Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
PJM stakeholders unanimously endorsed the 2021 reserve requirement study but requested more modeling on the impacts of extreme weather conditions.
The ERCOT Board of Directors agreed to approve the 2022-2023 biennial budget and to keep the administrative fee at its current rate.
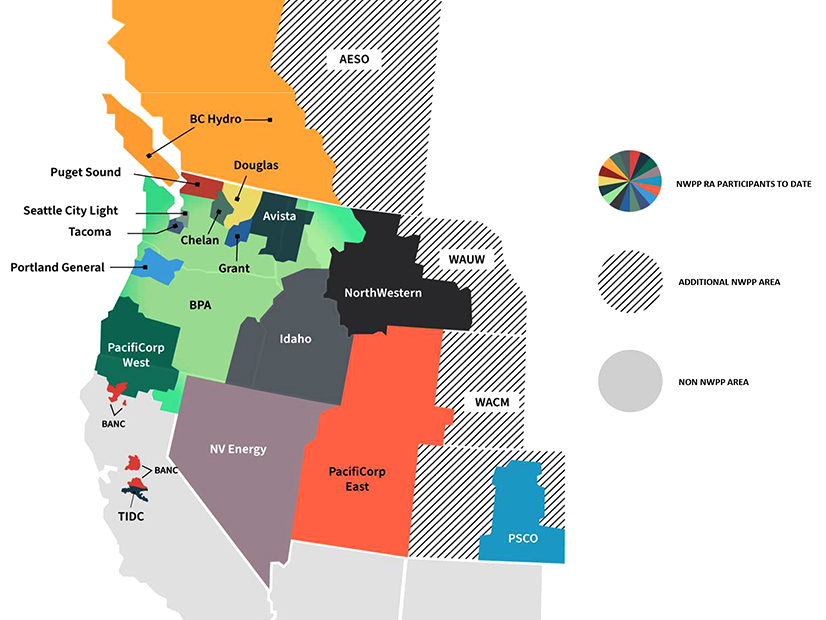
SPP continues to spread its footprint with an announcement Tuesday that it will operate Northwest Power Pool’s resource adequacy (RA) program in the Western Interconnection. The RTO will work with NWPP and its RA participants to help develop, implement and operate the program. As a program operator, SPP will perform forward-showing and operations program functions, …
Continue reading "SPP to Operate NWPP’s Resource Adequacy Program"
SPP released a comprehensive report on the week of February's severe winter storm, calling it the most operationally challenging week in its 80-year history.
ERCOT told the Texas PUC that it will change its outage-request procedures to avoid having too much generation offline at one time.
ERCOT stakeholders pushed back against interim CEO Brad Jones’ plan to convert TAC into an officer-level group and the increased use of ancillary services.
California Gov. Gavin Newsom signed an emergency declaration aimed at keeping the lights on this summer by waiving clean-air rules and paying more for demand response.
SPP, ERCOT and MISO are all taking action this week to meet high demand as sweltering summer temperatures kick in.
ERCOT has filed to finance $2.9 billion in market debt stemming from high-priced market transactions during February’s devastating winter storm.
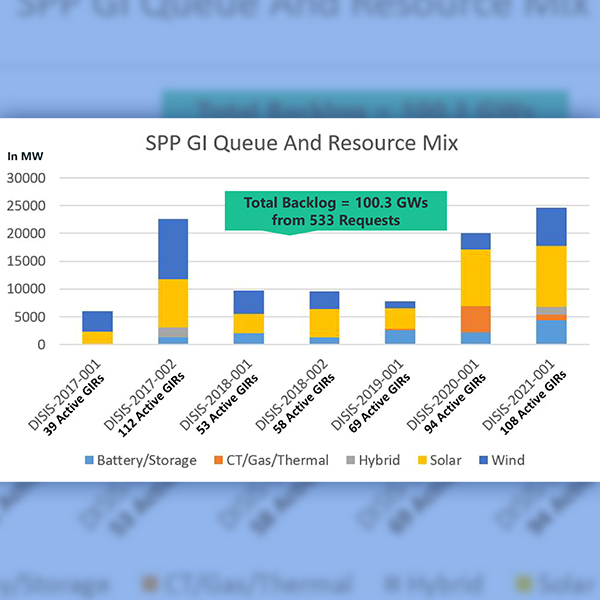
Renewable developers said SPP's plan to resolve a four-year backlog of GI requests by 2024 sets an example for the other RTOs to follow.
Want more? Advanced Search