Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
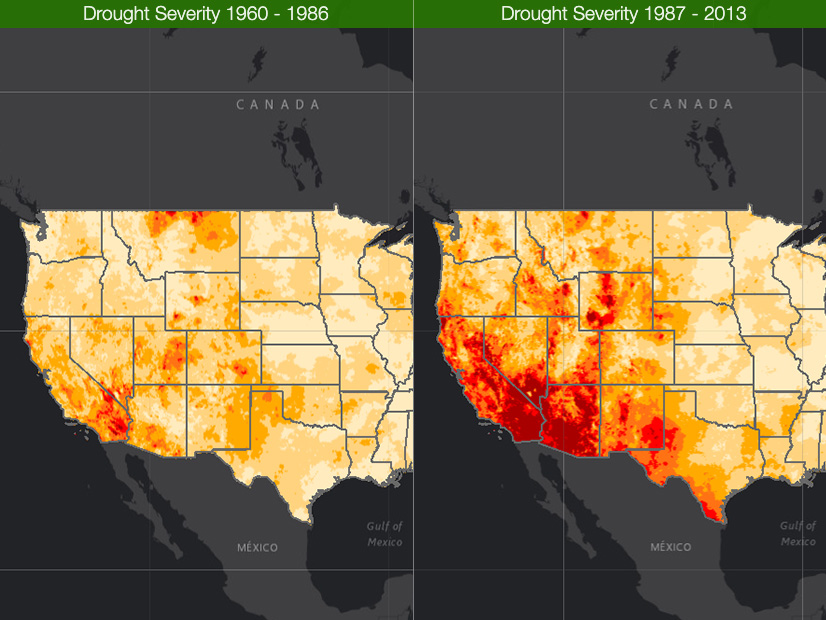
A drought in the West is cutting into hydropower supplies needed for summer reliability, especially in California, panelists in a USEA briefing said.
ERCOT stakeholders have endorsed the first system changes addressing system changes stemming from the winter weather that almost shut down the Texas grid.
The California PUC ordered an additional 11.5 GW of procurement by mid-decade but backpedaled on a plan to include up to 1,500 MW of fossil fuel generation in the mix.
The Public Utilities Commission of Nevada said a Western market would help alleviate supply shortfalls like those that occurred last August.
MISO execs say long-term transmission and a capacity market redesign are a must in response to rising climate risks and fleet change.

Matthew T Rader, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
ERCOT insiders at ACORE's Finance Forum spoke candidly on the causes and lessons learned from Texas' February outages.
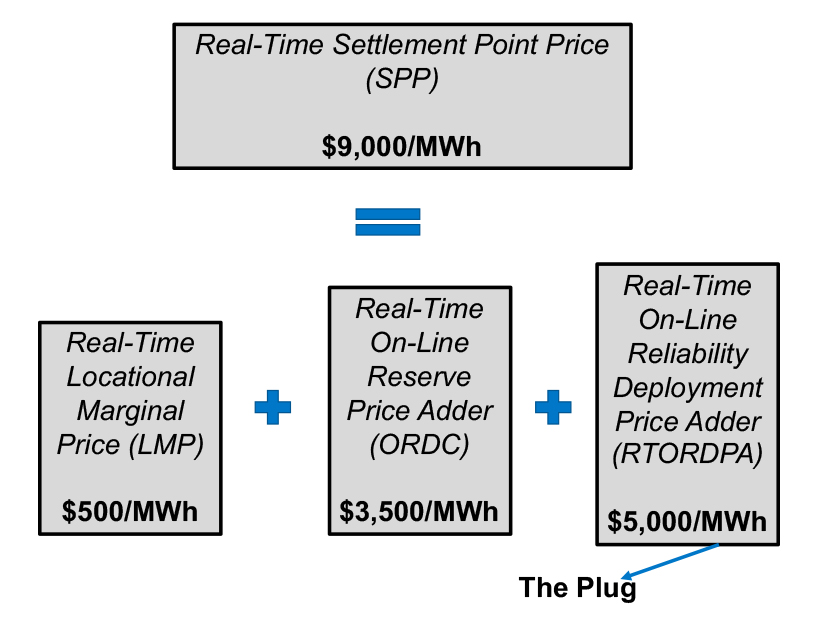
ERCOT asked for conservation measures through Friday as summer heat and 12.2 GW of forced outages erased whatever slim reserve margin it had.
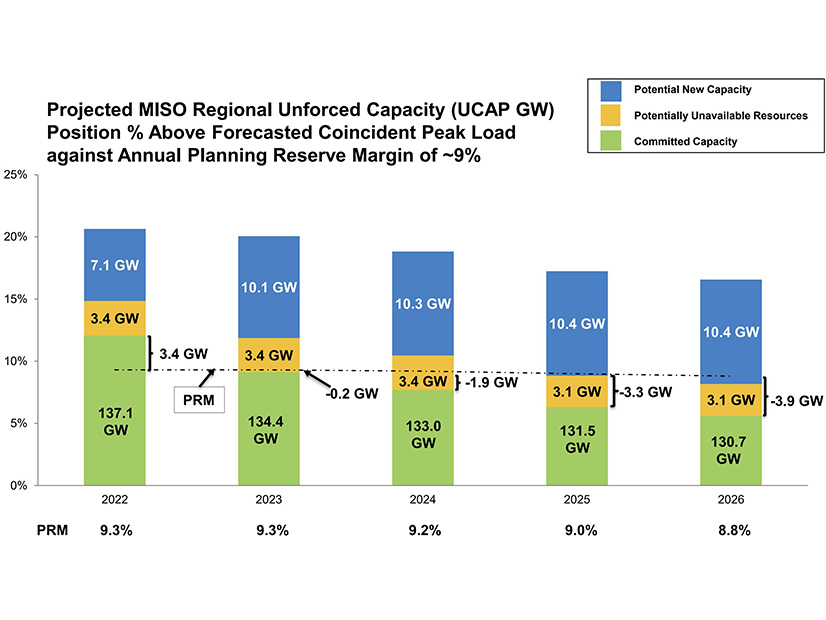
MISO and the Organization of MISO States said things are looking up in their annual resource adequacy assessment.
The MISO Market Subcommittee meeting ran the gamut of storage participation, discovery of a longstanding energy pricing error and FTR underfunding.
MISO concluded that its current suite of resource adequacy tools, and the in-progress projects it is working on, enable it to cope with extreme cold snaps.
Want more? Advanced Search