Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
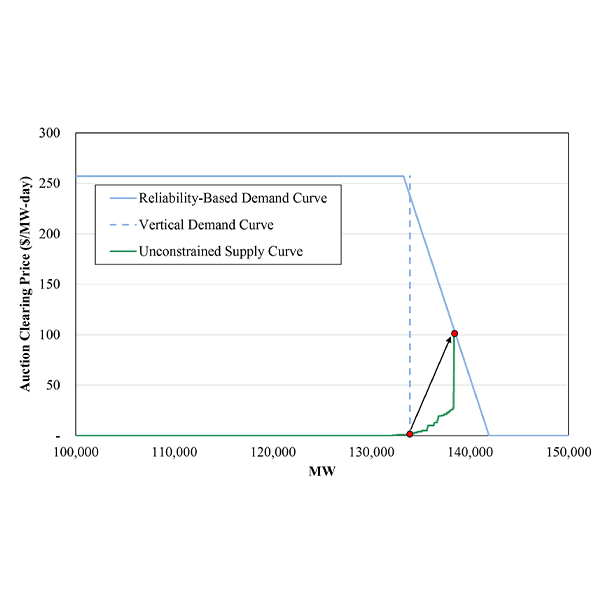
MISO's board may be coming around to the idea of using a sloped demand curve to price capacity as the RTO confronts the possibility of resource shortages.
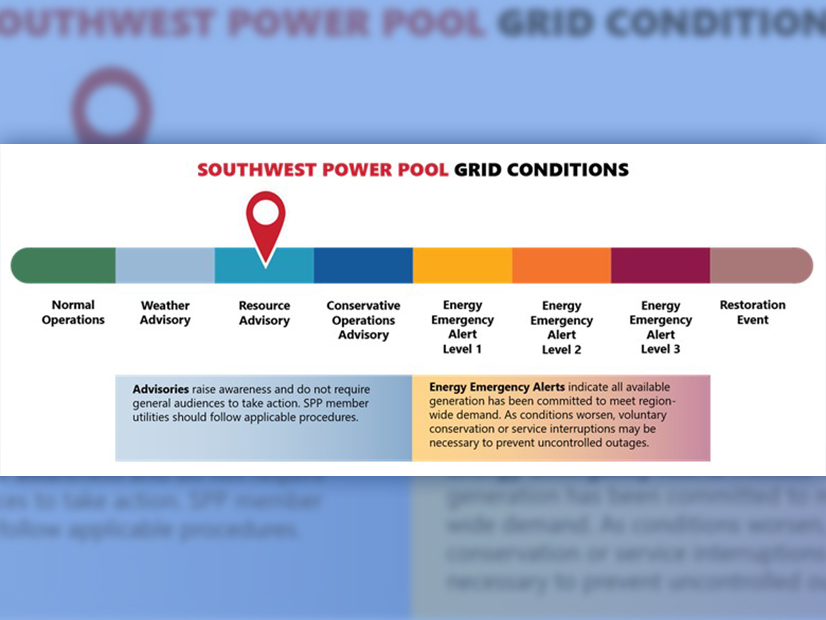
SPP issued a resource advisory for its entire 14-state Eastern Interconnection footprint, effective June 21 through June 24 because of high temperatures.
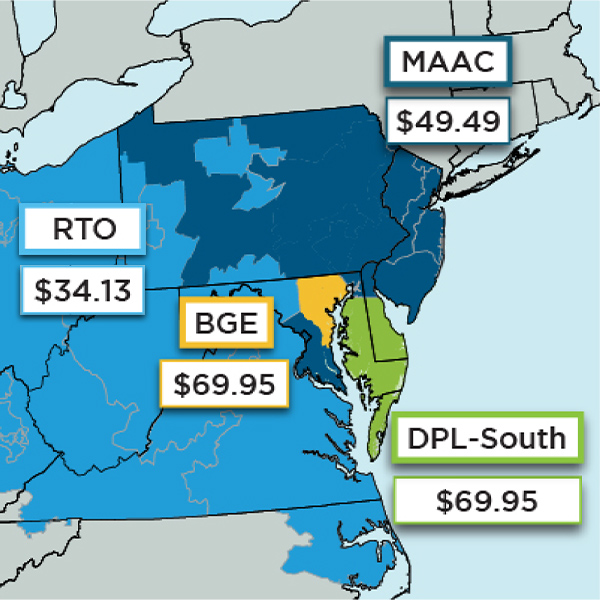
Capacity prices dropped by one-third to almost one-half in PJM’s auction for 2023/24, likely depressed by the end of the MOPR and a tougher price cap.
MISO executives issued warnings about its future resource adequacy in front of its board of directors while some state regulators and stakeholders pushed back.
