Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT)

Steven Baltakatei Sandoval, CC BY-SA-4.0, via Wikimedia
EPA received comments on its proposal to regulate greenhouse gases from power plants, with some, including ISO/RTOs, arguing the proposal needed major improvements to preserve reliability.
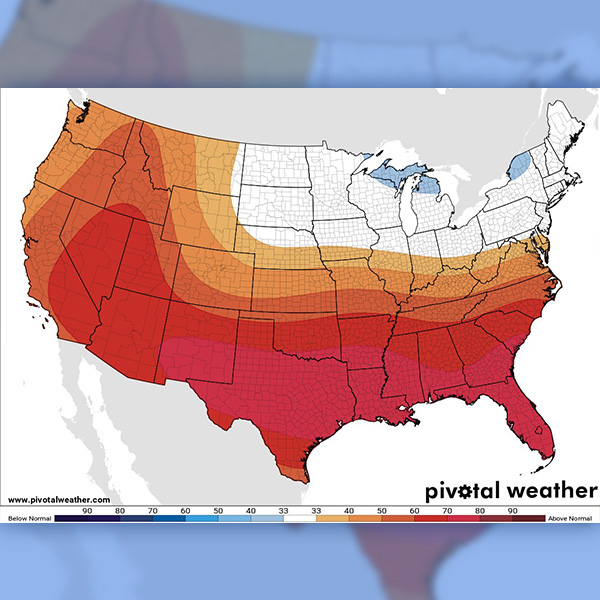
The ERCOT grid continues to operate under normal conditions, the grid operator said, even as this summer’s peak demand is 4.3% higher than last summer’s.
Texas regulators have approved ERCOT’s proposed modifications to the operating reserve demand curve that are designed to retain and attract dispatchable generation.
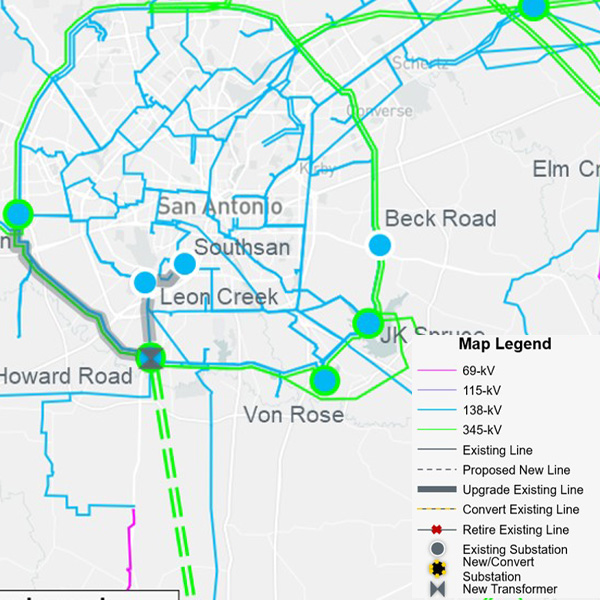
ERCOT stakeholders have endorsed a $329 million reliability project in the San Antonio area, sending it on the Board of Directors for final approval.
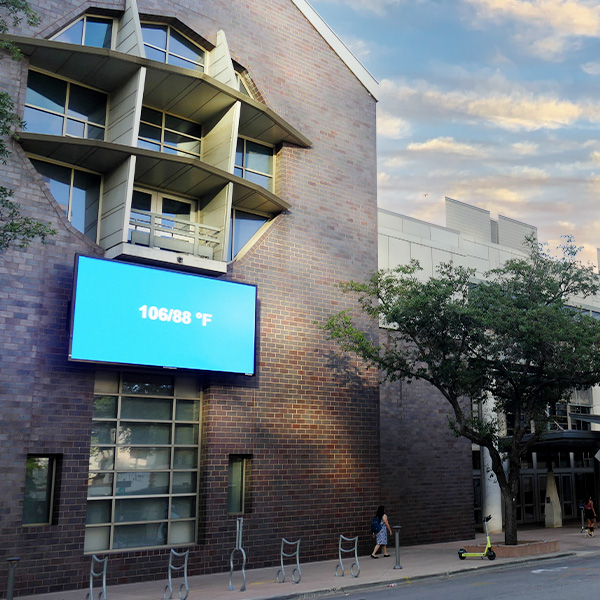
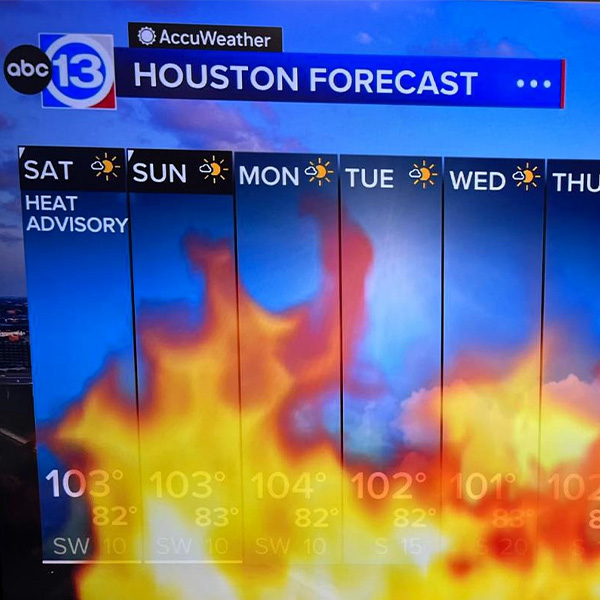
ERCOT's average load exceeded 83 GW for the first time as temperatures remain above 100 degrees in most parts of Texas.
Temperatures in Austin topped out at 105 degrees Fahrenheit, helping ERCOT to again set a record for hourly peak demand when load averaged 82.03 GW.
ERCOT appears to have set another peak demand record Monday, but if the grid operator’s projections hold out, the mark will be short-lived.
The Texas Public Utility Commission unanimously approved ERCOT’s request to nearly double compensation for its independent directors, the board’s first increase since 2012.
ERCOT staff said it faces a tight timeline to add a new ancillary service by Dec. 1, 2024, as required by the recent Texas legislative session.
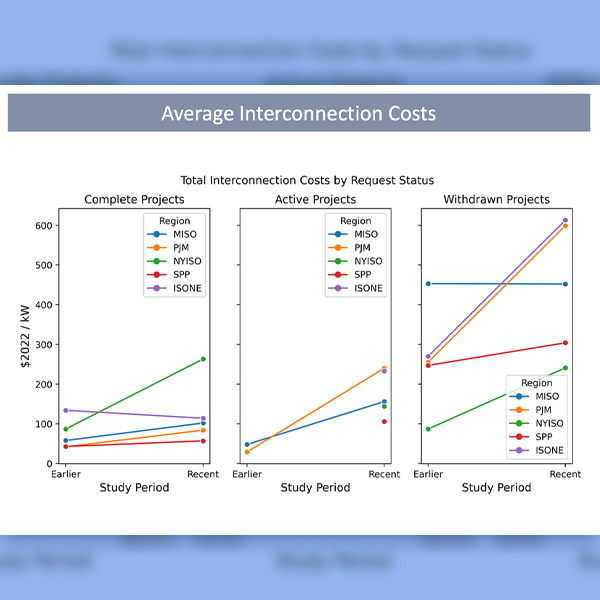
Interconnection costs are on the rise across the U.S., according to a Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory analysis of thousands of projects in five organized electricity markets.
Want more? Advanced Search