Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
Dominion expects to start installing monopiles for the Coastal Virginia Offshore Wind project between May 6 and 8, CEO Robert Blue told analysts during the company’s first-quarter earnings call.
Stakeholder voices criticizing the design of MISO’s proposed, probabilistic capacity accreditation outnumbered those expressing support before FERC.
Rising demand from data centers will lead to increased investment in transmission in PPL’s utility territories, executives said during a first-quarter earnings call.
The ongoing turnover of the generation fleet to cleaner resources, the recent return of demand growth and the need to stitch all that together with transmission expansion all came up at the Energy Bar Association’s Annual Meeting.
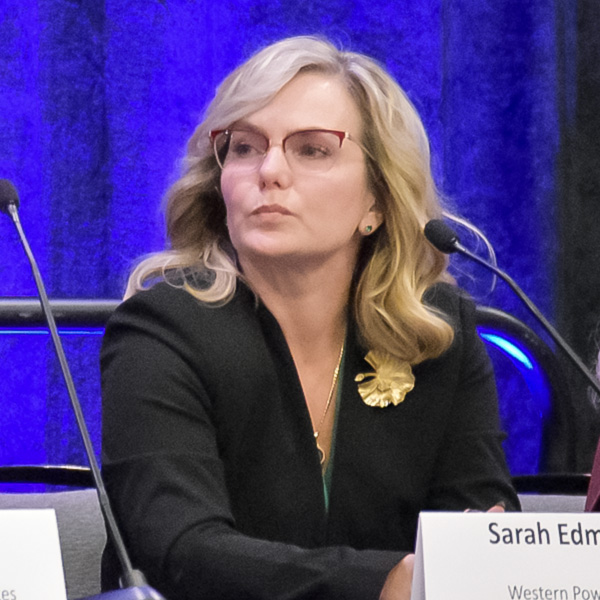
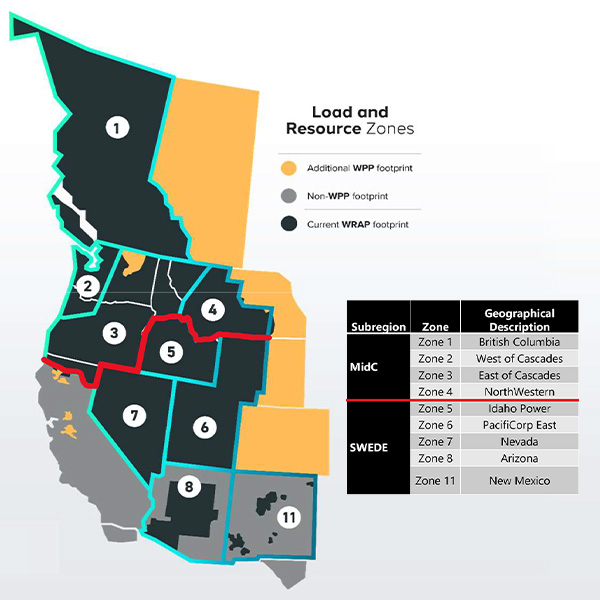
Western Resource Adequacy Program participants still strongly support the program despite recently appealing to delay its “binding” penalty phase by one year due to concerns about capacity shortages, WPP's Sarah Edmonds said.
ERCOT is searching for alternatives to replace capacity that will be lost with the planned retirement of three gas-fired units near San Antonio.
MISO announced that 123 GW of new generation spread across 600 applications are vying to enter its generator interconnection queue under the 2023 cycle.
Citing “significant new headwinds” to securing energy resources, participants in the Western Resource Adequacy Program are seeking to delay the program’s “binding” penalty phase by one year, to summer 2027.
The Gulf Coast Power Association Spring Conference tackled the vexing assignment of how to reliably serve Texas’ unprecedented surge in demand with a cleaner energy supply.
A DOE report on resource adequacy says firms investing in natural gas capacity could be retrofitted with carbon capture and storage, or the ability to burn clean hydrogen.
Want more? Advanced Search