Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
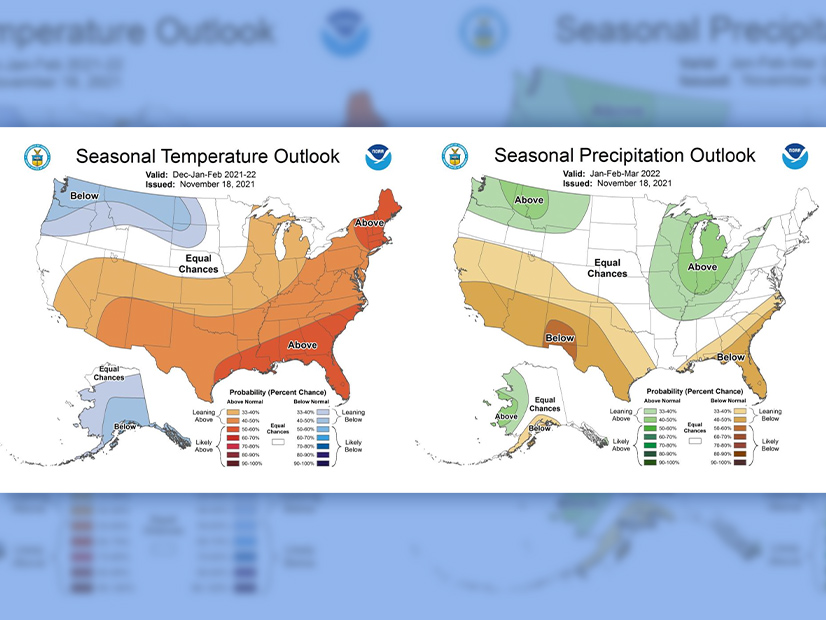
Stakeholders at MISO Board Week offered a few tips on how the footprint can weather a tough winter, a day after the RTO elevated wintertime risk levels.
Texas PUC Chair Peter Lake said "the lights will stay on" this winter, based on the commission's new weatherization rules and market changes.
MISO raised alarm bells about soaring forced outages should a severe arctic blast descend on the footprint this winter.
MISO will jettison the most inexpensive step of its operating reserve demand curve, explaining that $200/MWh pricing is too low during shortage conditions.
Limited fuel supplies put the New England grid at heightened risk of emergency actions — including controlled outages — this winter, ISO-NE said.
ISO-NE stakeholders approved tariff changes that incorporate a new transmission planning process focused beyond the RTO’s current 10-year planning horizon.
NYISO presented stakeholders with updates on its Grid in Transition initiative and a 2022 Master Plan for managing the changes to market rules.
The California Public Utilities Commission approved proposals to head off capacity shortfalls in summer 2022 and 2023, including increasing demand response.
FERC accepted a second round of changes from CAISO's stakeholder initiative on hybrid resources, including a contested exemption for renewables plus storage.
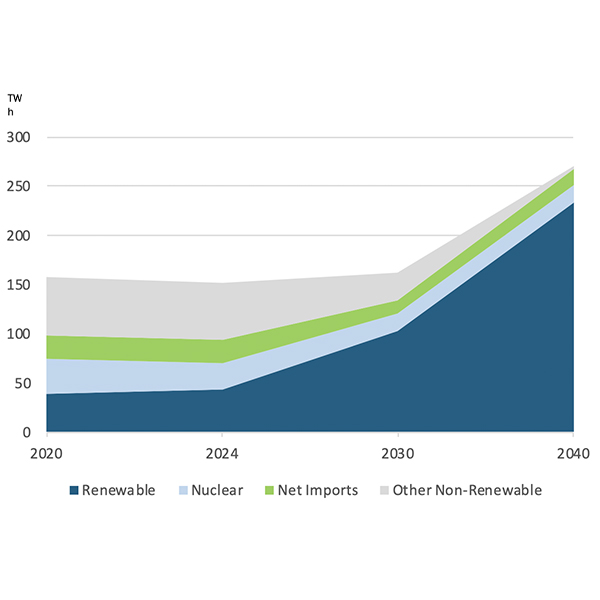
A new report from ACORE argues that industry needs to rethink the concept of resource adequacy to get more renewable energy online and decarbonize the grid.
Want more? Advanced Search