Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
NYISO CEO Rich Dewey opened the Management Committee meeting with a congratulations on getting through 2024 before looking ahead to the rest of 2025.
ACORE says Congress could take steps to establish more comprehensive transmission and generation planning within the TVA.
FERC has given MISO an all-clear to cap project hopefuls lining up for its overflowing generator interconnection queue at 50% of the RTO’s peak load.
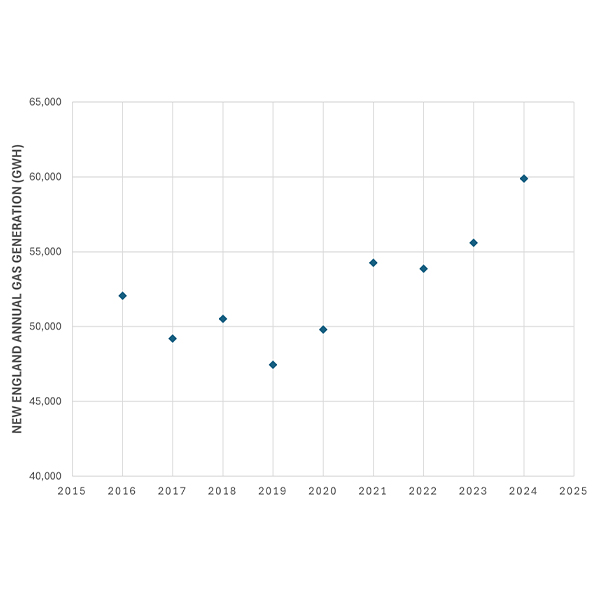
As overall power production ticked up in New England in 2024, natural gas generation reached its highest annual total in the region’s history, accounting for over 55% of all generation and 51% of net energy for load, according to new data from ISO-NE.
The Texas Public Utility Commission has opened an online portal on its website to accept registrations from cryptocurrency mining facilities with a demand of more than 75 MW.
The PJM Markets and Reliability Committee and Members Committee endorsed a proposal to rework the RTO’s rules around generation deactivations.
The Western Power Pool faced “real potential weaknesses” in 2024 due to staff shortages and outdated financial and accounting systems, the organization’s leadership said during their annual member meeting.
Groups of generation owners and developers have asked MISO to adopt a queue fast lane only as a last resort and employ a more limited process that involves scoring criteria to gain entry.
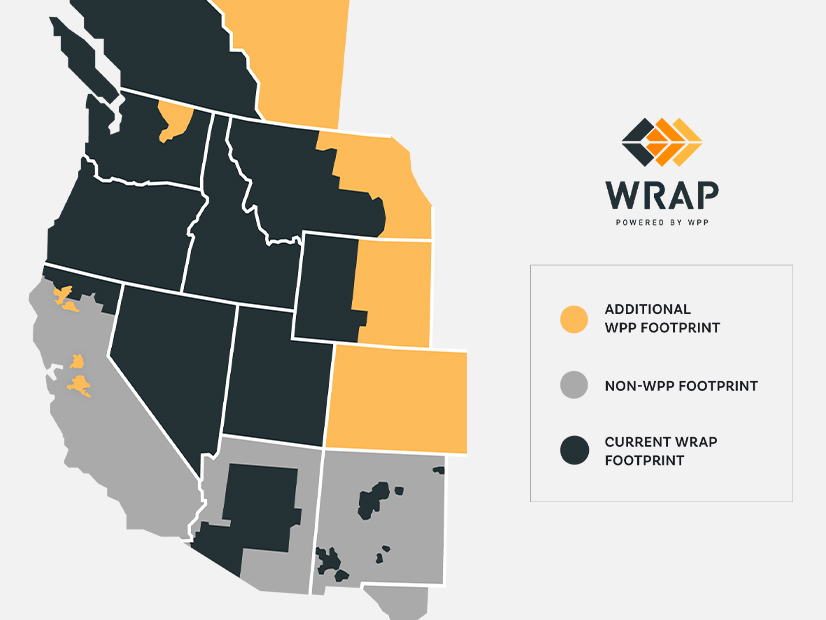
Members of a key WRAP stakeholder group voted to prioritize three topics of concern as the group continues developing the program aimed at addressing resource adequacy and reliability in the West.
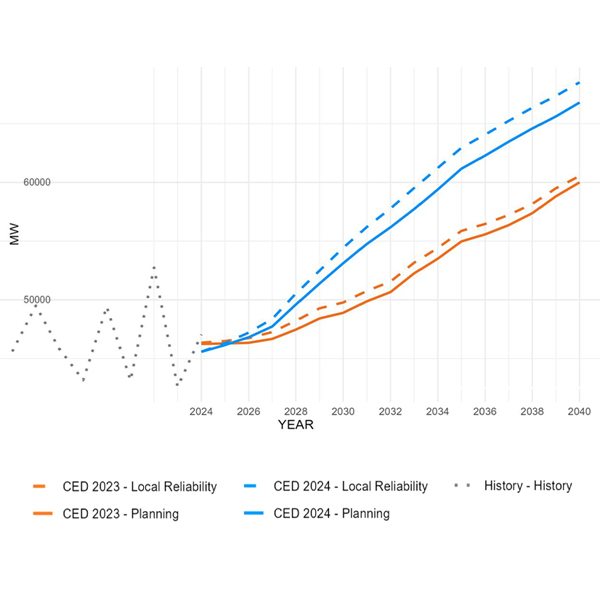
CAISO peak demand will grow from 48.3 GW in 2024 to about 68 GW in 2040, according to a new forecast that attributes much of the increase to data center load.
Want more? Advanced Search