Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
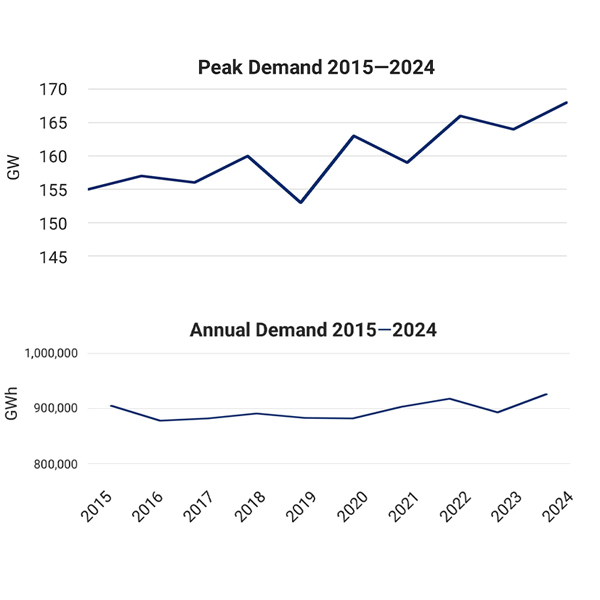
Peak demand in the Western Interconnection hit a record high of 168.2 GW in 2024, reflecting “early effects” of the growth in large loads such as data centers, according to a new WECC report.
MISO confirmed it will make a second bid to FERC to establish a temporary fast lane in its interconnection queue, this time limiting the process to 50 generation projects.
An EBA panel looked into the history of demand growth in light of its recent return, while a second panel looked at issues around utility credit ratings, as investments will have to ramp up to meet the new demand.
NYISO asked developers to tell the ISO about any dispatchable generation projects that have not yet been submitted to the interconnection queue by June 13.
The House of Representatives narrowly passed President Donald Trump’s “One, Big Beautiful Bill” that would extend tax cuts for individuals and render energy tax credits effectively useless.
President Donald Trump’s policies and the growth in demand from data centers and other new customers have changed the trajectory of the power system, speakers said at the Energy Future Forum.
BOEM lifted a stop-work order on the Empire Wind 1 project in a deal that will have New York work on expanding pipelines into the Northeast, a goal the White House has publicly sought since shortly after President Trump took office.
The California Public Utilities Commission has proposed a new framework that would take a “more programmatic approach” to load-serving entities’ resource procurement requirements compared with the agency’s recent practice of issuing procurement orders as needed.
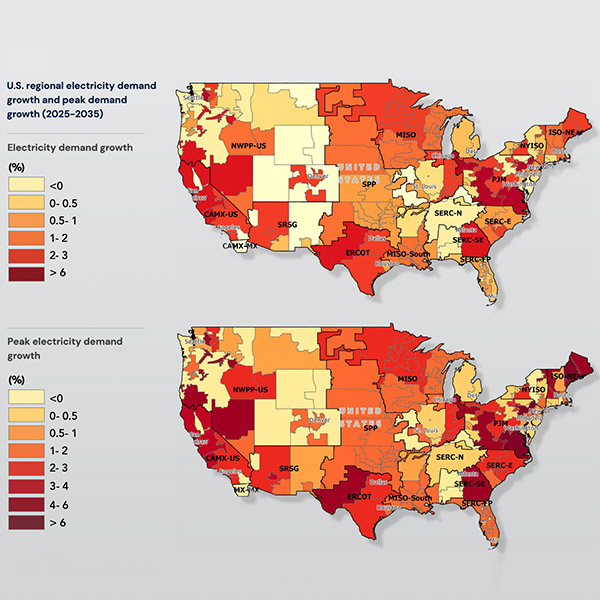
ICF International is projecting another rise in the rate of demand growth as more data centers seek to plug into the grid in the coming years, with a 25% increase from 2023 levels by 2030 and 78% by 2050.
Experts in the data center field discussed the challenges of meeting accelerating computational load during the PJM Annual Meeting, held in the core of Northern Virginia’s Data Center Alley.
Want more? Advanced Search