U.S. Enviromental Protection Agency (EPA)
EPA has rescinded its 2009 finding that greenhouse gases are air pollutants that endanger public health and thus require regulation under the Clean Air Act.
The complaint seeks to force EPA to reverse its termination of Solar for All, a $7 billion effort to expand lower-income Americans’ access to small-scale photovoltaics.
Three cabinet-level agencies announced coordinated policies that are meant to improve coal's position in the energy system by improving power plants, cutting environmental regulations and increasing mining of the fuel.
EPA Administrator Lee Zeldin proudly told NARUC attendees the agency’s proposed rescission of the 2009 endangerment finding would be the “largest deregulatory action in the history of the country.”
EPA is proposing to rescind its 2009 endangerment finding, which qualifies greenhouse gases as pollutants and has been used by Democratic presidential administrations to regulate emissions from power plants and other sources.
EPA proposed repealing rules passed by previous administrations that impose carbon limits on existing and new power plants and the 2024 updates to the Mercury and Air Toxics Standard.
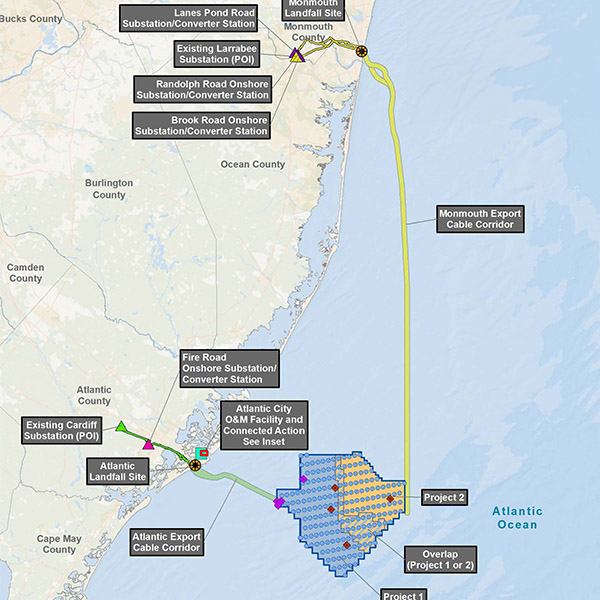
New Jersey’s Board of Public Utilities backed measures to keep on track one of its three remaining offshore wind projects and retool a large-scale solar incentive program.
The EPA’s Environmental Appeals Board has granted the agency’s motion for a “voluntary remand” on the air quality permit for the project, essentially returning it to EPA for re-evaluation in light of President Donald Trump’s Jan. 20 executive order on offshore wind.
In a rapid series of announcements, EPA Administrator Lee Zeldin unleashed a full-scale offensive on the agency’s regulatory authority, as it seeks to roll back as many as 31 regulations.
West Virginia is the fourth state to be granted primacy for permitting Class VI wells.
Want more? Advanced Search