Resource Adequacy
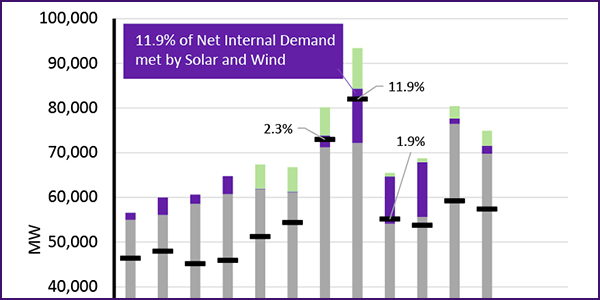
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
The expansion of renewables over the next decade is expected to “fundamentally” change how the grid is planned and operated, NERC said.
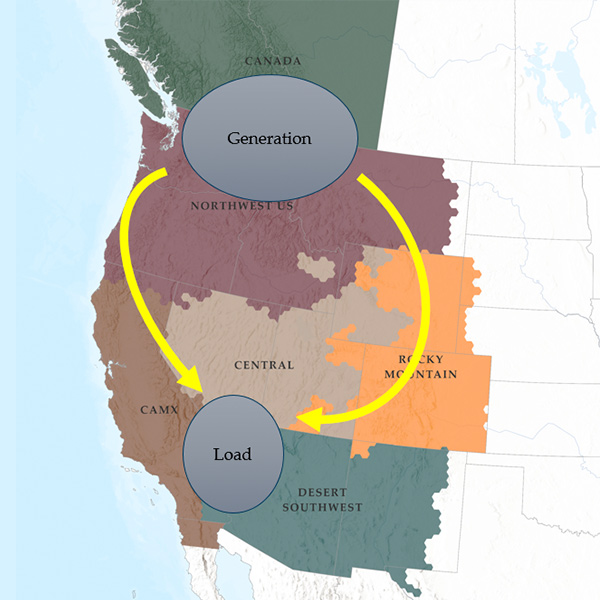
Western BAs should determine what caused errors in load and generation forecasts during August’s massive heat wave and fix their forecasting processes.
The Texas Reliability Entity bid farewell to CEO Lane Lanford, Chair Fred Day and Director Delores Etter during its annual meeting.
Top officials discussed CAISO’s handling of California’s mid-August blackouts and actions to avoid future shortages in a webinar.
U.S. energy leaders crossed the virtual border to Canada to share updates with APPrO at its annual energy and networking conference.
The Western Interconnection Regional Advisory Board recounted its accomplishments in 2020 and laid out what it hopes to achieve in 2021.
CAISO's new CEO, Elliot Mainzer, spoke with RTO Insider about his background, priorities and perspective on California's resource adequacy problem.
CAISO’s Market Monitor found no evidence of market manipulation or strategic outages during the rolling blackouts of mid-August.
The California Public Utilities Commission opened a proceeding to help prevent summer blackouts like those in August and September.
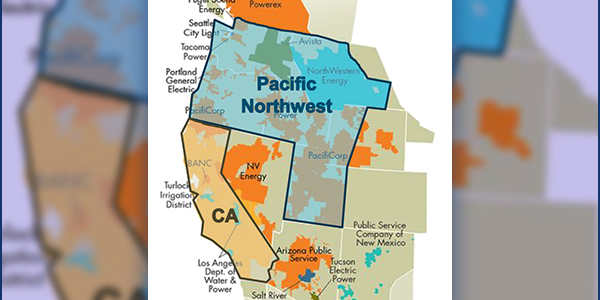
Western utility regulators have no time to waste in addressing the region’s looming resource adequacy shortfalls, industry experts said.
Want more? Advanced Search