Resource Adequacy
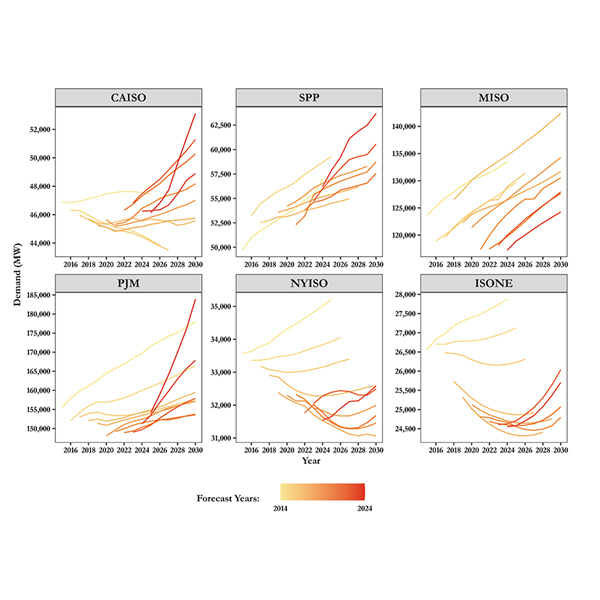
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
FERC's State of the Markets report showed lower wholesale energy prices but growing demand and higher capacity prices that signal a need to meet the coming load.
CERAWeek 2025 by S&P Global examined the changing energy landscape through 14 themes, from policy and regulation to climate and sustainability, but none seemed to draw more focus than the rapid expansion of AI and is potential transformative effects.
FERC is expected to rule on SPP’s proposed tariff revisions adding a winter season resource adequacy requirement and several other issues related to the grid operator.
ERCOT already operates a power system as large as those in several European countries, but demand growth is expected to bring it up to the level of PJM and MISO, which has the industry considering building a new system of 765-kV lines to transmit power around Texas.
MISO members haven’t landed on easy answers in getting the approximately 54 GW of unfinished generation that has cleared the interconnection queue online sooner.
Even if demand forecasts from new data centers are twice as large as what ends up being built, the growth is going to be at a scale where the power industry’s regulations need to change to keep up with it, former FERC Commissioner Allison Clements said.
Secretaries Chris Wright and Doug Burgum plugged the need for natural gas as the answer to the U.S.' energy needs during CERAWeek.
The Northwest Power and Conservation Council must ensure forecast models consider President Donald Trump’s shifting energy priorities to ensure the council’s upcoming 20-year regional power plan stays relevant, board members contended during a recent meeting.
PJM presented the Planning Committee with a draft amendment to the Deactivation Enhancement Senior Task Force’s issue charge to add a key work activity focused on creating pro forma language for reliability-must-run agreements with generation owners seeking to deactivate a unit identified as being necessary for reliability.
Attendees at Yes Energy's annual summit, EMPOWER 25, discussed the Trump administration, pending ERCOT market changes, the future of wind power generation and uses for artificial intelligence, among other topics.
Want more? Advanced Search