RENSELAER, N.Y. — NYISO’s Business Issues Committee on Wednesday approved revisions to the Installed Capacity (ICAP) Manual regarding external to rest of state deliverability rights (EDRs).
Ryan Patterson, a NYISO capacity market design associate, told the committee that EDRs in general function similarly to unforced capacity deliverability rights (UDRs), warranting updates to the ICAP Manual to include references to EDRs in several sections that mention UDRs.
The revised sections concern maximum allowances for ICAP provided by resources outside the New York Control Area, excluding resources using UDRs and EDRs, with revisions adding an additional table to show the EDR megawatts awarded.
The proposed changes also would provide the processes for requesting, using and offering megawatts associated with EDRs, parallel with those for UDRs, as well as establish the process for requesting EDRs.
One revision fixes a broken website link, which now links to the correct section and has the correct cross reference, which led one stakeholder to ask if all the ISO’s manuals have been checked for link faults since the grid operator updated its website in December.
Mark Seibert, NYISO manager of member relations, said document links continue to be updated as part of the ongoing review associated with the new website.
OKs New Zone J Operating Reserves
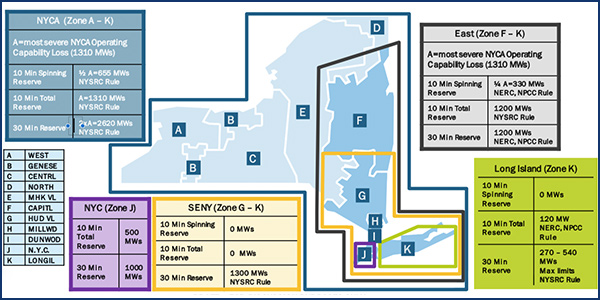
The BIC approved establishing operating reserve demand curves that assign a $25/MWh value to the proposed reserve requirements for Zone J (New York City), similar to the approach taken with the implementation of the Southeast New York (SENY) reserve region. (See “New Zone J Operating Reserves,” Imports/Exports Top Talk at NYISO Carbon Pricing Kick-off.)
The Zone J reserve requirement would necessitate procuring 500 MW of 10-minute reserves and 1,000 MW of 30-minute reserves.
Ashley Ferrer, NYISO energy market design specialist, told the BIC that the ISO is not proposing to revise the Zone J requirement during thunderstorm alert (TSA) events in order to ensure timely implementation of the curves for June.
The ISO has recognized that activating special case resources in its emergency demand response program to protect Zone J reserves represents a $500/MWh action, which implies that a $500/MWh demand curve price for Zone J reserve products could, in the longer term, be an appropriate value to consider.
However, use of a such a steep demand curve price, absent further evaluating the appropriate reserve requirements during TSA events, could result in unnecessarily high pricing outcomes during such events, Ferrer said.
TSAs are called when actual or anticipated severe weather conditions lead the ISO to reduce transmission limits into SENY.
Assuming Management Committee approval in March, the ISO would submit the proposal to the Board of Directors in April and file Tariff revisions with FERC, seeking approval to implement it in June.
Clarifying TCC Credit Calculation
Sheri Prevratil, the ISO’s manager of corporate credit, informed the BIC that there are three existing historic fixed price transmission congestion contracts (HFPTCCs) with start dates that do not match the first day of a capability period. NYISO identified the issue while developing software to use the market clearing price to calculate the credit requirement for fixed-price transmission congestion contracts (TCCs).
The ISO proposes to clarify in the Tariff how to calculate the holding requirement for HFPTCCs with start dates that do not align with the beginning of a capability period by using the proposed enhancements previously approved by stakeholders, Prevratil said. (See “Committee Approves Repricing TCC Credit Requirement,” NYISO Management Committee Briefs: Jan. 30, 2019.)
The Management Committee will consider the proposed incremental clarifying revisions on March 27.
NYISO, PJM Revising JOA for Tie Line Issues
NYISO and PJM are targeting an April stakeholder meeting to discuss revisions to their joint operating agreement, ISO Principal Economist Nicole Bouchez told the BIC in presenting the monthly Broader Regional Markets report.
The ISO and PJM last September filed with FERC a joint request for waiver of the JOA to permit them to add the East Towanda-Hillside tie line as a market-to-market (M2M) flowgate.
The requested waivers enable PJM to temporarily conduct redispatch operations to control flows to the more restrictive rating on the NYISO side of the line without violating its Tariff while the grid operators work to develop a permanent solution.The commission granted the waiver in November after both grid operators jointly responded to one stakeholder protest that it was a “broad, unlimited waiver,” Bouchez said. (See “NYISO, PJM Win JOA Waiver Request,” NYISO Business Issues Committee Briefs: Dec. 12, 2018.)
The ISO filed its first quarterly report with FERC addressing progress made toward developing JOA revisions to address the tie line issue, as required by the commission.
Natural Gas Prices down 122% in Feb.
NYISO locational-based marginal prices averaged $33.51/MWh in February, down by about 48% from January and only slightly from the same month a year ago, Bouchez said in delivering the monthly operations report. Year-to-date monthly energy prices averaged $44.93/MWh, a 38% decrease from a year ago.
Day-ahead and real-time load-weighted LBMPs came in lower compared to January. Average daily sendout was 436 GWh/day in February, compared with 449 GWh/day in January 2019 and 426 GWh/day in February 2018.
Transco Z6 hub natural gas prices averaged $2.75/MMBtu for the month, down 122% from January and 12.4% from a year ago.
Distillate prices were up about 2.4% year over year and gained from the previous month, with Jet Kerosene Gulf Coast averaging $14.21/MMBtu, up from $13.25/MMBtu, while Ultra Low Sulfur No. 2 Diesel NY Harbor rose to $14.02/MMBtu, compared with $13.20/MMBtu.
The ISO’s 11-cents/MWh local reliability share in February was down from 32 cents the previous month, while the statewide share climbed slightly to -55 cents/MWh from -57 cents in January.
— Michael Kuser