Reliability
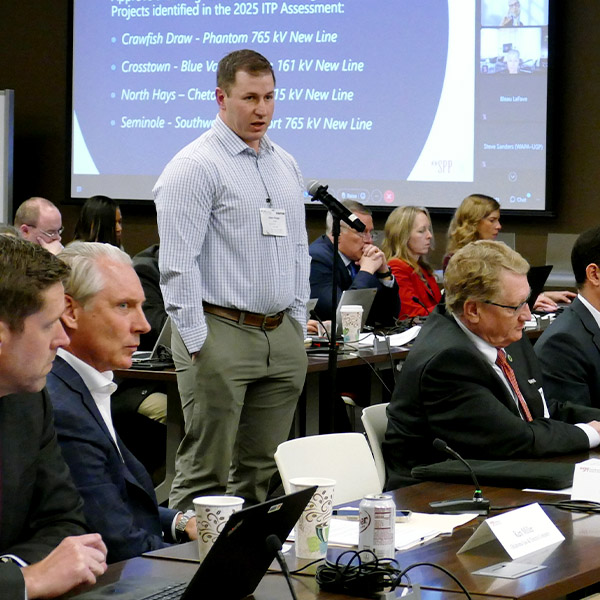
SPP's Board of Directors approved a framework for demand response and peak demand assessments despite opposition from members and stakeholders.
NERC officials appeared before an Organization of MISO States board meeting in an attempt to quell regulators’ discontent with MISO’s “high-risk” label in the 2025 Long-Term Reliability Assessment.
The challenges and opportunities of meeting demand from new large loads like data centers took center stage at the National Association of State Energy Officials’ recent Energy Policy Conference.
DOE's senior leadership highlighted how the grid relies on fossil fuels to make it through winter peaks.
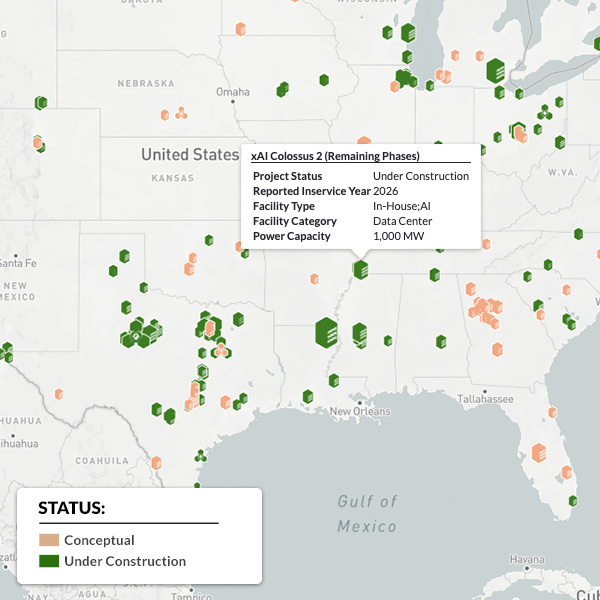
Cleanview released a report putting numbers to a trend where many hyperscale data center developers are building dirtier, more quickly available generation to cash in on the AI boom.
All five FERC commissioners faced questions from the House Energy and Commerce Subcommittee on Energy on how to balance reliability and affordability as demand grows.
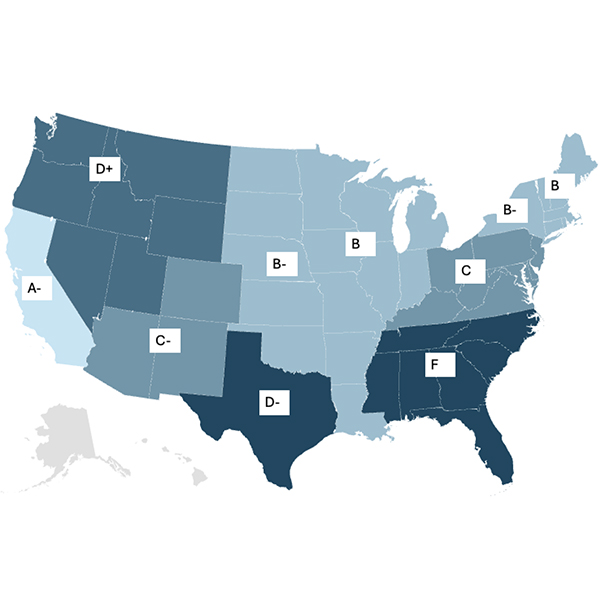
Americans for a Clean Energy Grid released an updated version of its report card, which generally shows improved scores as regions have implemented changes in the last couple of years.
NYISO began what is expected to be a yearlong effort of revising its Reliability Planning Process at a Transmission Planning Advisory Subcommittee meeting.
MISO said it likely will create interconnection reliability requirements and explore new rules that could bring large customers online in stages, as capacity becomes available, to get a handle on large loads eyeing MISO locales.
ERCOT says it leaned on Texas’ 15 mobile generating units and an RMR unit during the state’s first major cold-weather event since 2021’s disastrous Winter Storm Uri.
Want more? Advanced Search