Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
Infocast’s inaugural Midcontinent Clean Energy summit provided panelists a pulpit for critiquing MISO’s interconnection queue setup as it strains under the weight of hundreds of gigawatts intended to further fleet shift and meet load growth.
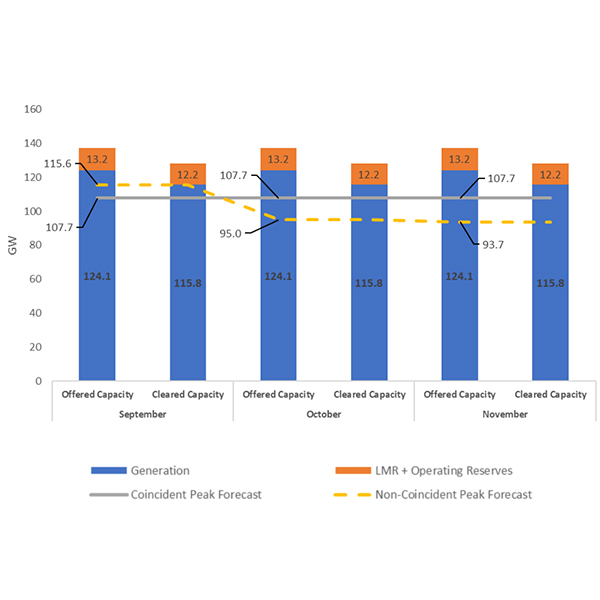
MISO doesn’t believe autumn will prove much trouble for it to tackle, though it faces a capacity shortfall in Missouri.
MISO's Todd Hillman described the pressure cooker environment of escalating data center demand, a precarious reliability situation and an overwhelmingly large interconnection queue at Infocast’s inaugural Midcontinent Clean Energy Summit.
MISO continues to try to get a bead on load growth and took stakeholder suggestions on how to best monitor sizable future load additions across the footprint.
The integration of Markets+ with the Western Resource Adequacy Program would be among a handful of key reliability benefits of SPP’s Western day-ahead offering, according to an “issue alert” published by 10 entities that backed development of the market.
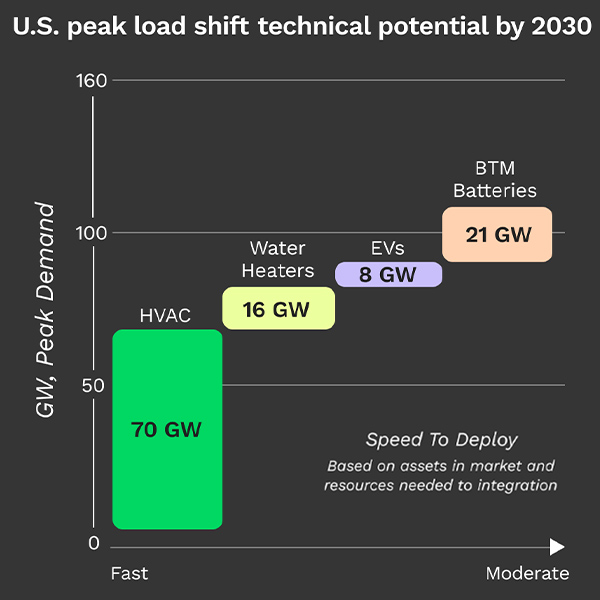
Home energy management company Renew Home has released a position paper arguing that VPPs can quickly be stood up to help meet growing demand.
SPP directors and regulators have approved the grid operator’s first winter planning reserve margin, endorsing a base PRM that is 3 percentage points higher than many of its utilities wanted.
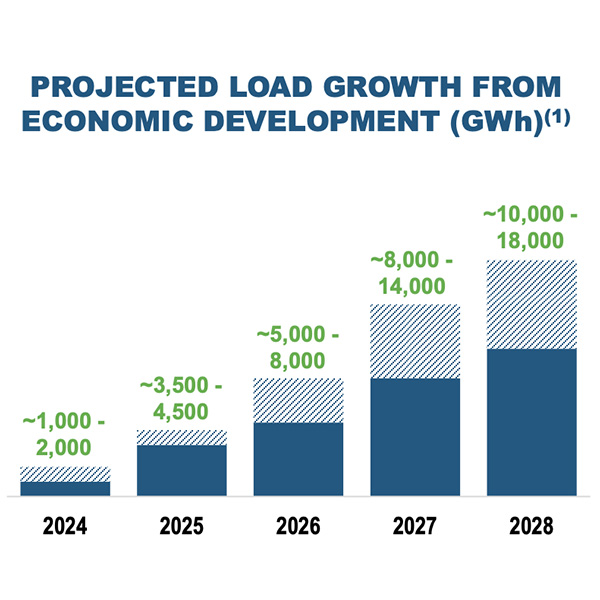
Five years ago, load growth from transportation electrification was a major issue for policymakers, according to speakers at a webinar. Now the focus has shifted to data centers.
Duke Energy executives highlighted how the return to load growth is impacting its utilities during its second-quarter earnings call with analysts.
PPL reported GAAP earnings of $190 million for the second quarter and executives focused on changing market dynamics in PJM during a teleconference with analysts.
Want more? Advanced Search