Resource Adequacy
Panelists at the annual meeting of the Western Conference of Public Service Commissioners emphasized the need for innovative regulatory frameworks in order to keep up with new technology seeking interconnection.
FERC’s resource adequacy technical conference zoomed out on the second day, June 5, with several panels examining ISO-NE, MISO and NYISO.
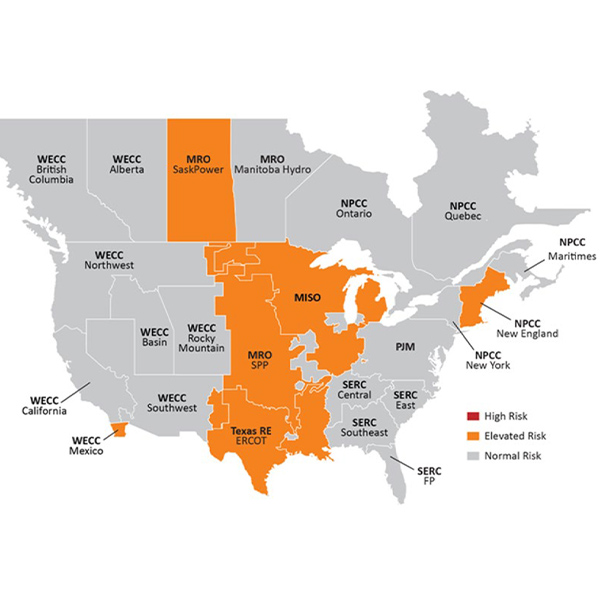
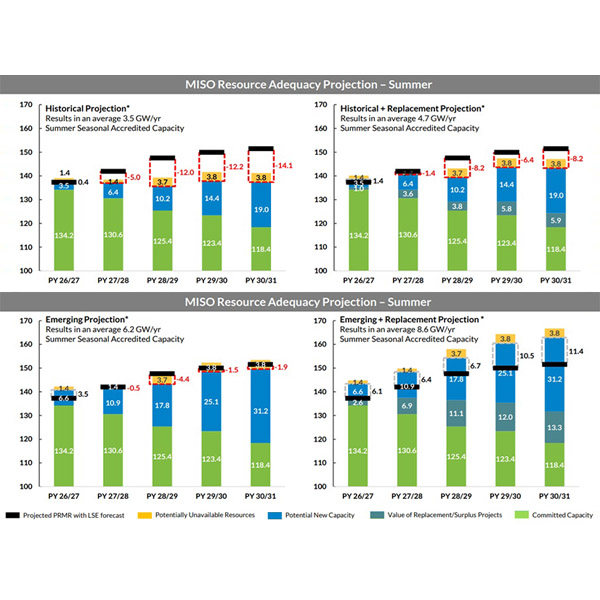
The Organization of MISO States and MISO are confident the footprint will be resource-sufficient in the 2026/27 planning year but said anything from an 11.4-GW surplus to a 14.1-GW deficit could be in store by the 2030/31 planning year.
FERC spent June 4-5 looking into resource adequacy across the markets it regulates.
Called to the podium by the New Orleans City Council, MISO and Entergy leadership agreed a perfect storm of factors merged to cause the Memorial Day weekend power outages.
BPA CEO John Hairston’s keynote at the annual meeting of the WCPSC spotlighted a theme that would dominate discussion at the event: the looming prospect of overwhelming growth in electricity demand in the West and across the U.S.
A new ACEG report says interregional transmission offers resource adequacy benefits and highlights how regions can take advantage of that.
FERC will hold a two-day technical conference June 4-5, where it will look at resource adequacy issues in the ISO/RTO markets, with most of the focus on those with capacity markets.
ERCOT's blossoming clean energy sector has been threatened by bills that would dampen its growth and future investment, but many of those laws appear to have fallen by the wayside in the Texas legislature's closing days.
Want more? Advanced Search