FERC & Federal
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission is an independent regulatory agency that oversees the transmission of electricity, natural gas and oil in interstate commerce, as well as regulating hydroelectric dams and natural gas facilities.
The Trump administration is gearing up — possibly — to terminate billions more in energy-related grants awarded under the Biden administration.
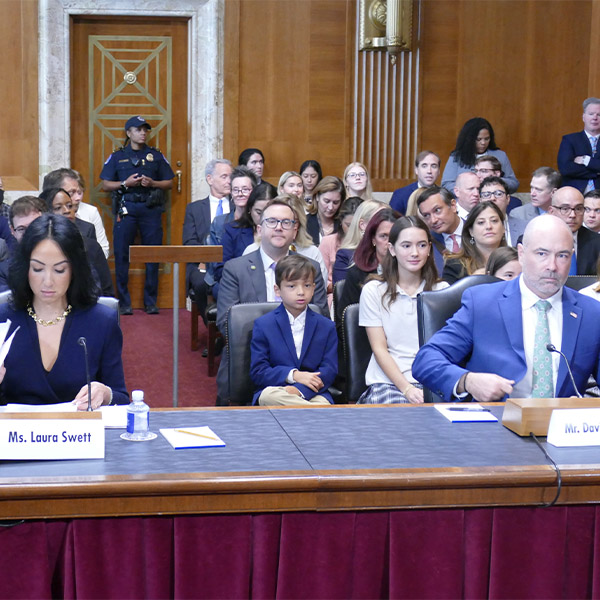
The Senate voted 51-47 along party lines to confirm over 100 nominees, including Laura Swett and David LaCerte to open seats on FERC.
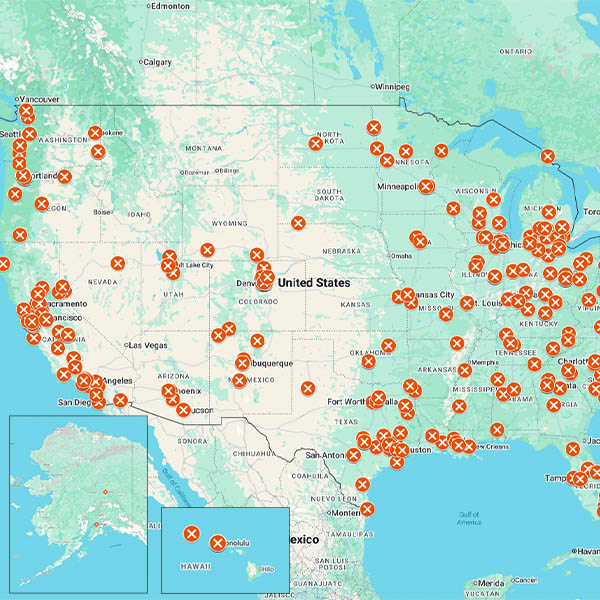
The U.S. Department of Energy has terminated 321 grants totaling $7.56 billion for 223 projects, apparently targeting Democratic-leaning states.
FERC issued a final rule and related Notice of Proposed Rulemaking on Oct. 1 to start “sunsetting” 53 regulations in response to an executive order from President Donald Trump.
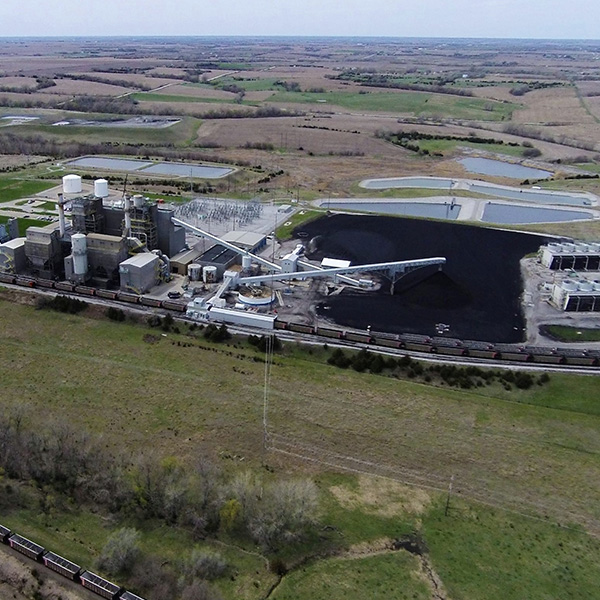
The Tennessee Valley Authority is closing in on a gas-for-coal swap at its Cumberland plant after the D.C. Circuit Court of Appeals rejected environmental groups’ arguments against FERC’s environmental review.
U.S. energy agencies including FERC laid out their plans for operations during the federal government shutdown.
The U.S. Department of Energy is looking for developers that want to build artificial intelligence data centers — and the power generation to run them — on two nuclear sites.
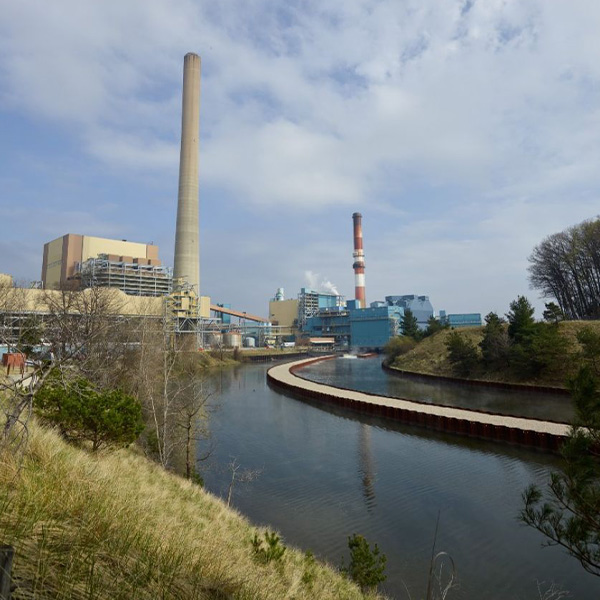
Three cabinet-level agencies announced coordinated policies that are meant to improve coal's position in the energy system by improving power plants, cutting environmental regulations and increasing mining of the fuel.
William & Mary Law School announced it has appointed former FERC Chair Mark Christie as the 2025 Lowance Fellow, a visiting professor of the practice of law and the founding director of the school’s new Center for Energy Law & Policy.
U.S. Energy Secretary Chris Wright said his department is working with utilities around the country to keep more coal plants slated for retirement open to help meet rising demand from data centers and other new large loads.
Want more? Advanced Search