Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
MISO announced that its first interconnection queue express lane application window turned up 47 projects at a little more than 26.5 GW of proposed new capacity, with natural gas generation accounting for about 20 GW.
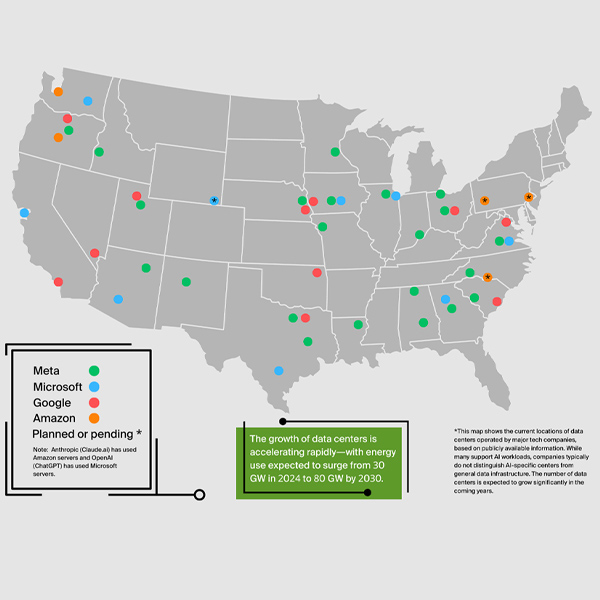
Green America launched a campaign to hold big tech to its clean energy promises as the shift to building data centers has led to higher emissions from the sector in the 2020s.
Adapting charging of electrical vehicles to real-time grid conditions could save utilities up to $30 billion annually and reduce peak energy demand, according to a new report by The Brattle Group and smart charging provider ev.energy.
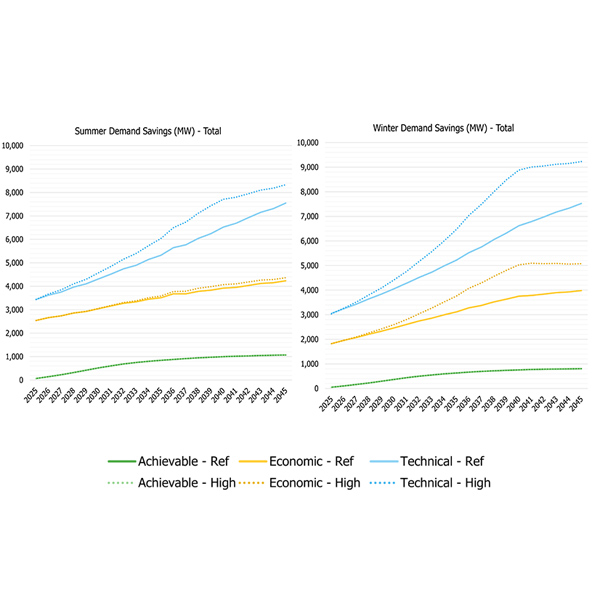
IESO officials say they will release more information on how the ISO constructed its study of the potential for incremental energy savings in Toronto after stakeholders complained they lack enough details to comment meaningfully.
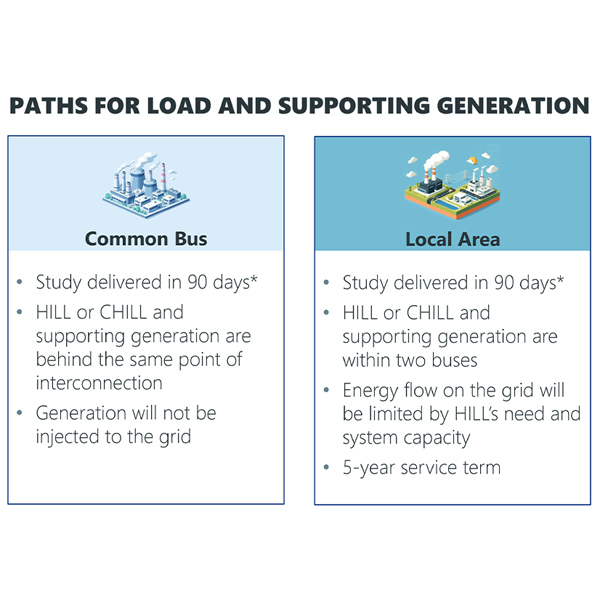
SPP stakeholders have approved a revised version of the grid operator’s fast-track study to integrate high-impact large loads during a special virtual meeting of the Markets and Operations Policy Committee.
The WRAP DAM Task Force is finalizing a concept paper that outlines proposed principles for the program under the new day-ahead market landscape.
The tone of Infocast’s 2025 Midcontinent Energy Summit was noticeably apprehensive compared with last year, owing to political and regulatory uncertainty, load growth ambiguity, fluctuating tariffs and a pending complaint against MISO’s long-range transmission plan.
Former FERC Chair Neil Chatterjee and former Texas Land Commissioner George P. Bush offered their thoughts on the impact of OBBBA on the energy sector during a webinar.
The U.S. Department of Energy has ordered the J.H. Campbell Generating Plant to remain available another 90 days, saying its capacity is needed to maintain MISO grid reliability.
A group of industry insiders looking at ways to meet data centers’ electricity demand found a common thread within their varied opinions: The power sector and its regulators need to be a lot nimbler.
Want more? Advanced Search