Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
MISO said it is close to completing a proposal to create a four-season capacity market after floating a rudimentary plan with skeptical stakeholders.
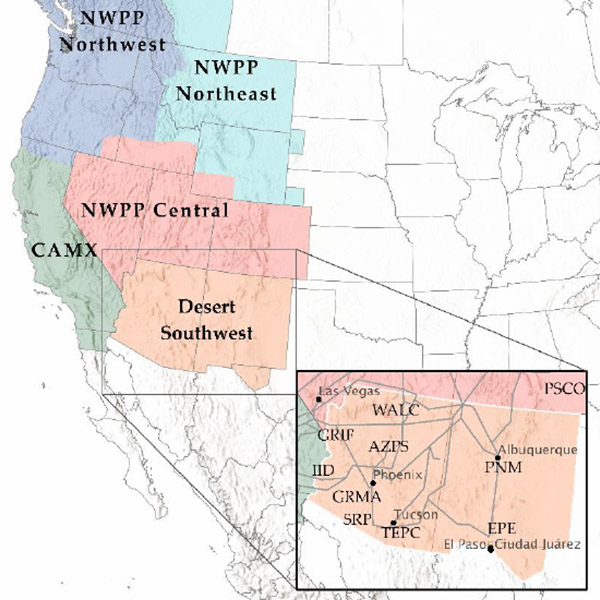
WECC's Desert Southwest region is at risk of failing to meet loads during its peak hour even under the most optimistic assumptions according to a new report
CAISO introduced a straw proposal that aims to attract supply this summer and head off shortfalls like those that led to rolling blackouts last year.
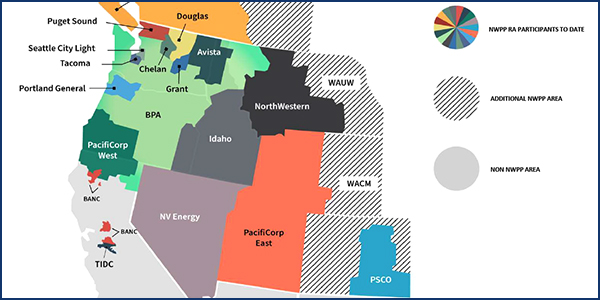
The Northwest Power Pool is moving to wrap up the design phase of its regional resource adequacy program, stakeholders heard.
Legislators in Sacramento introduced bills to ban natural gas from new construction, promote hydrogen as a fuel source and increase DR to head off blackouts
ISO-NE said stakeholders’ proposed schedule for the Phase 1 reliability and market analyses in the Future Grid Initiative is "aggressive but achievable."
The Western EIM Governing Body discussed CAISO’s summer energy shortfalls, pondering how the EIM could better serve participants during system stress.
A recent report concluded that a Western resource adequacy program could require state regulators & utilities to relinquish some control over IRP processes.
CAISO and state agencies released a final analysis of the August blackouts and steps they are taking to prevent capacity shortfalls this summer and beyond.
Gov. Andrew Cuomo presented an overview of government priorities in his State of the State address, ranking the transition to a green economy number five.
Want more? Advanced Search