Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
New York is looking at a broader array of solutions as fossil plants retire and not enough renewables come online.
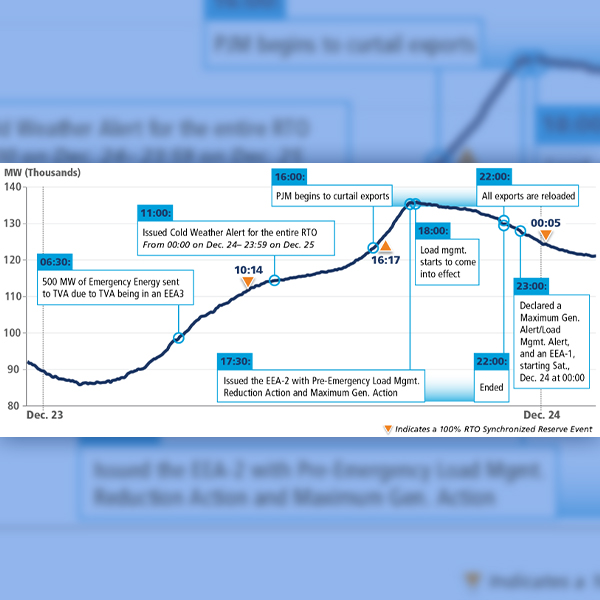
PJM released a report on the December 2022 winter storm detailing its emergency actions and recommended changes to its markets and operations to limit the impact of future severe weather.
Temperatures in Austin topped out at 105 degrees Fahrenheit, helping ERCOT to again set a record for hourly peak demand when load averaged 82.03 GW.
PJM completed its delivery of a sprawling presentation outlining its envisioned overhaul of the capacity market, followed by stakeholder presentations from Calpine, Daymark Energy Advisors and the East Kentucky Power Cooperative.
The committee discussed future energy deficiencies in New York City, NYISO's demand curve reset and impacts from extreme weather in the region.
The PJM Operating Committee discussed the roadmap for a slate of manual revisions related to its interconnection queue overhaul, with the next step being endorsement at the MRC.
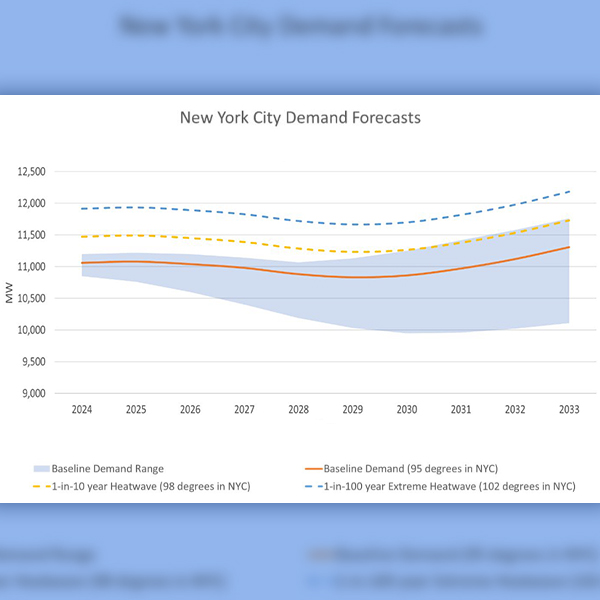
New York City faces a 446-MW shortfall in 2025 because of plant retirements and the delayed completion of the Champlain Hudson Power Express, NYISO said.
SPP stakeholders endorsed a tariff revision request that adds a winter resource adequacy requirement for load-responsible entities bound by the grid operator’s recent planning reserve margin increase.
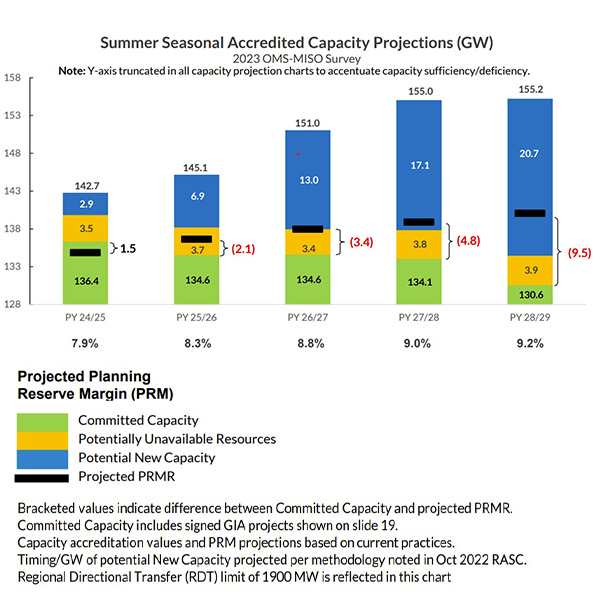
MISO and the Organization of MISO States’ resource adequacy survey warned that a more than 9-GW shortfall could loom by the decade’s end, though it painted an adequate supply picture for the upcoming year.
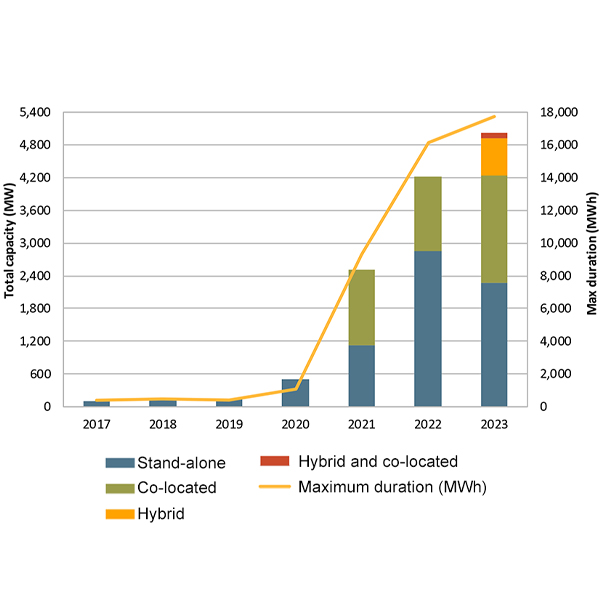
The more than 5,000 MW of batteries connected to the CAISO grid are playing in increasing role in maintaining reliability, a report from the ISO's Market Monitor shows.
Want more? Advanced Search