Energy Efficiency
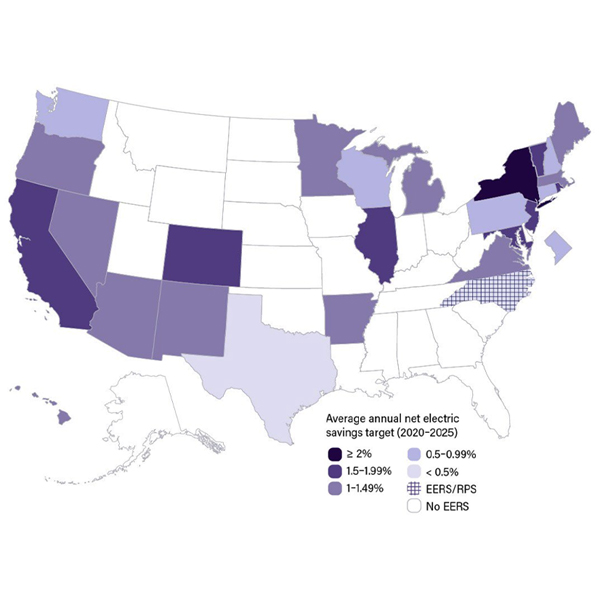
ACEEE released a report highlighting how states are moving forward with energy efficiency resource standards and laying out some best practices.
Vermont’s Public Utility Commission is recommending alternatives to the Clean Heat Standard it was tasked with developing.
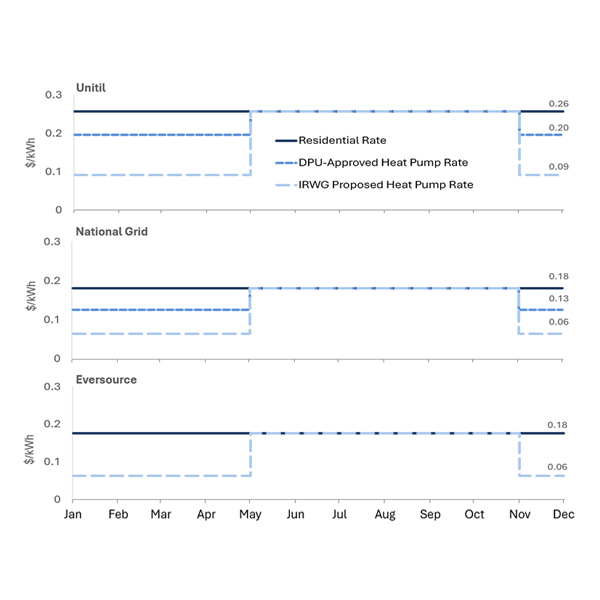
The adoption of simple near-term rate reforms could help Massachusetts achieve its electrification goals while minimizing effects on ratepayers, an interagency working group concluded.
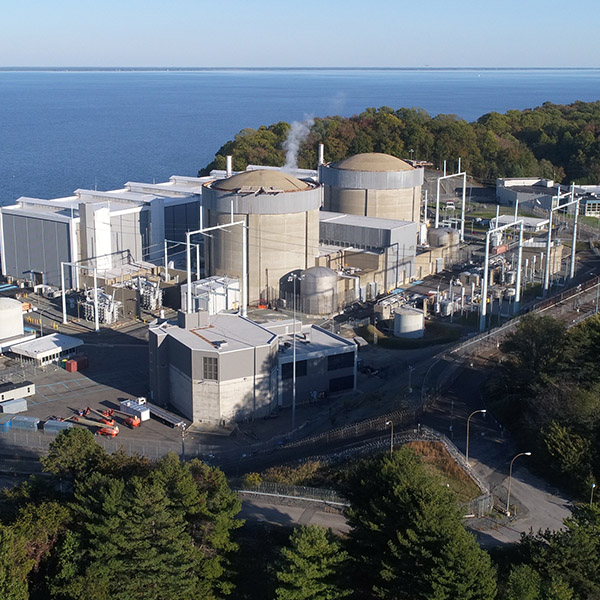
A first-of-its-kind power purchase agreement will send more than 10 million MWh of power to federal buildings and help Constellation Energy increase the output from its nuclear fleet.