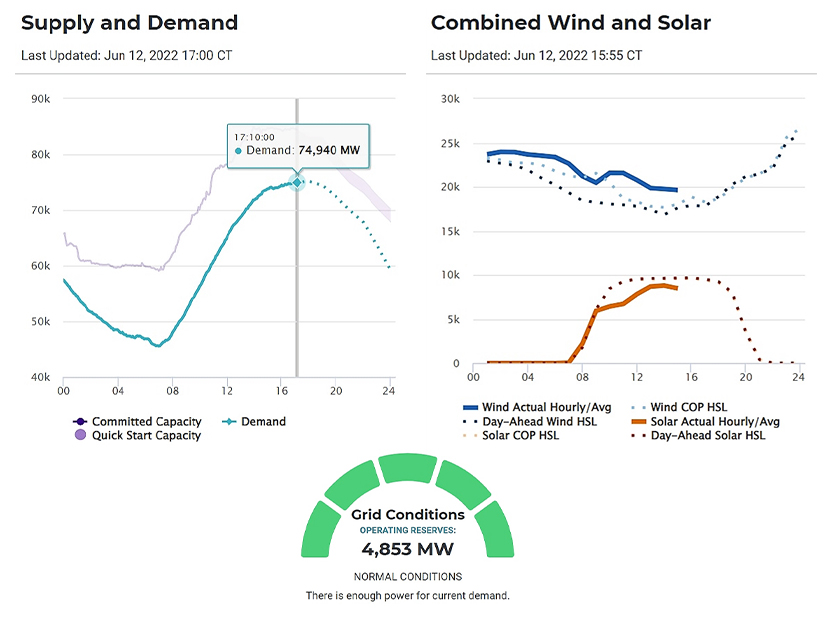
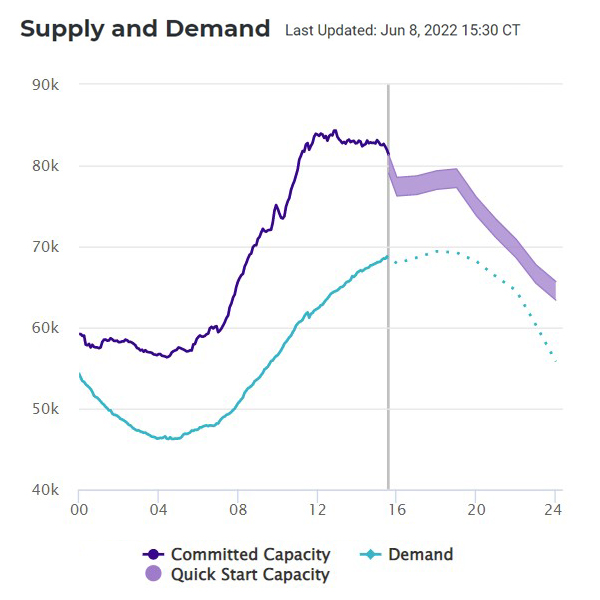
MISO’s board of directors gathering covered concern over slipping capacity reserves as heat blistered the footprint and forced emergency preparations.
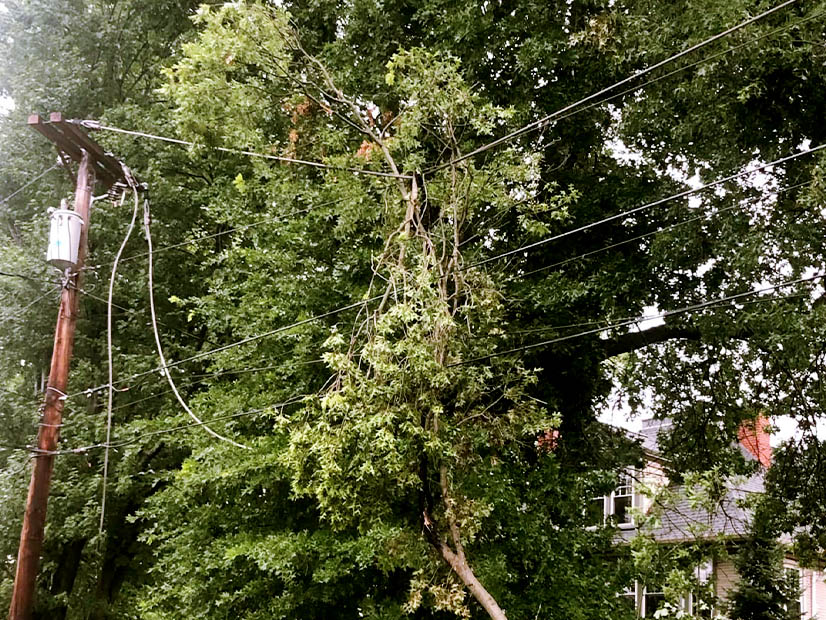
More than 200,000 AEP customers in Ohio lost power after storms damaged multiple transmission lines and forced load sheds on at least three 138-kV lines.
