ISO New England (ISO-NE)
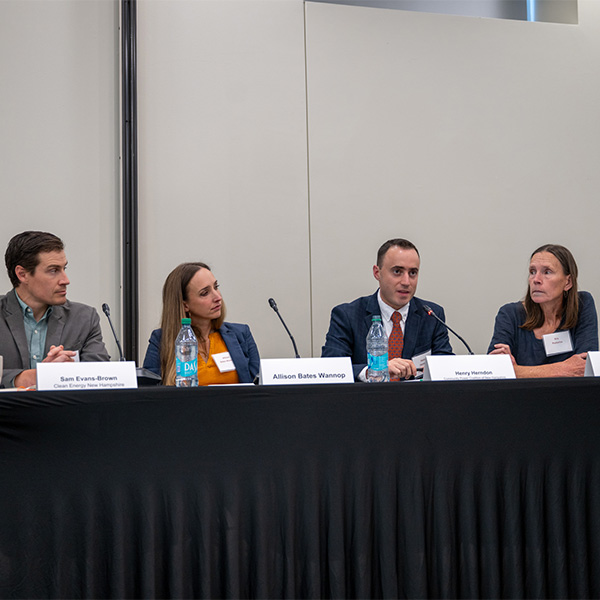
Several panelists and public commenters at the quarterly meeting of the ISO-NE Consumer Liaison Group criticized the RTO over its record on accountability and accessibility, as well as its policy related to distributed energy resources.
ISO-NE kicked off NEPOOL discussions for the second phase of its capacity auction reform project, beginning long-awaited talks on accreditation and seasonal capacity auction changes.
A new study looking at the business case for comparable behind-the-meter and front-of-the-meter battery storage systems in Massachusetts found that FTM storage “significantly outperformed” the BTM systems, despite significant programs and incentives supporting BTM storage in the state.
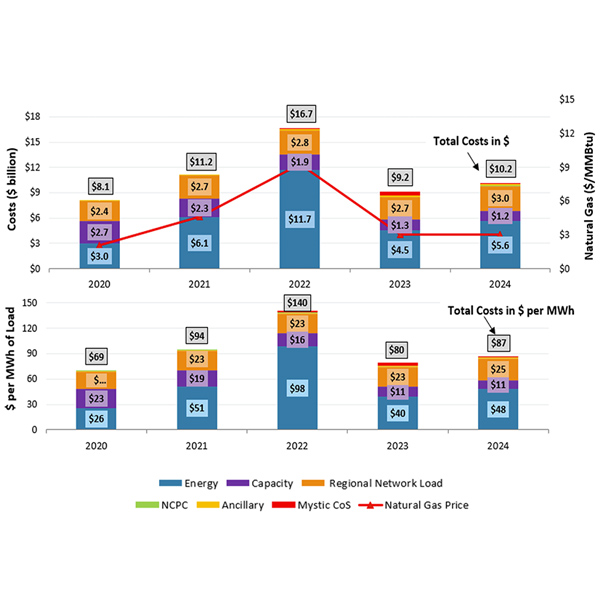
The New England wholesale electricity markets performed competitively in 2024, while decreased imports and higher emissions compliance rates increased overall market costs, the ISO-NE Internal Market Monitor told the NEPOOL Participants Committee.
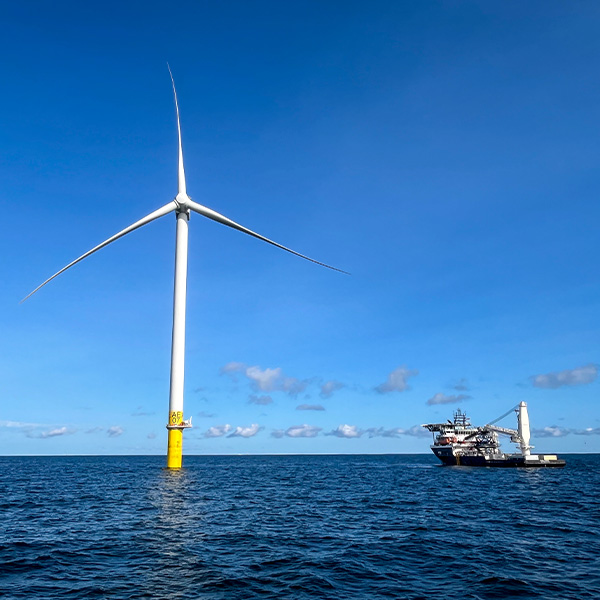
The Trump administration is moving to close the door on U.S. offshore wind development by remanding approvals for all projects not already under construction.
FERC approved a follow-up filing for ISO-NE’s compliance with Orders 2023 and 2023-A, authorizing variations from the final rule related to interconnection point modifications, cost allocation, and commercial readiness deposits.
ISO-NE said it is open to capping the balancing ratio used to calculate Pay-for-Performance payments to prevent capacity resources from being required to provide more power than their capacity supply obligations.
As the first phase of ISO-NE’s capacity market overhaul nears its final form, New England stakeholders remain mixed on the proposed move from a forward to a prompt capacity auction.
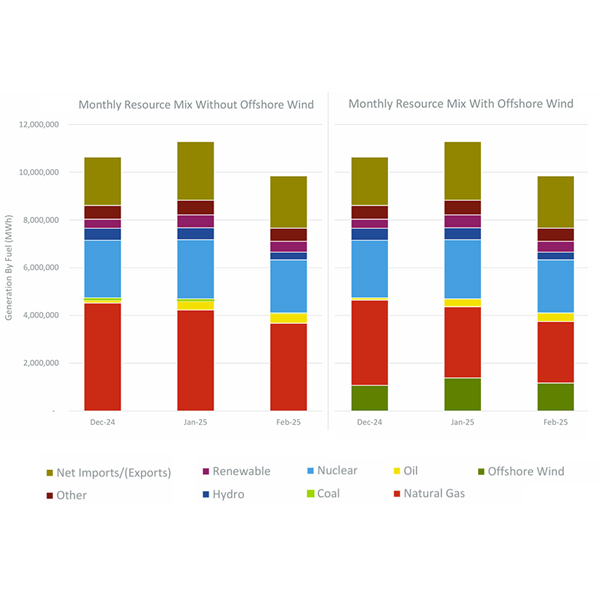
The addition of 3,500 MW of offshore wind capacity would have reduced ISO-NE energy market costs by about $400 million over the past winter, according to a recent study by Daymark Energy Advisors.
ISO-NE warned any significant delay of the Revolution Wind project will increase risk to the reliability of the New England grid and undermine the region’s economy.
Want more? Advanced Search