Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
IESO is adopting more “proactive” planning processes in response to a projected load increase of 75%.
The Ontario government’s ambitious energy plan could prove costly to ratepayers if load growth stalls or new nuclear plants produce cost overruns, said A.J. Goulding, president of London Economics International.
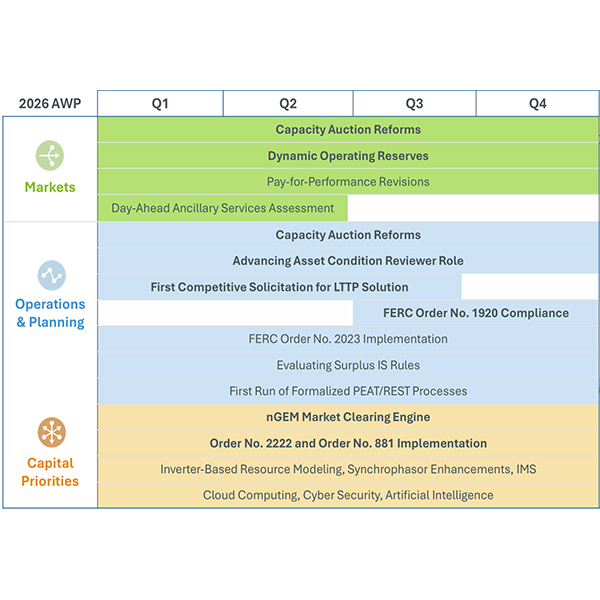
Capacity auction reforms, a new asset condition reviewer role, parallel transmission planning efforts, new reserve products, Pay-for-Performance changes and interconnection modifications are likely to be on the docket for ISO-NE in 2026.
NV Energy notified the Public Utilities Commission of Nevada that it plans to leave the Western Power Pool’s Western Resource Adequacy Program, citing five critical issues with the program’s design.
Duke Energy filed its long-range plan with the North Carolina Utilities Commission, calling for more natural gas-fired generation and batteries while keeping existing coal plants online to meet accelerated demand for electricity.
PacifiCorp asked the WPP’s Board of Directors to allow WRAP participants to defer their decision to commit to the program’s binding phase by at least one year.
Representatives of major gas pipeline companies said they are optimistic that political shifts at the federal and state levels will create opportunities for gas infrastructure expansion in New England.
Stakeholders told MISO they need a better explanation of the every-other-day capacity advisories issued for MISO South, which have become customary since the beginning of summer.
The Western Power Pool’s WRAP secured enough participants for the program to enter the first binding phase after 11 utilities reaffirmed their commitment.
The PJM Members Committee overwhelmingly voted to appoint Robert Ethier and Le Xie to fill two vacant positions on the RTO’s Board of Managers.
Want more? Advanced Search