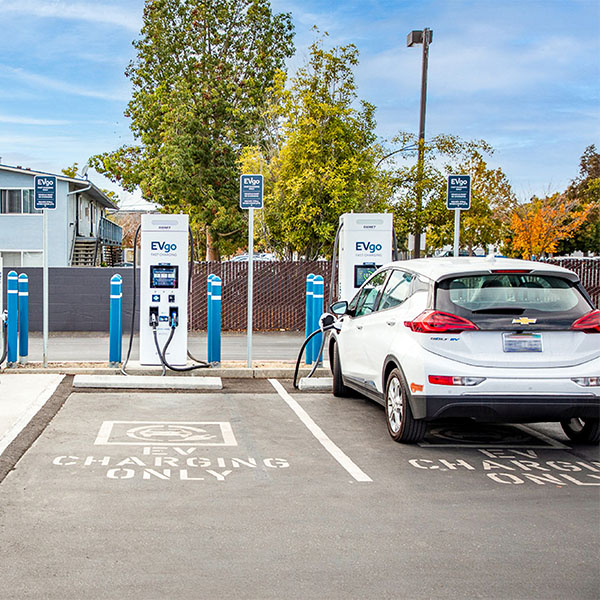
EVgo CEO Badar Khan said expanding the availability of fast chargers is “a key ingredient to the long-term competitiveness and sustainability of the U.S. automotive industry."
The best way to Trump-proof the IRA funds is to get them out the door as quickly as possible, some advocates are saying. Unspent money could be at risk of never being spent.
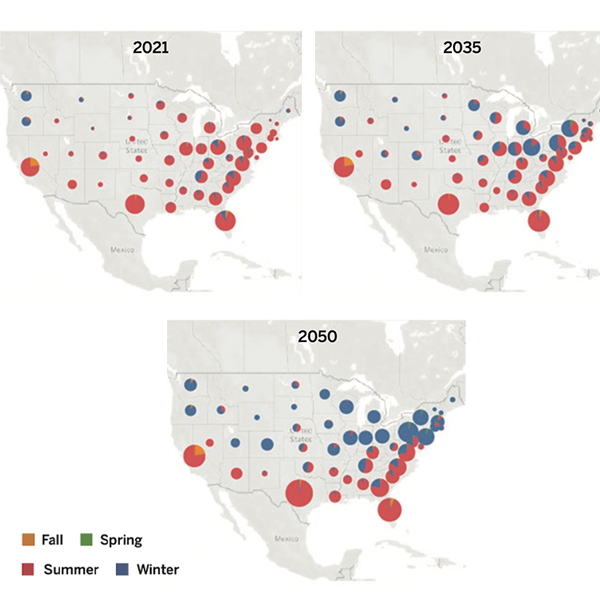
The new report argues that discussions about building electrification largely leave out one key issue: how to prepare the grid for the higher demand and new consumption patterns associated with the shift.
The average household should save $107 on utility bills every year because of the efficiency standards crafted by the Biden administration, according to a new analysis.
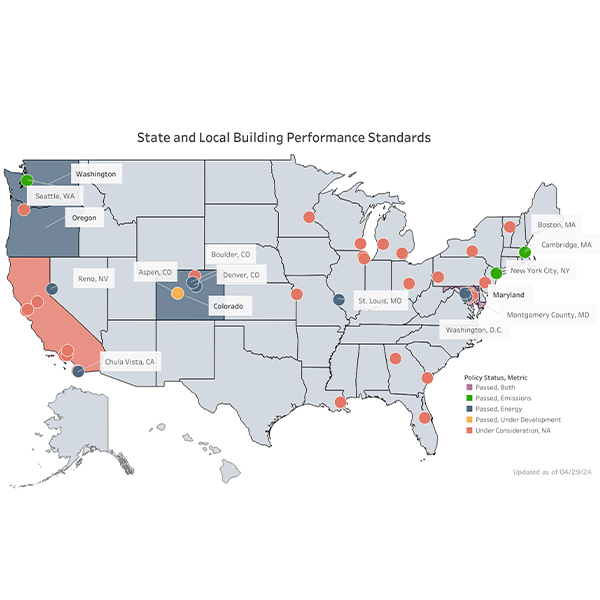
The Department of Energy aims to help cities and states reduce emissions with more than $240 million in grants to promote the adoption of building performance standards
New Jersey’s Board of Public Utilities awarded $3.4 million in grants to 18 proposals under a new program designed to help municipalities implement clean energy projects.
Want more? Advanced Search