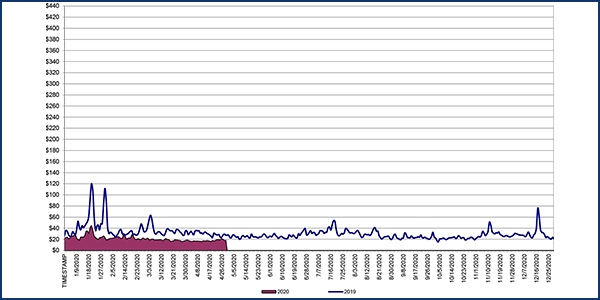
NYISO is seeing “historically low” load and prices, Senior Vice President of Market Structures Rana Mukerji told the Business Issues Committee on Wednesday.
Day-ahead and real-time load-weighted locational-based marginal prices were $15.77/MWh in April, a drop from $17.11/MWh in March and $28.01/MWh a year earlier.
Year-to-date costs through April were $22.38/MWh, a 44% decrease from the same period in 2019.
Average daily sendout was 344 GWh/day in April, a drop from 375 GWh/day in March and 371 GWh/day in April 2019, Mukerji said.
60-minute Rule
The BIC voted to recommend that the Management Committee approve changes to section 4.4.3.1.1 of the Services Tariff to only award energy storage resources (ESRs) energy schedules that are sustainable for at least 60 minutes during a reserve pick-up (RPU) event.
The change was prompted by concern that during an RPU, real-time dispatch may award a larger energy schedule than an ESR can sustain for 60 minutes, as required by the Northeast Power Coordinating Council.
This can occur because the real-time dispatch/corrective action mode used to perform an RPU must issue updated schedules very quickly and thus only looks out 10 minutes.
“This … could result in an ESR running out of energy and not being able to continue following basepoints during the critical 60-minute recovery period after loss of a resource or transmission element,” said Aaron Markham, director of grid operations.
The ISO is proposing additional Tariff authority and updated RPU software to limit awards that are sustainable for 60 minutes (or more).
Peak Load Forecasts and Minimum Unforced Capacity Requirements for LSEs
The BIC voted to recommend that the Management Committee approve revisions to the NYISO Market Administration and Control Area Services Tariff sections 2, 5.10 and 5.11 to address a concern regarding the peak load forecast and minimum unforced capacity requirements for load-serving entities.
The forecast is determined using the prior calendar year’s highest hourly actual load in the New York Control Area (NYCA), adjusted to “design conditions,” which are expected to occur on a non-holiday weekday in July and August. About 80% of the highest coincident NYCA peak load hours have occurred in July and August.
The minimum capacity requirement is allocated among individual LSEs, determined by their consumption during the highest hourly actual load in the NYCA, regardless of whether that is consistent with consumption at “design conditions.”
The ISO said it was concerned about situations in which the highest hourly actual load occurs outside the “design conditions” as in 2019, when the highest actual load occurred on a Saturday in July.
The proposed Tariff revision would require the use of the highest NYCA load hour occurring on a non-holiday weekday during July and August when calculating the NYCA peak load forecast. The change will ensure that each LSE’s share of the minimum capacity requirement is consistent with the “design conditions” used to calculate the minimum capacity requirement.
If the highest load hour occurs on a weekend or holiday, load would be adjusted to account for expected additional load that would have occurred if the highest load hour had been a non-holiday weekday. Similarly, load also would be adjusted when the highest load hour occurs outside July and August.
If the temperature is higher than the design temperature, load will be removed to reflect the expected lower load that would have occurred if the highest load hour had taken place at the “design” temperature. The ISO said the change should ensure the incentive to reduce peak demand aligns with when the peak demand is expected to occur.
The changes will be presented to the Management Committee for approval on June 16, with board approval and a FERC filing expected in July. If it wins FERC approval, the changes would be effective for 2021/22 capability year.
Manual, Bylaw Changes
Members also approved changes to the following:
- Accounting & Billing Manual — Changes apply to ESRs, including provisions on settlements, day-ahead bid production cost guarantee and margin assurance payments. The changes will be effective at the same time as related ESR Tariff revisions.
- Revenue Metering Requirements Manual (RM2) — Changes apply to responsibility for meter inventory-related information; creation of metering configuration sub-sections for behind-the-meter net generation resources and ESRs; and allowable duration for the use of telemetry meter data as a back-up source for revenue meter data.
- Public Policy Transmission Planning Process Manual — Updated to reflect Tariff revisions to clarify, streamline and improve the Public Policy Process approved in 2019 (ER19-528). (See NYISO Public Policy Tx Revisions Approved.) Other revisions address cost-containment provisions approved in February 2020 for competitive transmission projects (ER20-617).
- BIC Bylaws — Changes to attendance rules, including a revision to allow nonmembers to attend by teleconference.
- Installed Capacity Manual — Changes to reflect FERC order Dec. 20, 2019, accepting most of the ISO’s proposed Tariff revisions for compliance with Order 841 to accommodate and establish rules for participation of ESRs in ISO markets (ER19-467). (See FERC Partially Accepts NYISO Storage Compliance.)