Generation
CoalGeothermalHydrogenHydropowerNatural GasNuclear PowerOffshore WindOnshore WindOperating ReservesRooftop/distributed SolarUtility-scale Solar
California’s reliance on a large amount of imported electricity and fossil fuels is a potential weakness in the state’s energy security portfolio, a California Energy Commission staff report finds.
NIPSCO insisted to FERC that a MISO Midwest-wide cost allocation for the continued operation of an Indiana coal plant is the quickest solution.
Interior Secretary Doug Burgum said an appeal “absolutely” is coming on the stop-work orders that his agency imposed and judges lifted against five offshore wind projects.
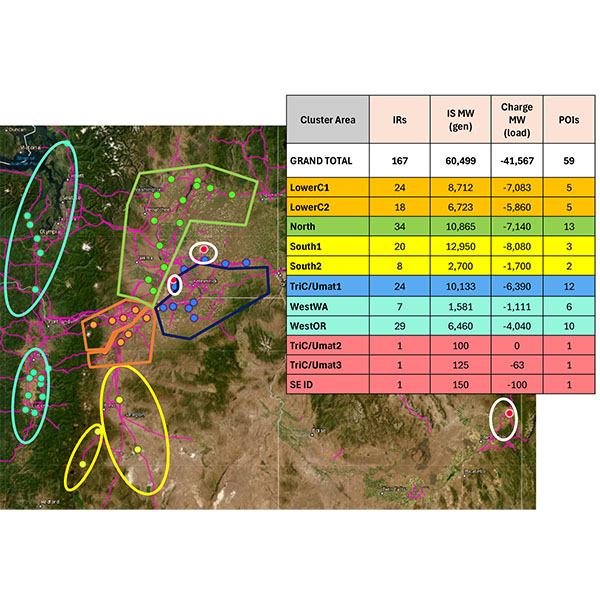
More than 60 GW of generation is a step closer to connecting to BPA's transmission system, following the release of Phase 1 of an interconnection cluster study.
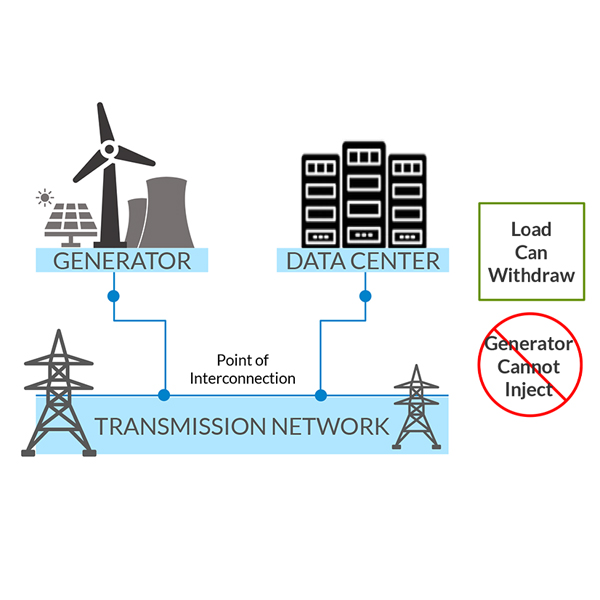
Limiting MISO large load solutions only to zero-injection scenarios misses the mark and can create a myriad of challenges now and in the future, writes David Sapper of the Clean Grid Alliance.
PJM’s Market Implementation Committee passed by acclamation a PJM issue charge seeking to more thoroughly define how storage resources participate in the energy and ancillary service markets.
While PJM experienced some of its highest peak loads ever during the late January winter storm, it overestimated load, with relatively high load forecasting errors, RTO officials told the Operating Committee.
Offshore wind experts urged the California Public Utilities Commission to reconsider a forecasted 6-year delay to the Golden State’s offshore wind project in Humboldt County.
In Massachusetts, a state with some of the most ambitious decarbonization policies in the country, fundamental disagreements between utilities and consumer advocates threaten to derail the transition from natural gas before it even gets off the ground.
The challenges and opportunities of meeting demand from new large loads like data centers took center stage at the National Association of State Energy Officials’ recent Energy Policy Conference.
Want more? Advanced Search