Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
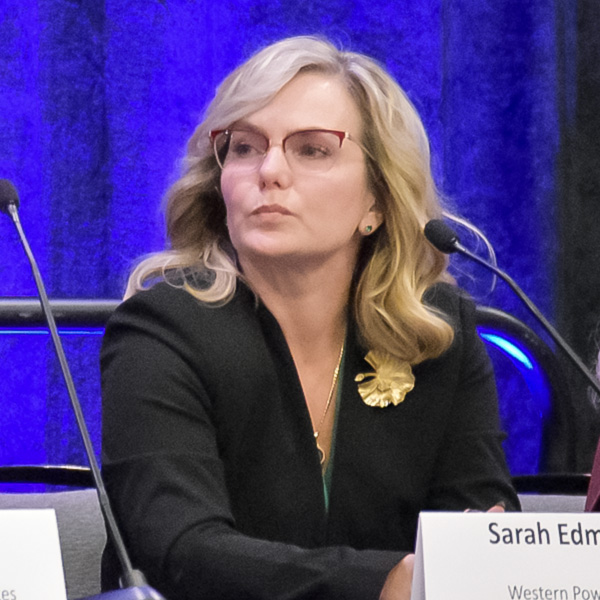
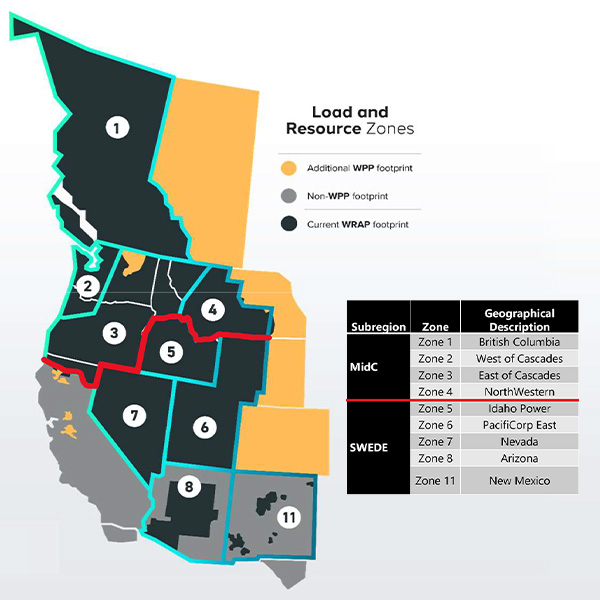
Western Resource Adequacy Program participants still strongly support the program despite recently appealing to delay its “binding” penalty phase by one year due to concerns about capacity shortages, WPP's Sarah Edmonds said.
ERCOT is searching for alternatives to replace capacity that will be lost with the planned retirement of three gas-fired units near San Antonio.
MISO announced that 123 GW of new generation spread across 600 applications are vying to enter its generator interconnection queue under the 2023 cycle.
Citing “significant new headwinds” to securing energy resources, participants in the Western Resource Adequacy Program are seeking to delay the program’s “binding” penalty phase by one year, to summer 2027.
The Gulf Coast Power Association Spring Conference tackled the vexing assignment of how to reliably serve Texas’ unprecedented surge in demand with a cleaner energy supply.
A DOE report on resource adequacy says firms investing in natural gas capacity could be retrofitted with carbon capture and storage, or the ability to burn clean hydrogen.
California could significantly cut power costs through increased use of VPPs, according to the study by The Brattle Group and GridLab.
Proposed supply agreements between Constellation and Massachusetts gas utilities which would keep the Everett Marine Terminal operating through 2030 are facing pushback from environmental organizations and the Attorney General’s Office.
SPP’s effort to impose capacity accreditation methodologies for thermal and renewable resources has drawn protests from public-interest and clean-energy groups at FERC.
While their net-zero emission targets might not kick in until the 2030s, the power industry already is dealing with the issues they create, panelists said at the Electric Power Supply Association’s Competitive Power Summit.
Want more? Advanced Search