Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
Two former FERC chairmen are pessimistic that MISO will be able to reign in shortages or high capacity prices anytime soon.
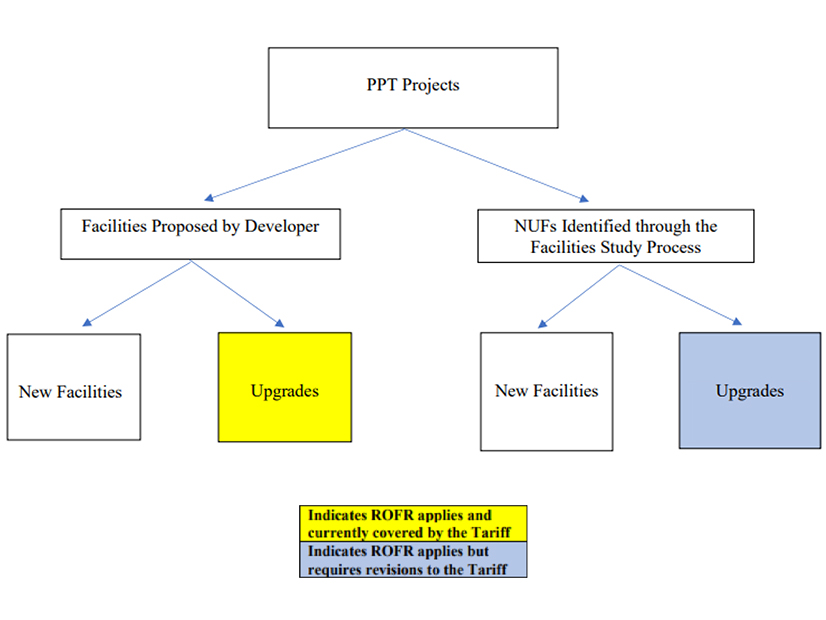
New York TOs proposed tariff amendments that would clarify their ability to exercise a ROFR for public policy transmission network upgrade facility upgrades.
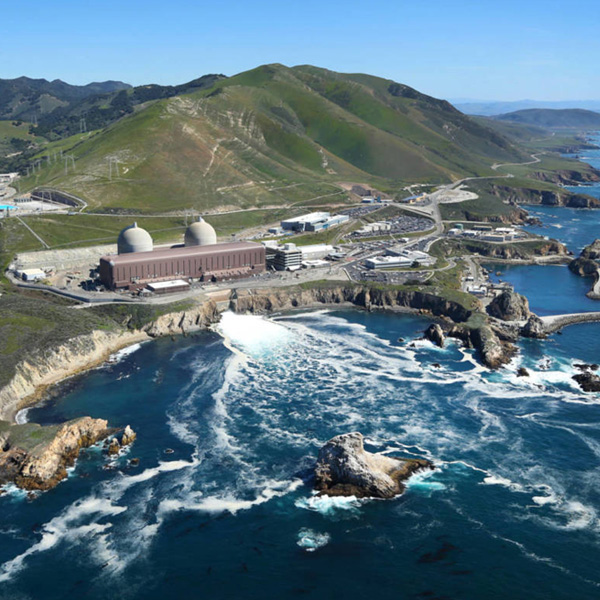
The Energy Department awarded PG&E more than $1 billion to keep California's last nuclear plant operating beyond its planned retirement for grid reliability.
The proposed governance structure for SPP's Markets+ service offering and resource adequacy are two key differences with CAISO's RTO proposal.
The annual NARUC meeting covered ground on rate design, energy storage and reliability while the energy portfolio undergoes renovation.
CAISO held its Stakeholder Symposium for the first time since 2018 and weighed the transmission needs of the West to deliver renewable resources.
At FERC’s annual reliability technical conference, commissioners focused on work needed to prepare the bulk power system for rapidly developing challenges.
The PJM Operating Committee has endorsed the winter weekly reserve target values, which are used to coordinate planned outages scheduled during winter.
PJM’s biannual General Session last week focused on how to ensure both reliability and equity during the transition to a clean energy-based generation mix.
Keynoting the Energy Bar Association Texas Chapter’s Energy Symposium, Lori Cobos said ERCOT stakeholders will soon get a look at the market’s redesign.
Want more? Advanced Search