Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
Gov. Gavin Newsom proclaimed a state of emergency to increase energy production and reduce demand in response to a heat wave hitting California.
Again this fall and winter, MISO will ask its thermal generators for fuel supply information via its weekly fuel surveys.
Forecasters say California and the Southwest will see extreme heat this weekend, with conditions like those that strained the grid over Labor Day weekend 2020.
The federal government is standing ready to help New England with fuel supply and grid reliability this winter, Energy Secretary Jennifer Granholm said.
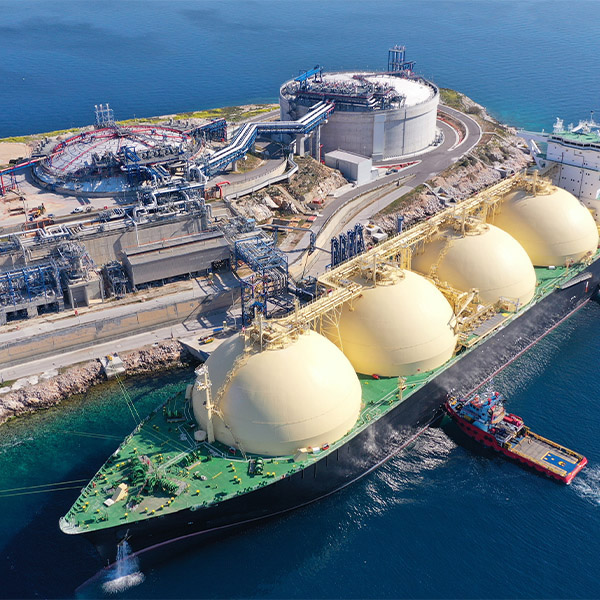
ISO-NE warns that the region’s near-term grid reliability depends on its access to LNG — and that access in turn relies on a single facility outside Boston.
MISO's Regional Resource Assessment found there will be a persistent risk of capacity shortfalls as fossil plants retire and more renewables come online.
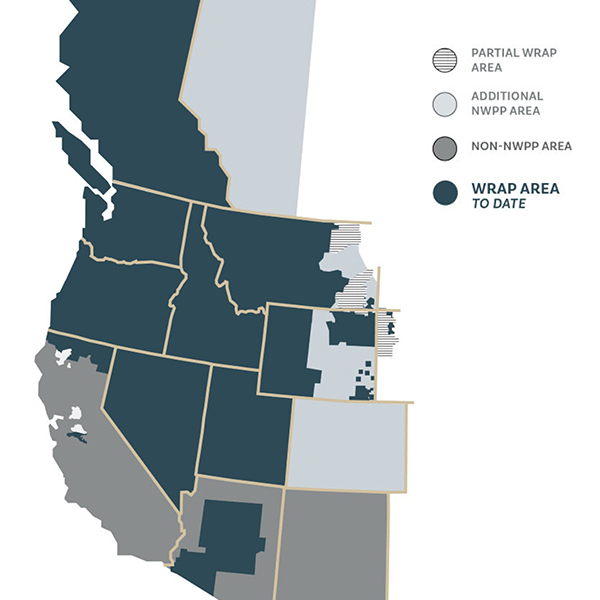
The Western Power Pool approved the tariff for its Western Resource Adequacy Program, readying the first-of-its-kind program for review by FERC.
SPP and Western entities interested in the RTO’s Markets+ “RTO light” offering continued to inch toward each other during another development session.
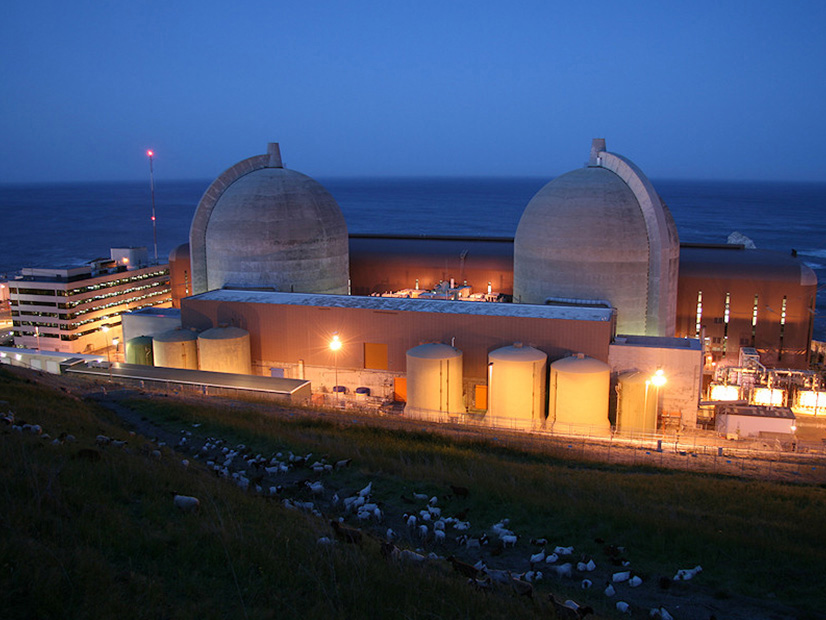
The movement to keep PG&E's Diablo Canyon nuclear plant open 10 years past its planned retirement date in 2025 has gained momentum and essential support.
State regulatory staff and MISO executives found no easy answers to solve a burgeoning reliability crisis after converging for a resource adequacy summit.
Want more? Advanced Search