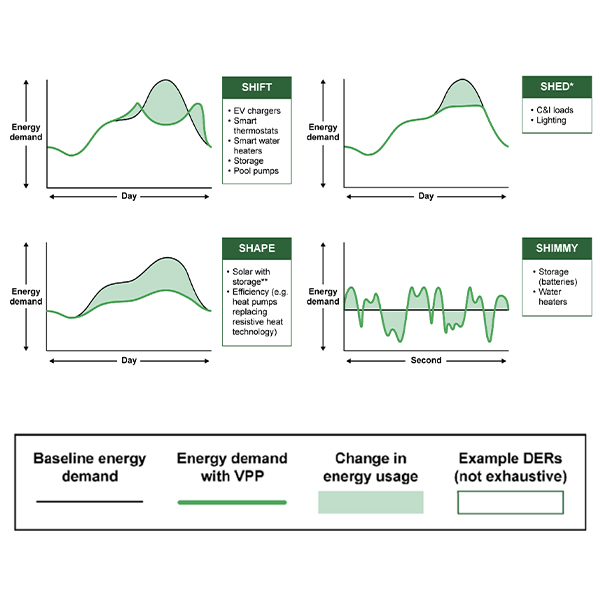
The Department of Energy released a report outlining how to bring more virtual power plants online, which can be a money-saving way of helping to balance the grid and maintain resource adequacy.
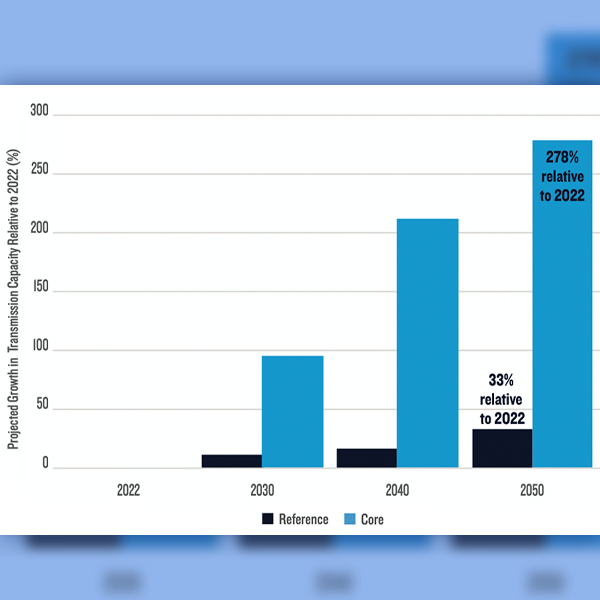
The U.S. must double the number of transmission projects permitted and built each year to meet its clean energy potential, according to the NRDC.
FERC got rehearing requests on its interconnection queue reforms in Order 2023 this week from around the industry.
The American Clean Power Association filed a petition at FERC asking the commission to take a universal look at capacity accreditation of different generation technologies.
Want more? Advanced Search