Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
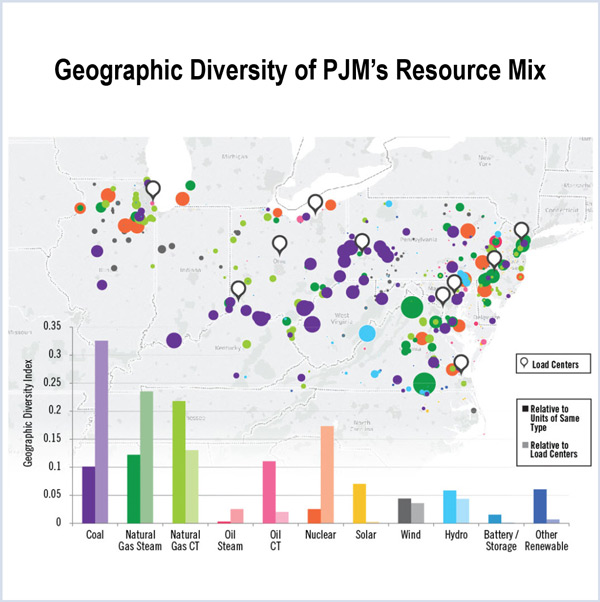
PJM can maintain adequate reliability with a generation fleet almost entirely composed of natural gas units, according to a study the RTO released.
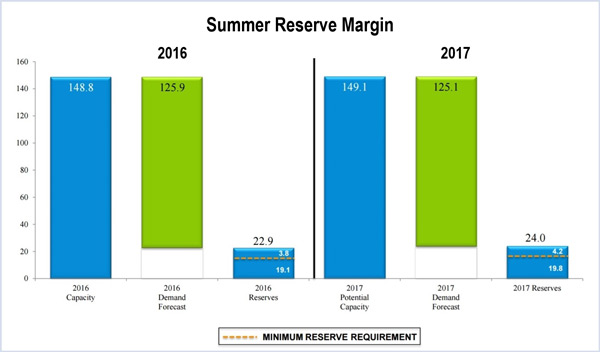
MISO expects a 19.2% planning reserve margin this summer, well above its 15.8% requirement, and a percentage point above its projection last year.
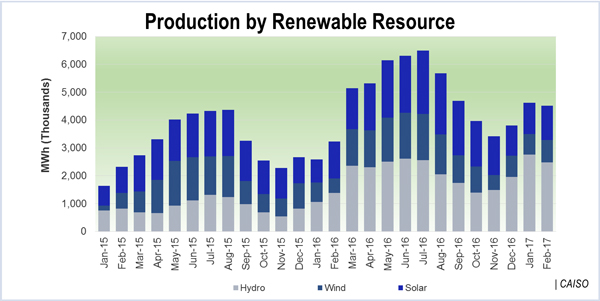
CAISO is preparing for spring oversupply, when unusually high levels of hydro output are expected to compound the impact of growing solar penetration.
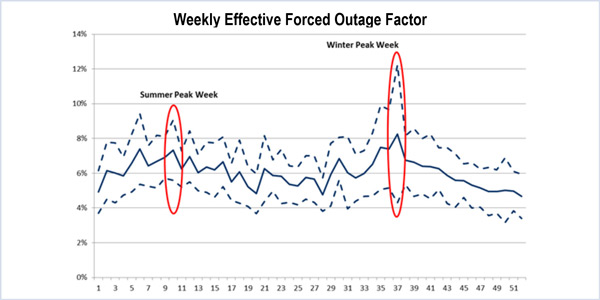
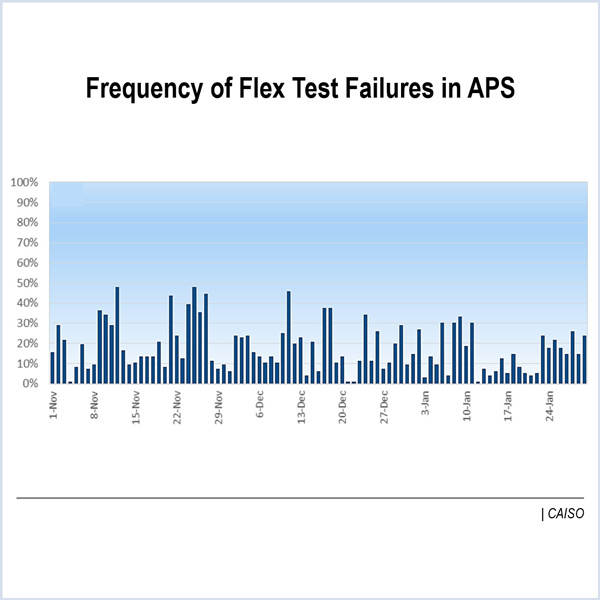
General assumptions regarding winter operations will need to be replaced with actual data to improve PJM’s winter resource adequacy analysis.
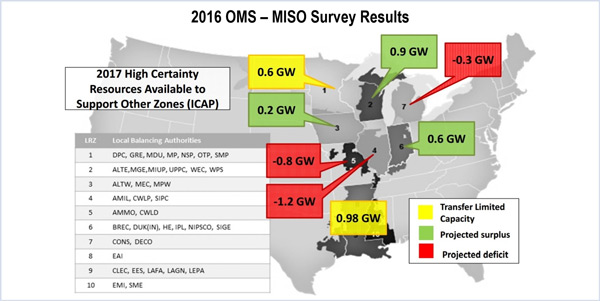
Load forecast data for the MISO 2017/18 PRA shows that all local resource zones have enough capacity to meet their clearing requirements.
MISO will roll some capacity sitting in the definitive planning phase of its interconnection queue into the annual OMS-MISO resource adequacy survey.
ERCOT’s latest seasonal assessment of resource adequacy indicates more than 82 GW of generation for an expected spring peak demand of 58 GW.
MISO is looking to improve its annual resource adequacy survey by expanding the scope of potential projects included.
Participants in the Energy Imbalance Market (EIM) should not rely on it to reduce their capacity requirements, CAISO cautioned.
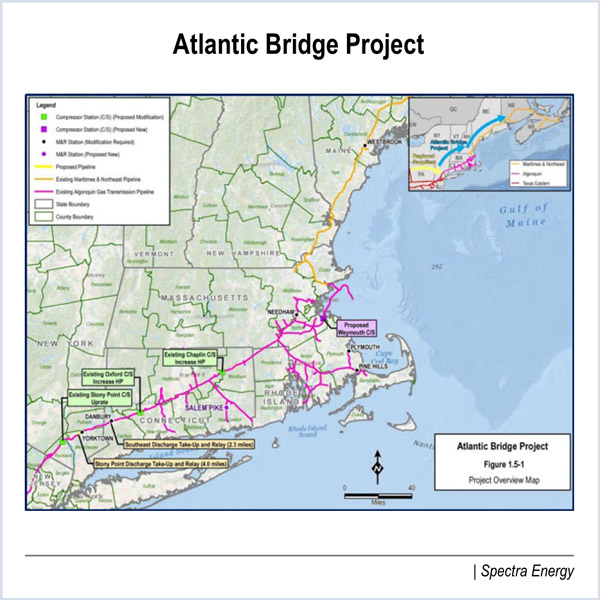
FERC approved the Atlantic Bridge pipeline project, which will expand natural gas delivery capacity in New York and New England.
Want more? Advanced Search