Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
The Public Service Enterprise Group is waiting for New Jersey to address the region’s predicted energy shortage as the utility continues to see a dramatic rise in potential demand from data centers.
Exelon's CEO said on an earnings call that the company remains interested in the possibility of utility-owned generation.
The pace of load growth has picked up across Eversource Energy’s service territories in the Northeast, the company said during its second-quarter earnings call.
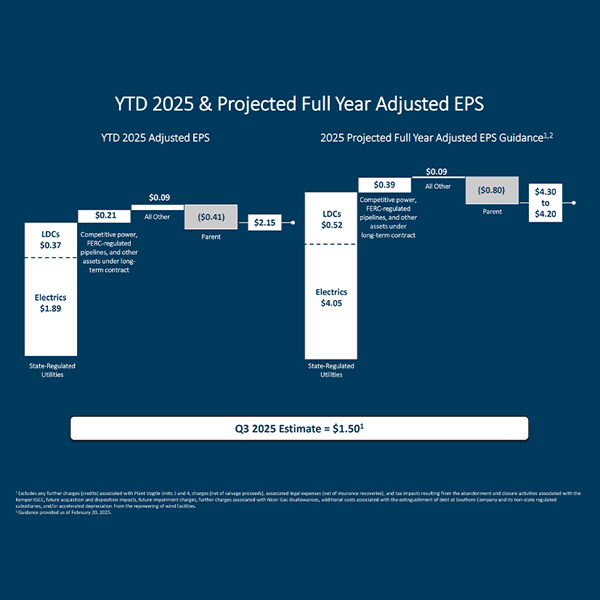
Southern Co.'s second-quarter earnings were down slightly from the prior year, but executives said they expect healthy growth from the continued addition of large loads such as data centers.
American Electric Power and Xcel Energy say clean energy projects are still a part of their plans, despite the hurdles placed in front of them by the federal government’s budget reconciliation bill.
The MISO Independent Market Monitor called on the RTO to develop a penalty system for generation for underperformance during emergencies.
The Michigan coal plant kept online by an emergency order from the U.S. Department of Energy cost $29 million to run in a little over a month.
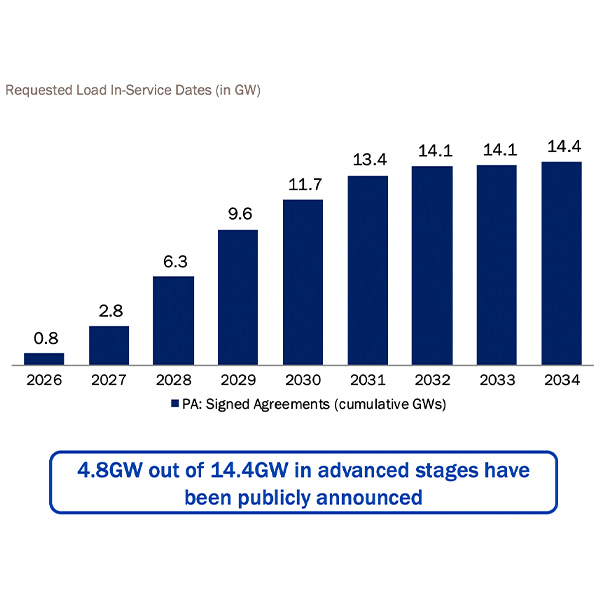
PPL expects the current surplus of generation in its Pennsylvania territory will be lost to demand growth from data centers in the next five years and said it has plans to help meet that growing demand with new generation.
Growing power demand from data centers dominated conversations at the NARUC Summer Policy Summit, where industry members and Trump administration officials advocated for the rapid addition of fossil fuel resources and infrastructure to meet load growth.
EPA Administrator Lee Zeldin proudly told NARUC attendees the agency’s proposed rescission of the 2009 endangerment finding would be the “largest deregulatory action in the history of the country.”
Want more? Advanced Search