PJM responded to its Market Monitor’s latest recommendations, noting that many of the issues are in the scope of current stakeholder discussions.
Sweltering heat has helped ERCOT finally set a new all-time peak demand mark after several close calls during the preceding week.
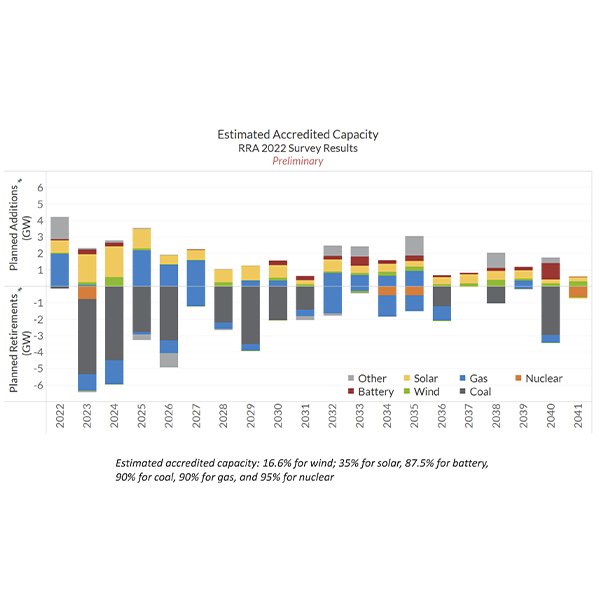
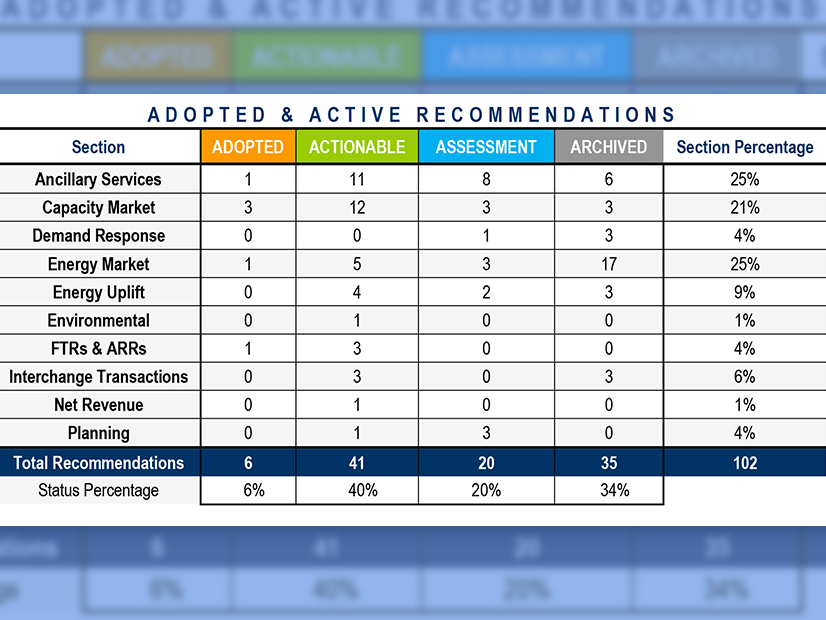
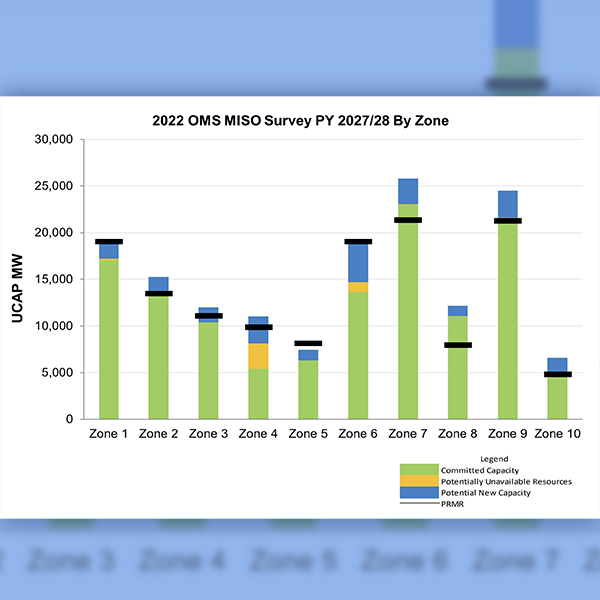
MISO and the Organization of MISO States’ 2022 resource adequacy survey again sounded the supply alarm rung from the 2022/23 capacity auction results.
ERCOT has issued its third operating condition notice since April, warning of extreme, hot temperatures in several of its weather zones this weekend.
Want more? Advanced Search