Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
California’s reliance on a large amount of imported electricity and fossil fuels is a potential weakness in the state’s energy security portfolio, a California Energy Commission staff report finds.
SPP's Board of Directors approved a framework for demand response and peak demand assessments despite opposition from members and stakeholders.
NERC officials appeared before an Organization of MISO States board meeting in an attempt to quell regulators’ discontent with MISO’s “high-risk” label in the 2025 Long-Term Reliability Assessment.
While PJM experienced some of its highest peak loads ever during the late January winter storm, it overestimated load, with relatively high load forecasting errors, RTO officials told the Operating Committee.
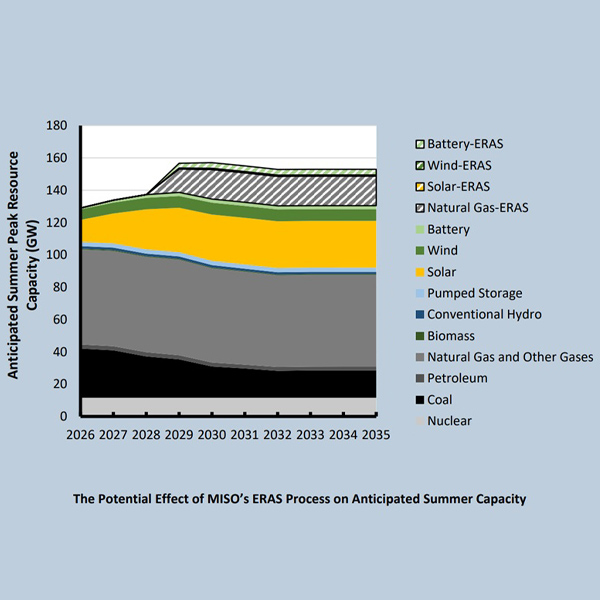
MISO state regulators are considering asking the RTO to keep tabs on resource adequacy risk indicators as they contemplate crafting a replacement standard in the footprint.
The challenges and opportunities of meeting demand from new large loads like data centers took center stage at the National Association of State Energy Officials’ recent Energy Policy Conference.
Members of the Organization of MISO States sent a letter to contradict aspects of NERC’s Long-Term Reliability Assessment, disputing the ERO’s label of MISO as being at “high risk.”
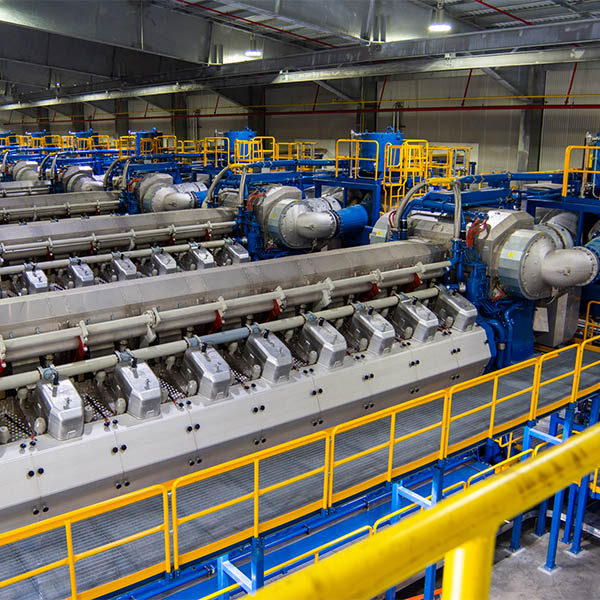
DOE's senior leadership highlighted how the grid relies on fossil fuels to make it through winter peaks.
Democrats in the New York Legislature have introduced legislation to create a three-year moratorium on the siting and permitting of new data centers statewide.
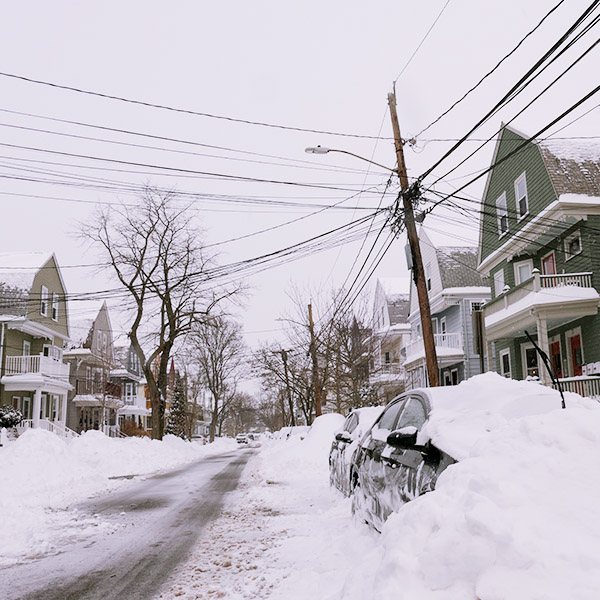
New England experienced record high energy costs in the month of January amid cold weather, high gas prices and a heavy reliance on oil-fired generation.
Want more? Advanced Search