Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
Maryland's 2026 legislative session could show how states facing explosive demand growth can achieve their clean energy and affordability goals despite the Trump administration’s resistance to solar, wind and storage, according to Livewire columnist K Kaufmann.
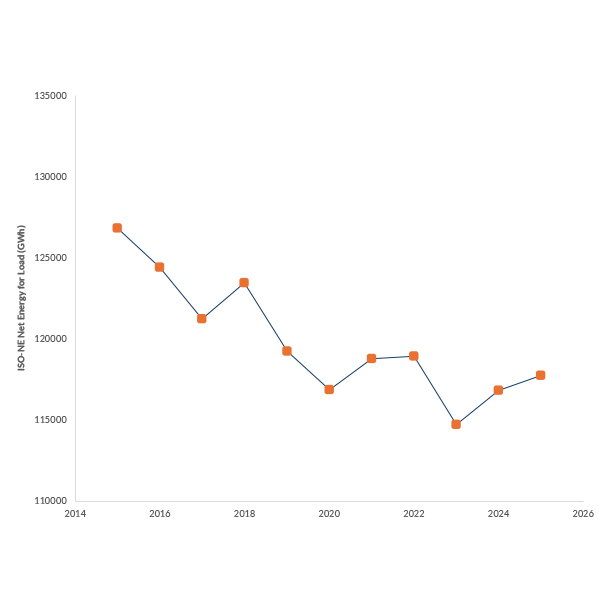
After years of declining or stagnant power demand in New England, annual energy demand ticked up for the second straight year in 2025, potentially indicating the start of a broader upward trend.
The Oregon Public Utility Commission questioned Portland General Electric’s proposals concerning grid infrastructure cost allocation for data centers, voicing concern that the utility risked prioritizing data centers over other customers.
State regulators in MISO asked FERC to let power industry stakeholders determine how to allocate the costs for an Indiana coal plant forced to stay online by the Trump administration’s Department of Energy.
The Electricity Customers Alliance released a paper offering some potential ideas FERC could take up to ensure affordability in a era of major load growth.
California’s two large offshore wind projects could be delayed by up to six years due to recent federal policy actions, a CPUC administrative law judge said.
ERCOT stakeholders used their first Technical Advisory Committee meeting of 2026 to mark the committee’s 30 years of existence and achievements, sharing memories of their work together and recognizing members.
The PJM Markets and Reliability Committee and Members Committee endorsed the RTO’s recommended installed reserve margin and forecast pool requirement for the third 2026/27 Incremental Auction.
PJM stakeholders kicked off discussions on creating a “backstop” auction to be held in September at the insistence of the Trump administration and the governors of the RTO’s 13 states.
The winter storm that moved through Texas and much of the Eastern Interconnection cut power to hundreds of thousands of people and stressed the bulk power system, but did not create major disruptions like other storms earlier this decade.
Want more? Advanced Search