PJM Presents Monthly Operating Statistics, Low Spin Response
VALLEY FORGE, Pa. — PJM’s Stephanie Schwarz presented the RTO’s monthly operating statistics, which showed an average hourly forecast error of 1.26% for February and an hourly peak error just over 3% over forecast on Feb. 3.
The month saw three shared reserve events, one spin event and three post-contingency local load relief warnings.
During the Feb. 24 spin event, which lasted about 12 minutes, Schwarz said 36% of the 2,689 MW spin response assignment for generation materialized as well as 7% of the 262 MW assignment for demand response. The total penalty for the event was 1,967 MW out of a 2,951 MW spin assignment. Generation without a spin assignment increased by 1,777 MW during the event.
The Reserve Certainty Senior Task Force (RCSTF) is considering changes to the reserve penalty rate for resources that fail to perform. Stakeholders in the OC argued that the response from generation without a reserve commitment shows there’s capability for intramarket resources to move on dispatch.
PJM’s Glen Boyle said the underperformance Feb. 24 was concentrated in a few units and overall figures would have looked much better if those resources met their obligations. In response to questions about how reserve assignments interact with the basepoints resources are expected to follow, Boyle said assignments are not included in basepoints; however, the RCSTF is considering ways of aligning the two so that reserve resources can follow dispatch and provide reserves at the same time.
PJM Preparing Forecast for April Solar Eclipse
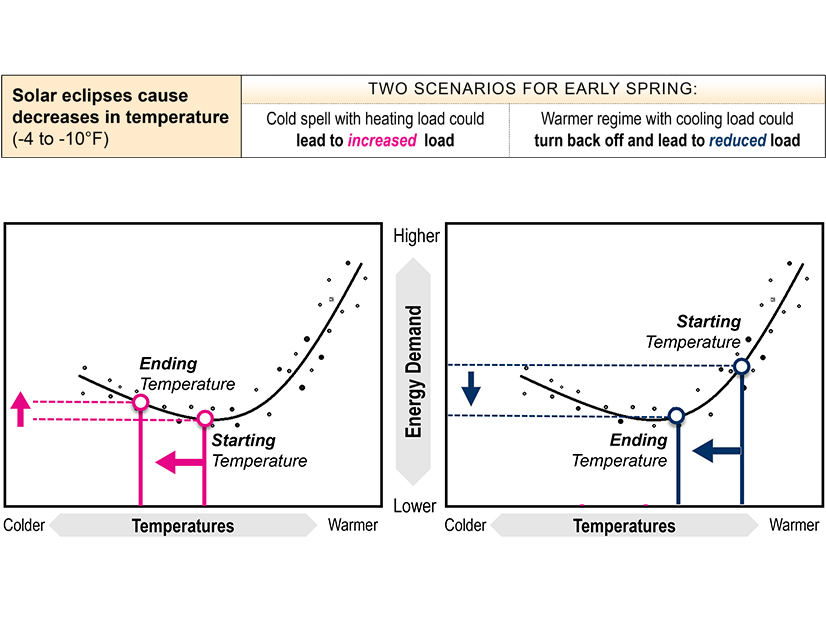
Pre-eclipse solar generation could decline by as much as 85% during the solar eclipse expected on April 8 and diminished temperatures during the event could result in varying outcomes for demand, PJM’s Michael Stewart presented to the OC.
Grid-connected solar generation could decrease by 1.8-6.7 GW based on cloud coverage, while the decrease in behind-the-meter solar could elevate net load by 4.8 GW on a sunny day or 2.2 GW under overcast conditions. Consumer behavior could also change load patterns, but the impact shouldn’t be as significant as that seen on holidays, Stewart said.
PJM’s Joe Mulhern said more generation may be needed to compensate for decreased solar output, particularly on a cooler day. Eclipses tend to cause temperatures to drop by between 4 and 10 degrees, which could increase load on a colder day as heating load increases, or decrease load on a hot day as air conditioning switches off. The tipping point tends to be between 55 and 65 degrees, depending on the region, Mulhern and Stewart told RTO Insider.
PJM Dispatch Manager Donnie Bielak said operators will be looking at best- and worse-case scenarios and will refine the actions that may be employed in the days leading up to the eclipse.
A similar relationship between diminished solar output and lower air conditioning load was reported during the wildfire smoke that blanketed the Northeast during summer 2023. (See RTOs Report Diminished Solar Output, Loads as Wildfire Smoke Passes.)
Periodic Review Manual Revisions Endorsed
Stakeholders endorsed revisions to Manual 12: Balancing Operations and Manual 37: Reliability Coordination through the documents’ periodic review.
The changes to Manual 12 align language and diagrams with portions of Manual 11 pertaining to real-time market operations and bilateral transactions and added detail to the economic minimum and emergency minimum parameters requirements for hybrid resources.
The revisions to Manual 37 reflect updated NERC standards around establishing and communicating system operating limits, such as thermal ratings and voltage or stability limits.
PJM Provides Security Update
PJM’s Jim Gluck said cybersecurity professionals are recommending individuals restart their internet routers and install security software updates to mitigate the risk that they could be exploited by the hacking group Volt Typhoon, which was the topic of a cybersecurity advisory issued by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency last month.
He also encouraged members to ensure that their data is secured both on internal networks and through any external parties they work with. He highlighted a data breach exposing a security vulnerability at a Canadian nuclear operator caused by an employee of a third party with access to the company’s data.



