Resource Adequacy
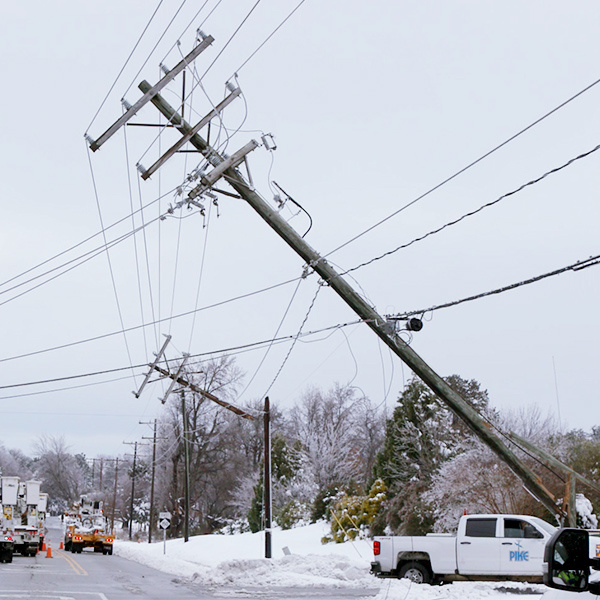
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
Panelists told FERC at a virtual technical conference that considering how climate change may affect the future grid is especially challenging.
The Texas Reliability Entity’s director of reliability services said that renewable energy will be crucial if the state is to survive another brutal summer.
ISO-NE said it should have the resources necessary this summer to meet demand during average and above-average temperatures.
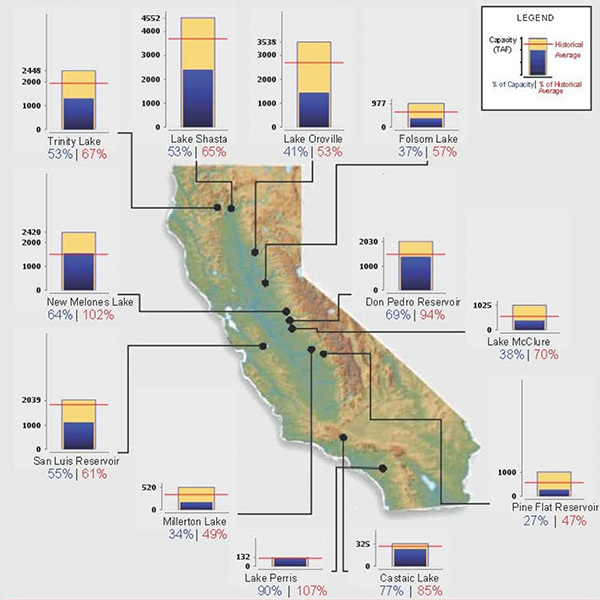
FERC OK'd CAISO tariff revisions intended to prevent the kind of supply shortages that triggered rolling blackouts in California last summer.
A FERC technical conference brought together a group of New England regulators, ISO-NE executives and the chair of the NEPOOL Participants Committee.
MISO has expanded its availability-based capacity accreditation proposal for generation resources by including hours that aren’t so risky.
The CPUC proposed requiring electric providers to procure 11.5 GW of new resources between 2023 and 2026 to meet the state’s reliability needs.
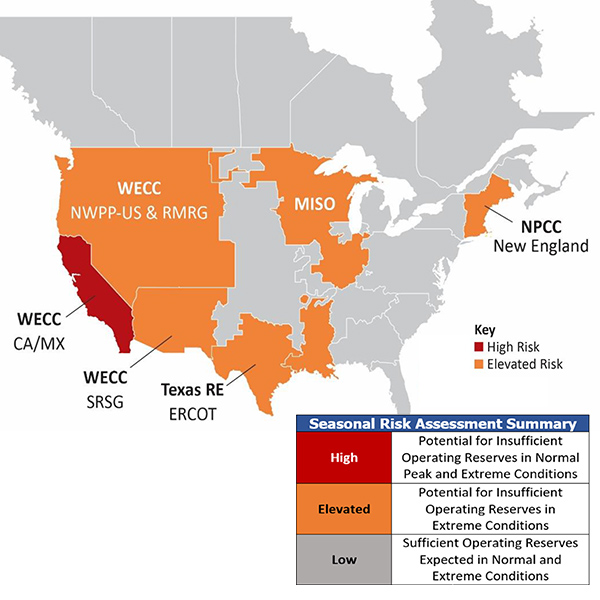
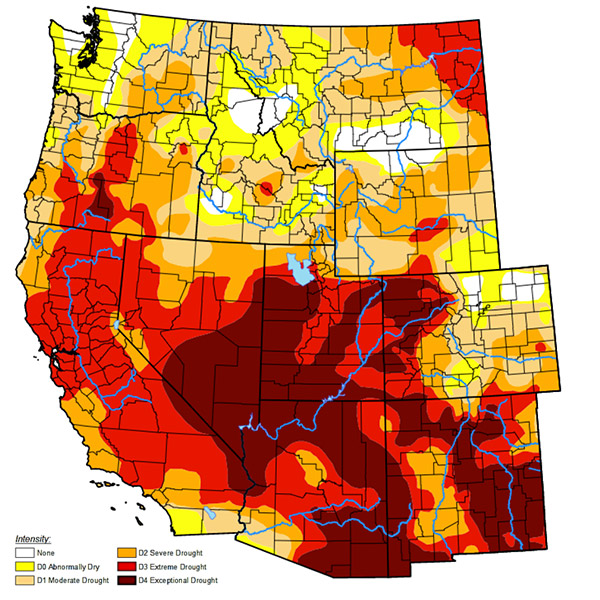
Extreme heat and drought conditions are a major cause for concern in the Western Interconnection, according to FERC’s summer assessment.
SPP said it expects normal conditions and no extreme operation situations within its balancing authority and reliability coordinator footprints this summer.
California could experience capacity shortfalls this summer during severe heat because of limited imports and low hydroelectric production, CAISO said.
Want more? Advanced Search