Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
ISO-NE will not incorporate an amendment approved by the NEPOOL Participants Committee to include pumped storage resources in its Inventoried Energy Program.
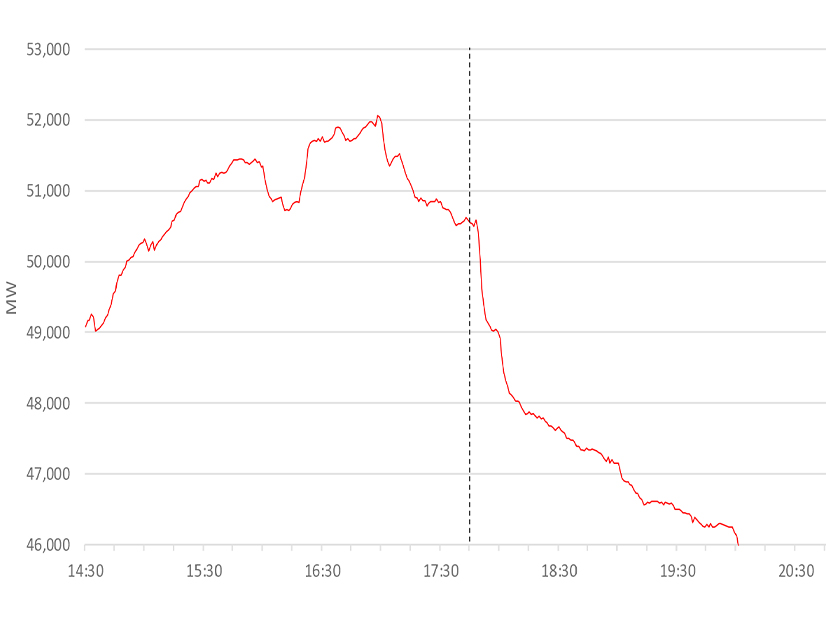
CAISO said it avoided September blackouts through a combination of public conservation, imported electricity and coordination with utilities and agencies.
WECC said the addition 80 GW of wind and solar resources to the Western grid in the next decade will require higher planning reserve margins than anticipated.
SPP’s board gave its state regulators the go-ahead to file a tariff change allowing LREs to receive exemptions for not meeting their PRM obligation.
MISO members reopened the idea that the grid operator enact resilience criteria within its footprint.
Buoyed by California's success this summer, New England state and grid officials are refining plans to use conservation pleas in case of an energy emergency.
FERC approved an agreement that will keep an Ameren Missouri coal plant online past its planned retirement date to maintain MISO grid reliability.
FERC staff said the grid seems well positioned to weather the cold months. However, rising demand is expected to drive gas prices higher than last year’s.
MISO expects to easily navigate normal winter conditions with its firm supply but said a worst-case winter storm in January could exhaust emergency reserves.
SPP staff have chosen a hybrid approach to improve its transmission and congestion-hedging markets, focusing on equitably allocating congestion rights first.
Want more? Advanced Search